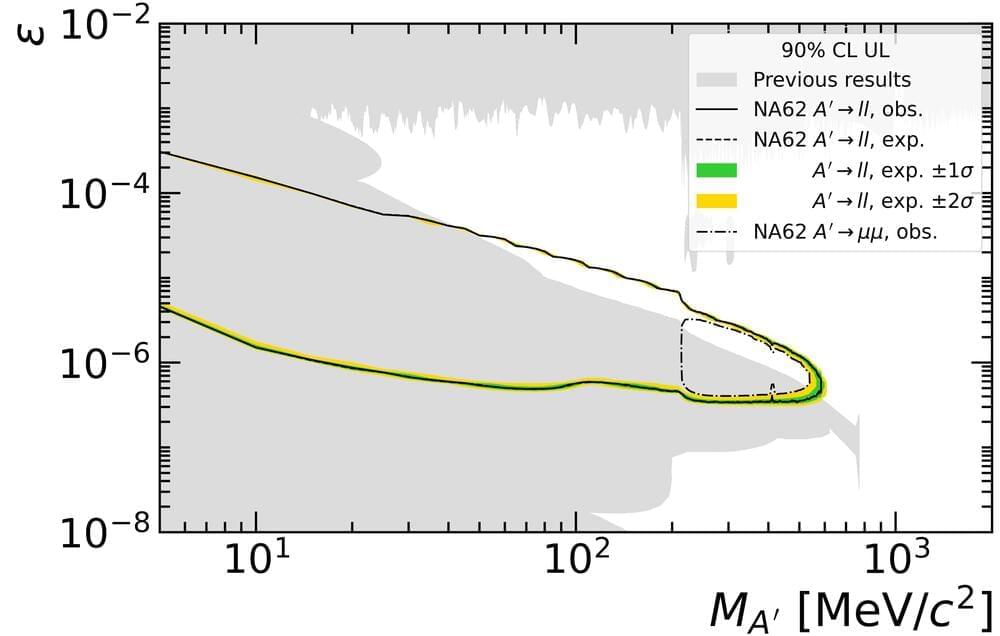
In 2022, a nuclear-fusion experiment yielded more energy than was delivered by the lasers that ignited the fusion reaction (see Viewpoint: Nuclear-Fusion Reaction Beats Breakeven). That demonstration was an example of indirect-drive inertial-confinement fusion, in which lasers collapse a fuel pellet by heating a gold can that surrounds it. This approach is less efficient than heating the pellet directly since the pellet absorbs less of the lasers’ energy. Nevertheless, it has been favored by researchers at the largest laser facilities because it is less sensitive to nonuniform laser illumination. Now Duncan Barlow at the University of Bordeaux, France, and his colleagues have devised an efficient way to improve illumination uniformity in direct-drive inertial-confinement fusion [1]. This advance helps overcome a remaining barrier to high-yield direct-drive fusion using existing facilities.
Triggering self-sustaining fusion by inertial confinement requires pressures and temperatures that are achievable only if the fuel pellet implodes with high uniformity. Such uniformity can be prevented by heterogeneities in the laser illumination and in the way the beams interact with the resulting plasma. Usually, researchers identify the laser configuration that minimizes these heterogeneities by iterating radiation-hydrodynamics simulations that are computationally expensive and labor intensive. Barlow and his colleagues developed an automatic, algorithmic approach that bypasses the need for such iterative simulations by approximating some of the beam–plasma interactions.
Compared with an experiment using a spherical, plastic target at the National Ignition Facility in California, the team’s optimization method should deliver an implosion that reaches 2 times the density and 3 times the pressure. But the approach can also be applied to other pellet geometries and at other facilities.