Our brain doesn’t passively receive visual input—it actively orchestrates a symphony of neural oscillations to process the complex, dynamic scenes we see in everyday life.
Here are five recent innovative bioprinting and bioink studies that are building synthetic biological structures.
An optogenetic method for controlling the movement of starfish oocytes has been developed, which could have applications for drug delivery.
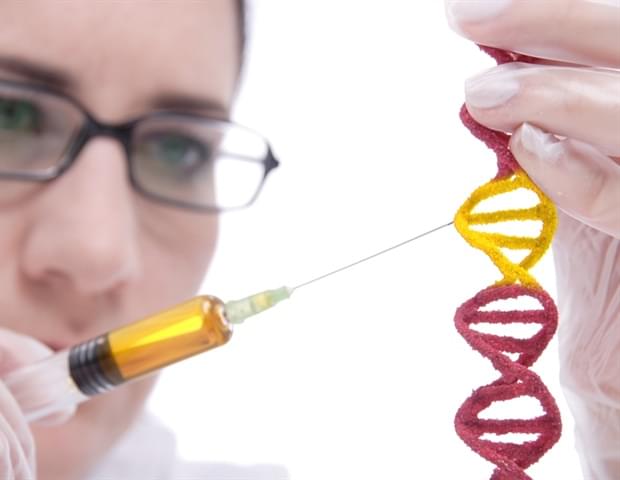
Genome editing has advanced at a rapid pace with promising results for treating genetic conditions-but there is always room for improvement. A new paper by investigators from Mass General Brigham published in Nature showcases the power of scalable protein engineering combined with machine learning to boost progress in the field of gene and cell therapy. In their study, authors developed a machine learning algorithm-known as PAMmla-that can predict the properties of about 64 million genome editing enzymes. The work could help reduce off-target effects and improve editing safety, enhance editing efficiency, and enable researchers to predict customized enzymes for new therapeutic targets. Their results are published in Nature.
“Our study is a first step in dramatically expanding our repertoire of effective and safe CRISPR-Cas9 enzymes. In our manuscript we demonstrate the utility of these PAMmla-predicted enzymes to precisely edit disease-causing sequences in primary human cells and in mice,” said corresponding author Ben Kleinstiver, PhD, Kayden-Lambert MGH Research Scholar associate investigator at Massachusetts General Hospital (MGH), a founding member of the Mass General Brigham healthcare system. “Building on these findings, we are excited to have these tools utilized by the community and also apply this framework to other properties and enzymes in the genome editing repertoire.”
CRISPR-Cas9 enzymes can be used to edit genes at locations throughout the genomes, but there are limitations to this technology. Traditional CRISPR-Cas9 enzymes can have off-target effects, cleaving or otherwise modifying DNA at unintended sites in the genome. The newly published study aims to improve this by using machine learning to better predict and tailor enzymes to hit their targets with greater specificity. The approach also offers a scalable solution-other attempts at engineering enzymes have had a lower throughput and typically yielded orders of magnitude fewer enzymes.
Extreme ‘zombie star’ capable of ripping human atoms apart is shooting through the Milky Way — and nobody knows where it came from
Posted in particle physics, space | Leave a Comment on Extreme ‘zombie star’ capable of ripping human atoms apart is shooting through the Milky Way — and nobody knows where it came from
Astronomers have discovered that the magnetar SGR 0501+4516 is speeding through our galaxy at more than 110,000 mph. This unusually fast speed hints that it was not born as expected, which could help explain the puzzling origin of some fast radio bursts.
America has unveiled a new project that can collect 4000 tons of seawater at a time. The new system from US based startup Equatic has the world shocked.
From the universe’s age to “missing link” black holes, Hubble’s mysteries range from big to bigger.
Prebiotic molecules central to life’s earliest metabolic processes—chemical reactions in cells that change food into energy—may have been born in deep space long before Earth existed, according to new research from the University of Hawaiʻi at Mānoa Department of Chemistry.
Scientists in the W. M. Keck Research Laboratory in Astrochemistry have recreated the extreme conditions found in dense interstellar clouds and discovered a way for the complete set of complex carboxylic acids—critical ingredients in modern metabolism—to form without life on timescales equivalent to a few million years.
The study, published in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, focused on molecules such as those in the Krebs cycle, a fundamental metabolic pathway used by nearly all living organisms. These molecules, which help break down nutrients to release energy, may have cosmic origins, forming in the icy, low-temperature environments of interstellar space.
Check out my own quantum mechanics course on Brilliant! First 30 days are free and 20% off the annual premium subscription when you use our link ➜ https://brilliant.org/sabine.
Chaos doesn’t exist in the world of quantum physics, as quantum physics is a linear theory. So how come we observe chaos all around us? Researchers have now come one step closer to understanding how it happens. They have for the first time measured a “quantum scar”, that is a quantum effect which deviates from chaos. Why does this matter and what could it be good for? Let’s take a look.
Paper: https://www.nature.com/articles/s4158… lovely animation for the spread of the wavefunction in the stadium and heart come from the Quantum Physics Corner: • Quantum heart billiard 🤓 Check out my new quiz app ➜ http://quizwithit.com/ 💌 Support me on Donorbox ➜ https://donorbox.org/swtg 📝 Transcripts and written news on Substack ➜ https://sciencewtg.substack.com/ 👉 Transcript with links to references on Patreon ➜
/ sabine 📩 Free weekly science newsletter ➜ https://sabinehossenfelder.com/newsle… 👂 Audio only podcast ➜ https://open.spotify.com/show/0MkNfXl… 🔗 Join this channel to get access to perks ➜
/ @sabinehossenfelder 🖼️ On instagram ➜
/ sciencewtg #science #sciencenews #physics #quantumphysics.
The lovely animation for the spread of the wavefunction in the stadium and heart come from the Quantum Physics Corner: • Quantum heart billiard.
🤓 Check out my new quiz app ➜ http://quizwithit.com/
💌 Support me on Donorbox ➜ https://donorbox.org/swtg.
📝 Transcripts and written news on Substack ➜ https://sciencewtg.substack.com/
👉 Transcript with links to references on Patreon ➜ / sabine.
📩 Free weekly science newsletter ➜ https://sabinehossenfelder.com/newsle…
👂 Audio only podcast ➜ https://open.spotify.com/show/0MkNfXl…
🔗 Join this channel to get access to perks ➜
/ @sabinehossenfelder.
🖼️ On instagram ➜ / sciencewtg.
#science #sciencenews #physics #quantumphysics
Source — http://serious-science.org/videos/40
MIT Prof. Daniel Kleppner on uncertainty principle of quantum mechanics, the butterfly effect, and «quantum chaology»