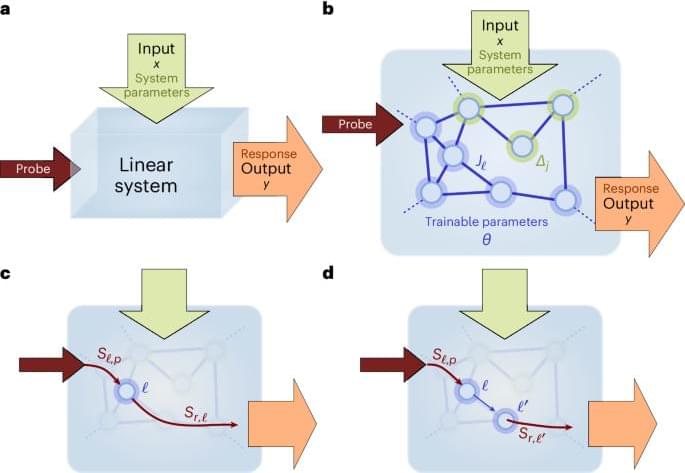
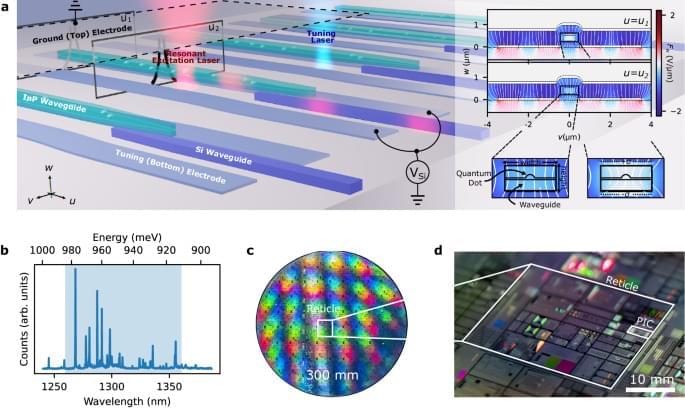
As the energy consumption of neural networks continues to grow, different approaches to deep learning are needed. A neuromorphic method offering nonlinear computation based on linear wave scattering can be implemented using integrated photonics.

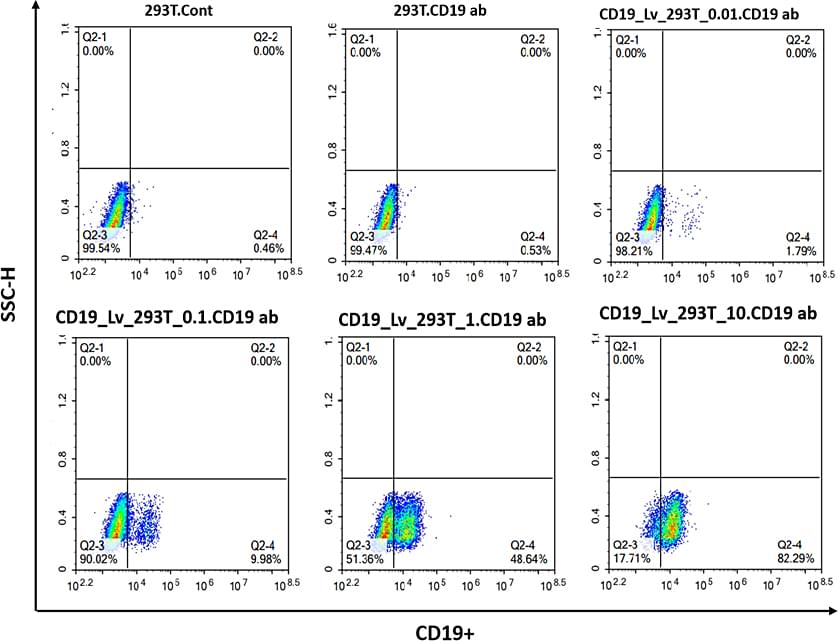
Cyagen has built a one-stop service platform for in vivo and in vitro CAR-T cell therapy research. The platform is available to researchers worldwide, which includes scFv sequence screening, CAR molecular design, and full-process services to develop the foundational research for your CAR-T cell therapy.
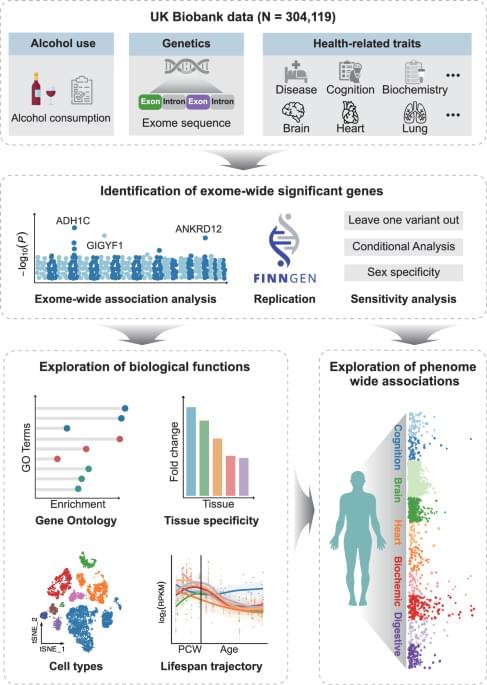
Over the recent decades, comprehensive genome-wide association studies (GWAS) have indicated the potential influence of genetic factors on one’s alcohol consumption volume and identified over 100 related variants6,7. However, a predominant proportion of the identified variants are localized within noncoding regions, and their effect sizes tend to be small, making interpretation and identification of the causal gene challenging8. In addition, previous GWAS mainly utilized imputed genotype data, which only cover limited regions of the genome, and thus may have missed many potential genes. Furthermore, GWAS studies focused mainly on common variants, and few studies have investigated rare variants associated with alcohol consumption, which yield greater potential to interpret biological function and elucidate mechanisms9. Although there are studies that have attempted to leverage exome chip data to identify rare variants contributing to alcohol consumption, the sample size was small and limited regions of the whole exome were examined10.
The introduction of whole exome sequencing (WES) provides a great chance to overcome the limitations of previous genetic studies on alcohol consumption with a substantially larger amount of rare and ultra-rare protein-coding variants11,12,13. Collapsing of loss-of-function (LOF) variants helps estimate the effect direction of associated genes13,14. When combined with large-scale population cohorts with multi-modal phenotypic data, WES would greatly facilitate our understanding of the genetic underpinnings of alcohol consumption as well as its implication on physical and mental health6. However, to our knowledge, there have been few large-scale WES studies on alcohol consumption, let alone elucidating the potential implications of the identified genes10,15. Meanwhile, as indicated by a previous genome-wide association study, significant genetic associations existed between alcohol consumption and several body health phenotypes7. The application of phenome-wide analysis for alcohol-related genes can help extend and deepen our current comprehension of the association between alcohol consumption and human health.
Hence, aiming to refine the genetic architecture of alcohol consumption, we conduct an exome-wide association study (ExWAS) for alcohol consumption among 304,119 individuals from the UK Biobank (UKB). We also examine the rare-variant associations with genes reported by previous GWAS6,7,16,17. Finally, we provide biological insights into the identified genes via bioinformatics analyses and phenome-wide association analysis (PheWAS).

Genome editing stands as one of the most transformative scientific breakthroughs of our time. It allows us to dive into the very code of life and make precise modifications. Imagine being able to rewrite the genetic instructions that determine almost everything about an organism—how it looks, behaves, interacts with its environment, and its unique characteristics. This is the power of genome editing.
We use genome editing tools to tweak the genetic sequences of microbes, animals, and plants. Our goal? To develop desired traits and eliminate unwanted ones. This technology’s impact has been felt across biotechnology, human therapeutics, and agriculture, bringing rapid advancements and solutions.
The most widely used proteins in genome editing are Cas9 and Cas12a. These proteins are like the scissors of the genetic world, allowing us to cut and edit DNA. However, they are quite bulky, consisting of 1,000–1,350 amino acids. Advanced editing technologies like base editing and prime editing require the fusion of additional proteins with Cas9 and Cas12a, making them even bulkier. This bulkiness poses a challenge to delivering these proteins efficiently into cells, where the genetic material resides.
Are you ready to discover the future of AI with GPT-5? In this video, we’ll explore the latest upd…

Skild AI, a startup that’s developing artificial intelligence-powered brains for robots, said today it has closed on a bumper $300 million early-stage funding round, bringing its valuation to a cool $1.5 billion.
The Series A round was led by a host of top-tier venture capital firms, including Lightspeed Venture Partners, Coatue, Softbank Group Corp. and Jeff Bezos’s Bezos Expeditions. It also saw participation from the likes of Felicis Ventures, Sequoia, Menlo Ventures, General Catalyst, CRV, Amazon, SV Angel and Carnegie Mellon University.
Skild AI is building what it says is a “shared, general-purpose brain” that will be able to equip a diverse group of robots that can perform multiple kinds of tasks in a wide range of scenarios, such as manipulating objects, locomotion and navigation. It says its AI intelligence can be integrated with any kind of robot, including humanoid bots with advanced computer vision skills designed to perform dexterous manipulation of objects in the home and in industrial settings, and more resilient quadruped robots that can navigate any physical environment.
Lecture by Dr Jack Szostak, 2009 Nobel laureate in Physiology or Medicine, at the Molecular Frontiers Symposium \.

Scientists have for the first time observed how atoms in magnesium oxide morph and melt under ultra-harsh conditions, providing new insights into this key mineral within Earth’s mantle that is known to influence planet formation.
High-energy laser experiments — which subjected tiny crystals of the mineral to the type of heat and pressure found deep inside a rocky planet’s mantle — suggest the compound could be the earliest mineral to solidify out of magma oceans in forming “super-Earth” exoplanets.
“Magnesium oxide could be the most important solid controlling the thermodynamics of young super-Earths,” said June Wicks, an assistant professor of Earth and Planetary Sciences at Johns Hopkins University who led the research. “If it has this very high melting temperature, it would be the first solid to crystallize when a hot, rocky planet starts to cool down and its interior separates into a core and a mantle.”