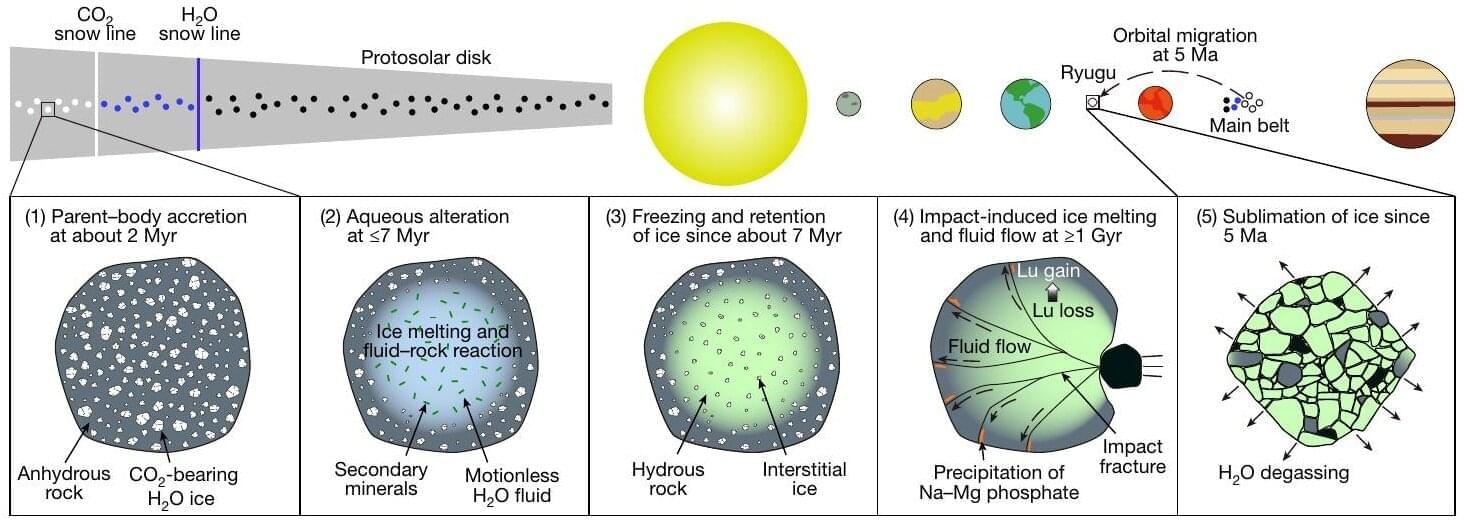
A team of researchers, including those at the University of Tokyo, discovered that liquid water once flowed on the asteroid that spawned near-Earth asteroid Ryugu more than a billion years after it first formed. The finding, based on tiny rock fragments returned by the Hayabusa2 spacecraft of the Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency (JAXA), overturns long-held assumptions that water activity on asteroids only occurred in the earliest moments of solar system history. This could impact current models, including those describing the formation of Earth.
We have a relatively good understanding of how the solar system formed, but of course there are many gaps. One such gap in our knowledge is how Earth came to possess so much water. It’s long been known that so-called carbonaceous asteroids like Ryugu formed from ice and dust in the outer solar system supplied water to Earth.
Ryugu was famously visited by the Hayabusa2 spacecraft in 2018, the first visit of its kind, where not only were in-situ data collected, but small samples of material were brought back to Earth too. And it’s thanks to this endeavor that researchers can help fill in some missing details in the picture of our creation.