Despite billion-dollar investments, the technology faces hurdles that keeps its future uncertain



We show that an agentic large language model (LLM) (OpenAI o3 with deep research) can autonomously reason, write code, and iteratively refine hypotheses to derive a physically interpretable equation for competitive adsorption on metal-organic layers (MOLs)—an open problem our lab had struggled with for months. In a single 29-min session, o3 formulated the governing equations, generated fitting scripts, diagnosed shortcomings, and produced a compact three-parameter model that quantitatively matches experiments across a dozen carboxylic acids.
Timothy Donald Cook (born November 1, 1960) [ 1 ] is an American business executive who is the current chief executive officer of Apple. Cook had previously been the company’s chief operating officer under its co-founder Steve Jobs. [ 2 ] Cook joined Apple in March 1998 as a senior vice president for worldwide operations, and then as vice president for worldwide sales and operations. [ 3 ] He was appointed chief executive of Apple on August 24, 2011, after Jobs resigned.
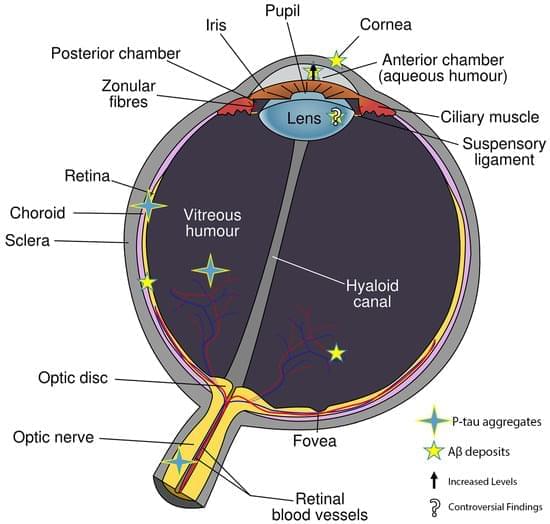
In the early stages of Alzheimer–Perusini’s disease (AD), individuals often experience vision-related issues such as color vision impairment, reduced contrast sensitivity, and visual acuity problems. As the disease progresses, there is a connection with glaucoma and age-related macular degeneration (AMD) leading to retinal cell death. The retina’s involvement suggests a link with the hippocampus, where most AD forms start. A thinning of the retinal nerve fiber layer (RNFL) due to the loss of retinal ganglion cells (RGCs) is seen as a potential AD diagnostic marker using electroretinography (ERG) and optical coherence tomography (OCT). Amyloid beta fragments (Aβ), found in the eye’s vitreous and aqueous humor, are also present in the cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) and accumulate in the retina. Aβ is known to cause tau hyperphosphorylation, leading to its buildup in various retinal layers.
Hypertriglyceridemia-associated acute pancreatitis (HLAP) is a severe gastrointestinal condition characterized by an increased risk of multiple organ dysfunction and elevated mortality. Intestinal microbiota, often described as the second human genome, plays a key role in maintaining gastrointestinal and systemic homeostasis. Among its various metabolites, short-chain fatty acids (SCFAs) are particularly abundant and functionally significant. Current evidence indicates a strong relationship between SCFAs and the pathogenesis and progression of HLAP. SCFAs contribute to the restoration of intestinal homeostasis by modulating the composition of gut microbiota, enhancing the integrity of the intestinal epithelial barrier, and regulating mucosal immune responses. Furthermore, SCFAs attenuate systemic inflammatory responses, promote pancreatic tissue repair, and reduce the risk of multiple organ dysfunction. These protective effects indicate that SCFAs represent a promising therapeutic target for gut-centered interventions in HLAP. This review summarizes the changes in intestinal microbiota and SCFA levels following HLAP onset, elucidates the underlying mechanisms by which SCFAs exert protective effects, and evaluates their potential therapeutic applications, thereby providing a theoretical basis for the development of gut-targeted strategies in the management of HLAP.
Acute pancreatitis (AP) is characterized by acute inflammation and cellular injury within the pancreas and is recognized as a common cause of acute abdominal disorders. With improvements in living standards and shifts in dietary habits, the incidence of hypertriglyceridemia-associated acute pancreatitis (HLAP) has significantly increased, surpassing alcoholic pancreatitis to become the second leading cause of AP (Chinese Pancreatic Surgery Association, and Chinese Society of Surgery, Chinese Medical Association, 2021). Additionally, HLAP is increasingly observed in younger adults and is associated with severe clinical presentations, including a higher incidence of complications such as acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS), acute kidney injury (AKI), and multiple organ dysfunction syndrome (MODS) (Li et al., 2018).
Over the past several decades, researchers have been making rapid progress in harnessing light to enable all sorts of scientific and industrial applications. From creating stupendously accurate clocks to processing the petabytes of information zipping through data centers, the demand for turnkey technologies that can reliably generate and manipulate light has become a global market worth hundreds of billions of dollars.
One challenge that has stymied scientists is the creation of a compact source of light that fits onto a chip, which makes it much easier to integrate with existing hardware. In particular, researchers have long sought to design chips that can convert one color of laser light into a rainbow of additional colors—a necessary ingredient for building certain kinds of quantum computers and making precision measurements of frequency or time.
Now, researchers at JQI have designed and tested new chips that reliably convert one color of light into a trio of hues. Remarkably, the chips all work without any active inputs or painstaking optimization—a major improvement over previous methods. The team described their results in the journal Science on Nov. 6, 2025.

A particle accelerator that produces intense X-rays could be squeezed into a device that fits on a table, my colleagues and I have found in a new research project.
The way that intense X-rays are currently produced is through a facility called a synchrotron light source. These are used to study materials, drug molecules, and biological tissues. Even the smallest existing synchrotrons, however, are about the size of a football stadium.
Our research, which has been accepted for publication in the journal Physical Review Letters, shows how tiny structures called carbon nanotubes and laser light could generate brilliant X-rays on a microchip. Although the device is still at the concept stage, the development has the potential to transform medicine, materials science, and other disciplines.
A new water-based plasma technique is opening fresh possibilities for carbon conversion.
Chinese researchers have created stable high-entropy alloy nanoparticles—containing five metals in nearly equal ratios—directly in solution, thereby overcoming long-standing challenges in nanoscale alloy synthesis.
These particles form a self-protecting, oxidized shell, delivering strong photothermal performance that utilizes visible and infrared light to drive carbon dioxide into carbon monoxide more efficiently than single-metal catalysts.