TamperedChef spreads through fake installers and SEO abuse, delivering a persistent JavaScript backdoor across multiple sectors.



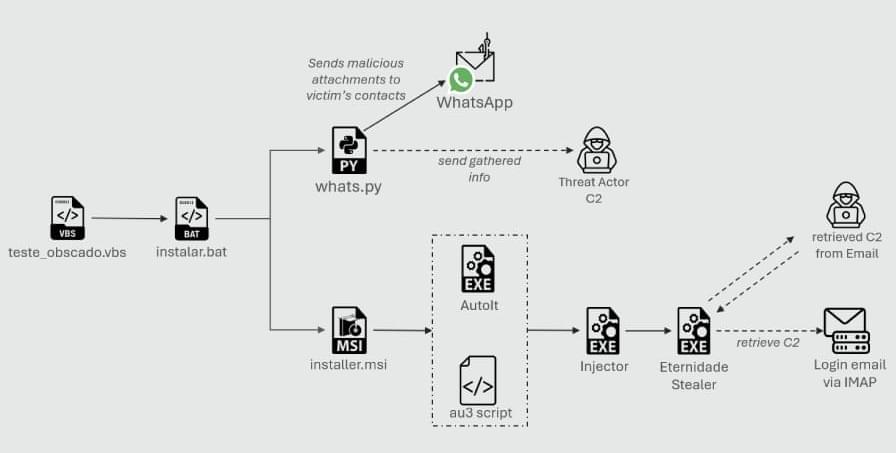
Cybersecurity researchers have disclosed details of a new campaign that leverages a combination of social engineering and WhatsApp hijacking to distribute a Delphi-based banking trojan named Eternidade Stealer as part of attacks targeting users in Brazil.
“It uses Internet Message Access Protocol (IMAP) to dynamically retrieve command-and-control (C2) addresses, allowing the threat actor to update its C2 server,” Trustwave SpiderLabs researchers Nathaniel Morales, John Basmayor, and Nikita Kazymirskyi said in a technical breakdown of the campaign shared with The Hacker News.
It is distributed through a WhatsApp worm campaign, with the actor now deploying a Python script, a shift from previous PowerShell-based scripts to hijack WhatsApp and spread malicious attachments.


In a move that could redefine the web, Google is testing AI-powered, UI-based answers for its AI mode.
Up until now, Google AI mode, which is an optional feature, has allowed you to interact with a large language model using text or images.
When you use Google AI mode, Google responds with AI-generated content that it scrapes from websites without their permission and includes a couple of links.

A critical flaw in the W3 Total Cache (W3TC) WordPress plugin can be exploited to run PHP commands on the server by posting a comment that contains a malicious payload.
The vulnerability, tracked as CVE-2025–9501, affects all versions of the W3TC plugin prior to 2.8.13 and is described as an unauthenticated command injection.
W3TC is installed on more than one million websites to increase performance and reduce load times.

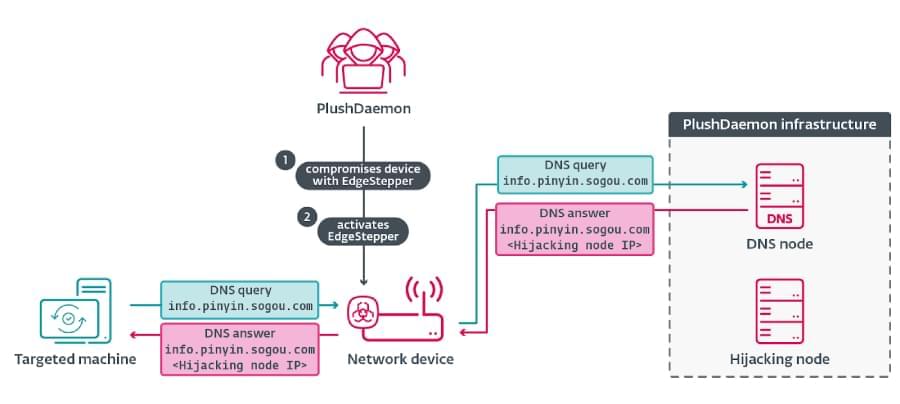
Thousands of ASUS WRT routers, mostly end-of-life or outdated devices, have been hijacked in a global campaign called Operation WrtHug that exploits six vulnerabilities.
Over the past six months, scanners looking for ASUS devices compromised in Operation WrtHug identified “roughly 50,000 unique IPs” around the globe.
Most of the compromised devices have IP addresses located in Taiwan, while others are distributed across Southeast Asia, Russia, Central Europe, and the United States.
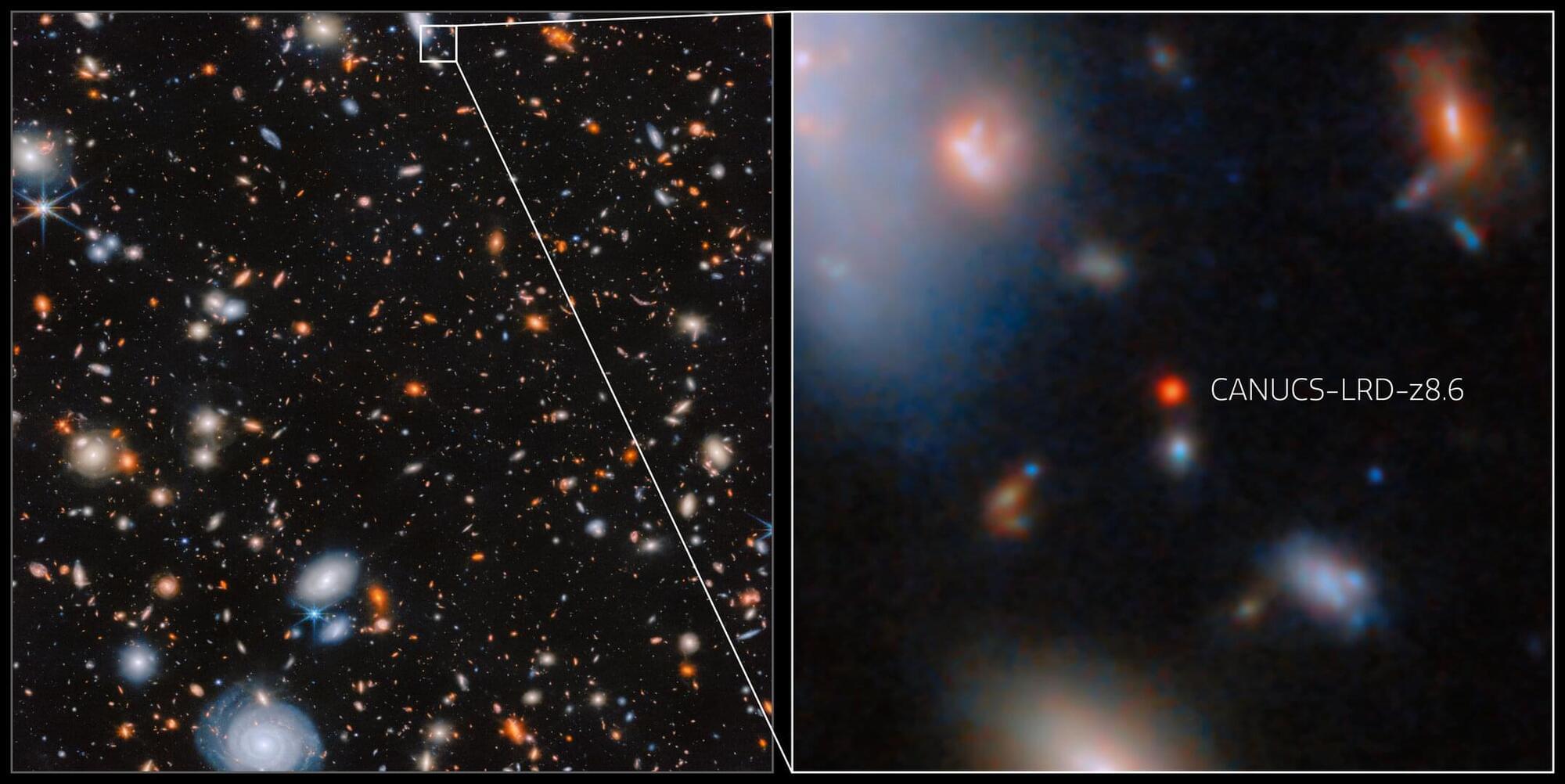
Researchers using the NASA/ESA/CSA James Webb Space Telescope have confirmed an actively growing supermassive black hole within a galaxy just 570 million years after the Big Bang. Part of a class of small, very distant galaxies that have mystified astronomers, CANUCS-LRD-z8.6 represents a vital piece of this puzzle and challenges existing theories about the formation of galaxies and black holes in the early Universe. The discovery connects early black holes with the luminous quasars we observe today.
Over its first three years, Webb’s surveys of the early Universe have turned up an increasing number of small, extremely distant, and strikingly red objects. These so-called Little Red Dots (LRDs) remain a tantalising mystery to astronomers, despite their unexpected abundance. The discovery in CANUCS-LRD-z8.6, made possible by Webb’s exceptional capabilities, has assisted in this hunt for answers. Webb’s Near-Infrared Spectrograph (NIRSpec) enabled researchers to observe the faint light from this distant galaxy and detect key spectral features that point to the presence of an accreting black hole.
Roberta Tripodi, lead author of the study and a researcher of the University of Ljubljana FMF, in Slovenia and INAF — Osservatorio Astronomico di Roma, in Italy, explained: “This discovery is truly remarkable. We’ve observed a galaxy from less than 600 million years after the Big Bang, and not only is it hosting a supermassive black hole, but the black hole is growing rapidly – far faster than we would expect in such a galaxy at this early time. This challenges our understanding of black hole and galaxy formation in the early Universe and opens up new avenues of research into how these objects came to be.”