Scientists at the Herbert Irving Comprehensive Cancer Center (HICCC) have discovered a key mechanism that makes prostate cancer cells resistant to the latest drugs used to treat them. Their findings, reported in the current issue of Nature, solve a longstanding puzzle in tumor biology and present preclinical data on a drug compound that could soon enter the clinic.
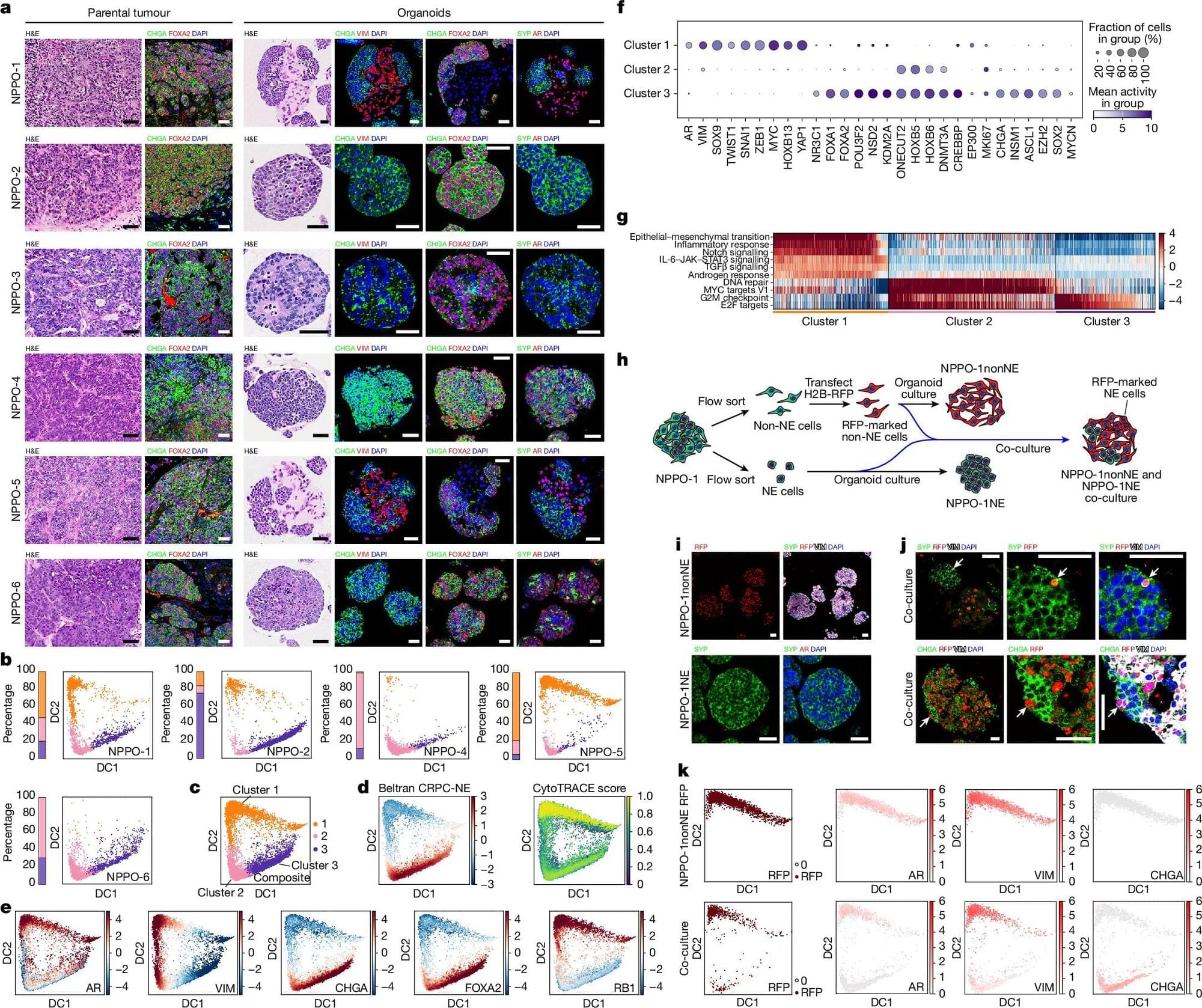
The work grew out of decades of prostate cancer research by Michael Shen, Ph.D., co-leader of the Tumor Biology and Microenvironment research program at the HICCC. Shen’s research focuses on lineage plasticity, the ability of cancer cells to reprogram themselves to impersonate other types of cells.
“Plasticity is a hallmark of cancer in general and a very important feature of advanced prostate cancer, particularly when it comes to the emergence of treatment resistance,” says Shen. Treatment with androgen receptor inhibitors, which have become the standard of care in recent years, often stimulate prostate tumor cells to adopt neuroendocrine characteristics, rendering them resistant to the drugs.