Images from the James Webb Space Telescope and the Chandra X-ray Observatory have been combined to reveal how the Crab Nebula’s neutron star is changing.
Get the latest international news and world events from around the world.

Quantum Theory Unveils Surprising Black Hole Shortage
Quantum field theory reveals potential flaws in models predicting numerous primordial black holes, suggesting fewer exist, which may impact theories of dark matter and the universe’s structure.
Researchers have applied the well-understood and highly verified quantum field theory, usually applied to the study of the very small, to a new target, the early universe. Their exploration led to the conclusion that there ought to be far fewer miniature black holes than most models suggest, though observations to confirm this should soon be possible. The specific kind of black hole in question could be a contender for dark matter.
The study, which was published recently in Physical Review Letters, was conducted by researchers at the Research Center for the Early Universe (RESCEU) and Kavli Institute for the Physics and Mathematics of the Universe (Kavli IPMU, WPI) at the University of Tokyo.

A Portal to the Past: Hubble Reveals an Ancient Witness to a Galactic Merger
NGC 2005, a globular cluster in the Large Magellanic Cloud, serves as a crucial piece of evidence supporting the theory of galaxies evolving through mergers.
This mesmerizing image from the Hubble Space Telescope features the globular cluster NGC 2005. While it is not unusual in and of itself, it is a peculiarity in relation to its surroundings.
NGC 2005 is located about 750 light-years from the heart of the Large Magellanic Cloud (LMC), which is the Milky Way ’s largest satellite galaxy and which itself lies about 162,000 light-years from Earth. Globular clusters are densely packed clusters that can constitute tens of thousands or millions of stars. Their density means that they are tightly gravitationally bound and are therefore very stable. This stability contributes to their longevity: globular clusters can be billions of years old, and as such often comprise very old stars.

Interstellar Intruder: The Cosmic Event That Rewrote Earth’s Climate History
New astrophysical research highlights a significant cosmic event two million years ago when the solar system passed through a dense interstellar cloud. This possibly altered Earth’s climate by exposing it to enhanced cosmic radiation, supported by increased isotopes found in geological records.
Earth was a very different place around two million years ago, with our early human ancestors living alongside saber-toothed tigers, mastodons, and enormous rodents. And, depending on where they were, they may have been cold: Earth had fallen into a deep freeze, with multiple ice ages coming and going until about 12,000 years ago. Scientists theorize that ice ages occur for a number of reasons, including the planet’s tilt and rotation, shifting plate tectonics, volcanic eruptions, and carbon dioxide levels in the atmosphere.
But what if drastic changes like these are not only a result of Earth’s environment, but also the sun’s location in the galaxy?
The Millionaire Movement to Live Forever
Longevity equals crazy here. I did leave a comment.
Get ready for the Summer Season in style! Click the links below & receive your crazy offer for 24h only👇🏽 Check out over thousands of styles at GlassesUSA.com 👇🏽 Eyeglasses: https://glassesusa.me/3133_EmmaThorne_Eyeglasses https://glassesusa.me/3133_EmmaThorne… Muse Cherish Muse Cherish: https://glassesusa.me/EmmaThorne_Muse… Ottoto Everard https://glassesusa.me/3132_OttotoEver… Revel Relay https://glassesusa.me/3132_RevelRelay… Today we’re taking a look at anti-aging activists: the movement of wealthy individuals competing to reduce their biological age. How much of it is Silicon Valley pseudoscience? Join this channel to get stompid emmotes (see what I did there) / @emmathornevideos Captions by David Glennon: [email protected] Like and subscribe if you enjoyed! Website: https://www.emma-thorne.co.uk Emma Thorne Extra:
/ @emmathornebackstage Gaming Channel:
/ littleduckgaming Twitch:
/ emmalittleduck Instagram: @emmainashes Twitter: @EmmaTheGoblin Patreon:
/ emmathornevideos Merch: https://emma-thorne.com Ko-Fi: https://ko-fi.com/emmathorne PO BOX: Emma Thorne PO Box 78,387 LONDON E4 0HY Timcodes: 00:00 Bryan Johnson 10:49 Dave Pascoe 15:48 Rejuvination Olympics 19:51 Is Biological Age Testing Legit? 23:20 Blood Boys 27:59 Blue Zones Huge thank you to my Colossal Quackers and Giant Chickens on Patreon! Aspen Bill Garrett Brent Bartlett Chaotic Quakka Chocolate Jesus Douglas Steingraber 2 Fat Houdini Jaderian Jason Haase Jeremy Buck John E. John newman Kori Gailliot Lord Nibbles Dankworth IX Mike Nick Muggio Philip Doherty Purple_Pug_2013 Robi Groves Samandme59 Sean Hamill Vermont1777 Squeaky Fish 2 Al Sweigart Andrew Andy is ducking around April Washburn Azku Ben Eiynk Bert Whitehead Brandon Brian McKemey Buddmeister2.0 Cartoon Fan Ceilidh Chantale Cindarella Santonen Connla “Chicken Maximus” Lyons Darren McHaffie Darth_Rondoudou Dave Kircher Dave Smith Daylin Dreffed FalcorTheGinger Farron Sutton Faye The Succubus Flash prez Bluewolf Geeeee (NOT FOR VIDEOS) Henry Curtis Jan Bojarp Jason Runcie jaxjanjy jedidragonwarriorqueen Jim Lathrop Jo Ro John Fry Kevin Levites King Skippus Laker Sparks Lizzy Gayle Lulidine Matthew Green Mattus McChicken Nuggetus Mordlex 200 Mr Smeeth NotMyselfThisTime ohsosmooth Paul McGinty paul mueller PaulM Peter Kyrouac PJ Lesbirel Quique León Ralti razbitom Richard Jackson RileyTheTortoise Rosyna Keller RPGMP3 Sarah Chavis Sean Siliconself Simping on Emma Thorne SIRIUSLY SquidSuperHunk Tank Lowe Tax Man The Shropshire Lad ThmsR Thomas V Lohmeier Valyrie VinceWasSu WeirdyBeardy Will Crouch Willow the Wendigo Wrongtown.

AI Used to Predict Potential New Antibiotics
A new study used machine learning to predict potential new antibiotics in the global microbiome, which study authors say marks a significant advance in the use of artificial intelligence in antibiotic resistance research…
For this study, the researchers collected genomes and meta-genomes stored in publicly available databases and looked for DNA snippets that could have antimicrobial activity. To validate those predictions, they used chemistry to synthesize 100 of those molecules in the laboratory and then test them to determine if they could actually kill bacteria, including ‘some of the most dangerous pathogens in our society’, de la Fuente said.
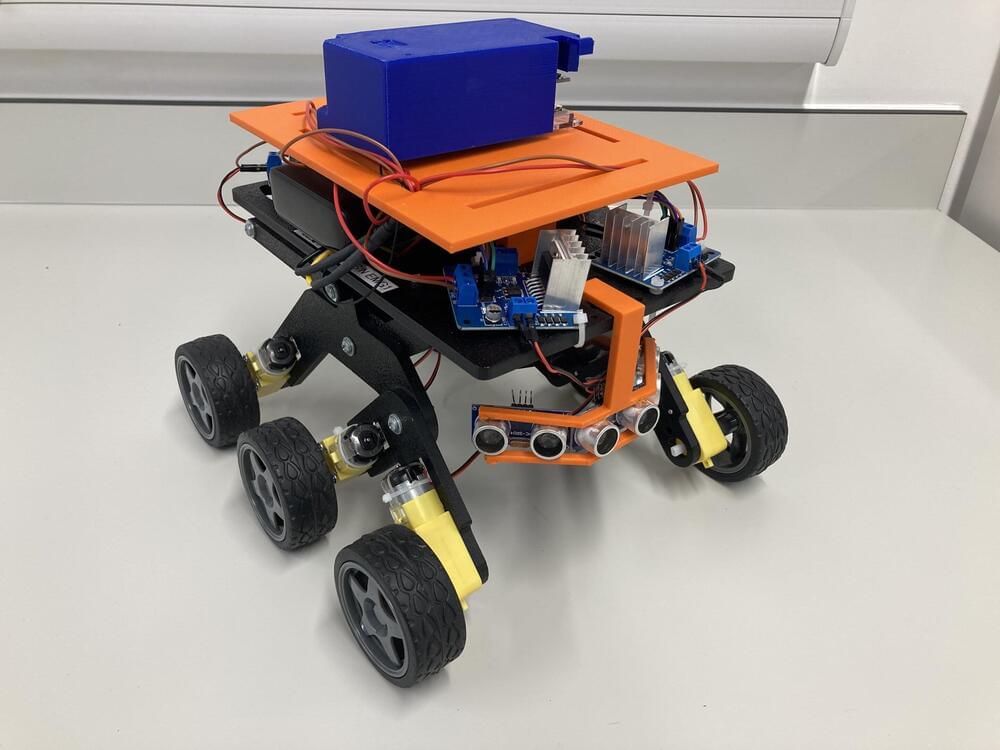

New method could allow multi-robot teams to autonomously and reliably explore other planets
While roboticists have developed increasingly sophisticated systems over the past decades, ensuring that these systems can autonomously operate in real-world settings without mishaps often proves challenging. This is particularly difficult when these robots are designed to be deployed in complex environments, including space and other planets.
New study reveals gut microbiome’s critical role in aging and heart disease
🧬❤️👩🔬 https://www.news-medical.net/news/20240609/New-study-reveals…al-role-in
In a recent study published in the journal Nature Medicine, a team of researchers in China conducted a prospective analysis of metabolic multimorbidity clusters based on 21 metabolic parameters to investigate gut microbiome signatures associated with metabolism and age to better understand the relationship between metabolism, age, and the long term risk of cardiovascular disease.
Study: Divergent age-associated and metabolism-associated gut microbiome signatures modulate cardiovascular disease risk. Image Credit: Kateryna Kon / Shutterstock.
Background
Cardiovascular disease is the major cause of global mortality, and metabolic perturbations and age, which are also intricately connected, are believed to contribute significantly to the risk of cardiovascular disease. Metabolic disturbances increase in complexity and prevalence with age, and older adults typically develop cardiovascular disease in a multimorbidity context.