The global food system faces growing risks as modern farming practices undermine the resilience of the world’s soils, according to new research.

Palladium is one of the keys to jump-starting a hydrogen-based energy economy. The silvery metal is a natural gatekeeper against every gas except hydrogen, which it readily lets through. For its exceptional selectivity, palladium is considered one of the most effective materials at filtering gas mixtures to produce pure hydrogen.
Today, palladium-based membranes are used at commercial scale to provide pure hydrogen for semiconductor manufacturing, food processing, and fertilizer production, among other applications in which the membranes operate at modest temperatures. If palladium membranes get much hotter than around 800 Kelvin, they can break down.
Now, MIT engineers have developed a new palladium membrane that remains resilient at much higher temperatures. Rather than being made as a continuous film, as most membranes are, the new design is made from palladium that is deposited as “plugs” into the pores of an underlying supporting material. At high temperatures, the snug-fitting plugs remain stable and continue separating out hydrogen, rather than degrading as a surface film would.
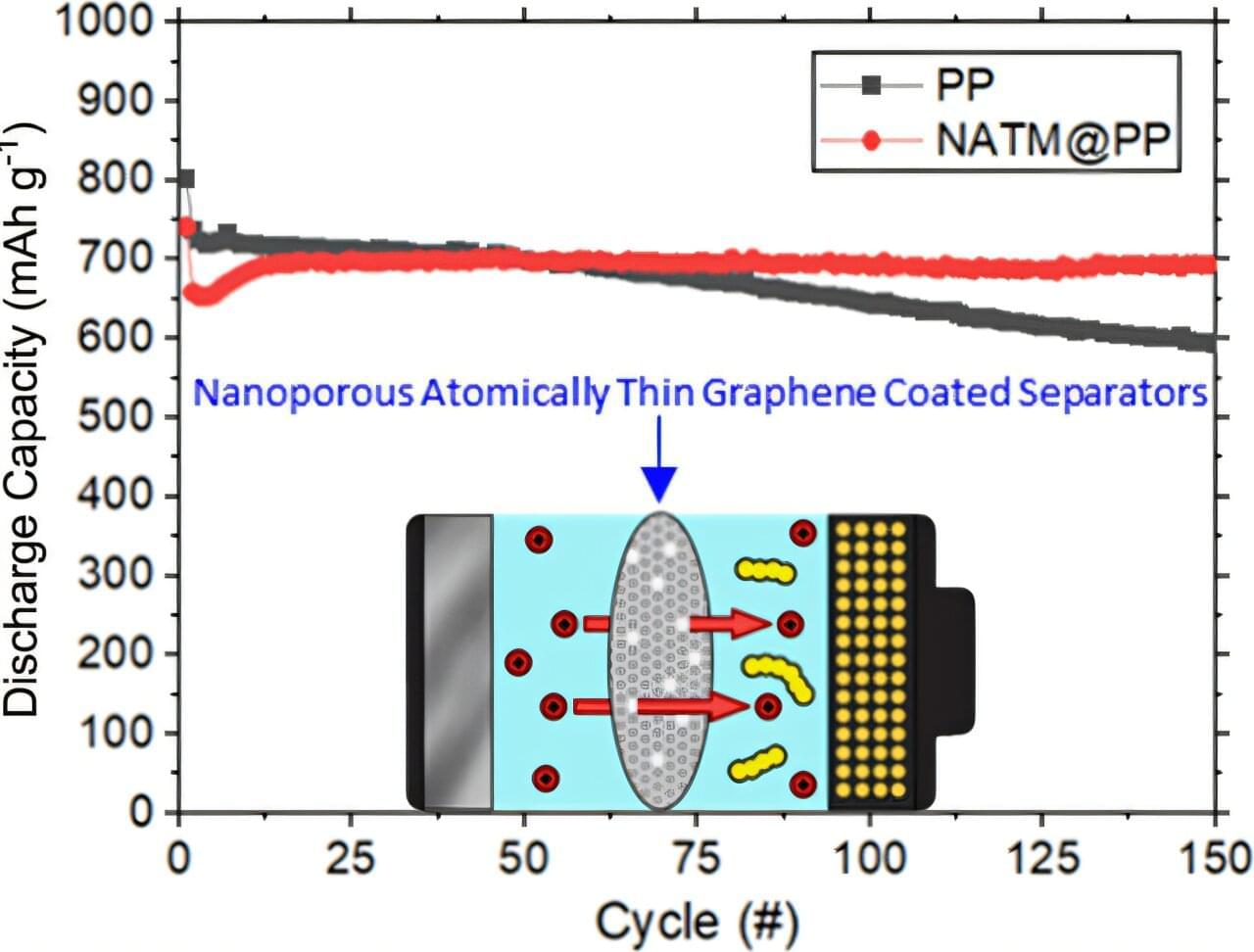
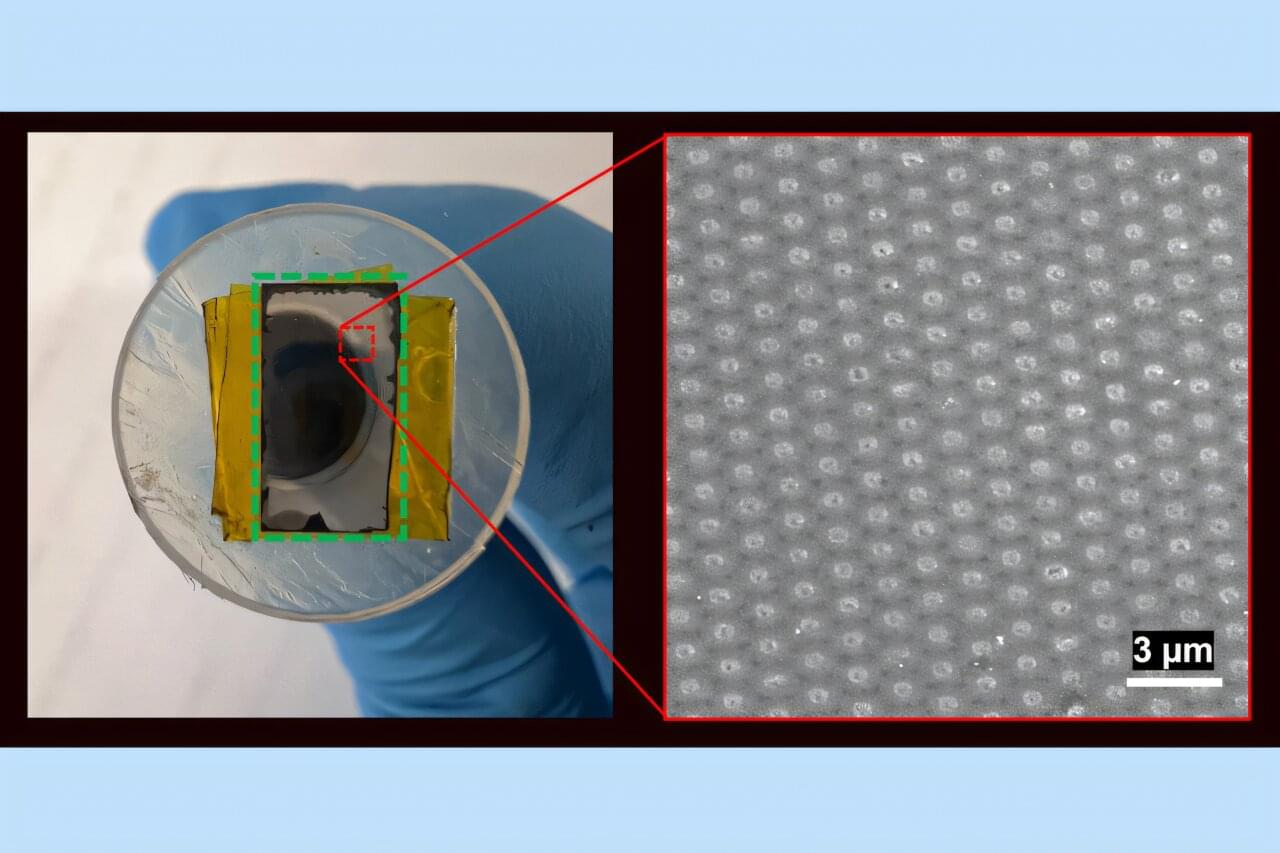
Longer-lasting phones, lighter drones, electric cars that drive farther. These are just some of the possibilities thanks to a new battery separator design from University of Florida researchers and their partners.
Think of a tiny coffee filter, but this one works inside a battery. The team recently showed that a one-atom-thick filter can block sulfur chains from shuttling within the battery, potentially unlocking the long-awaited promise of lithium–sulfur batteries.
While lithium–sulfur batteries are lighter and pack more power in a lighter package compared to the more conventional lithium-ion batteries, their fatal flaw is the sulfur doesn’t cooperate well inside the system. It clumps into long chains that clog up the works, draining the battery’s power and cutting its lifespan.
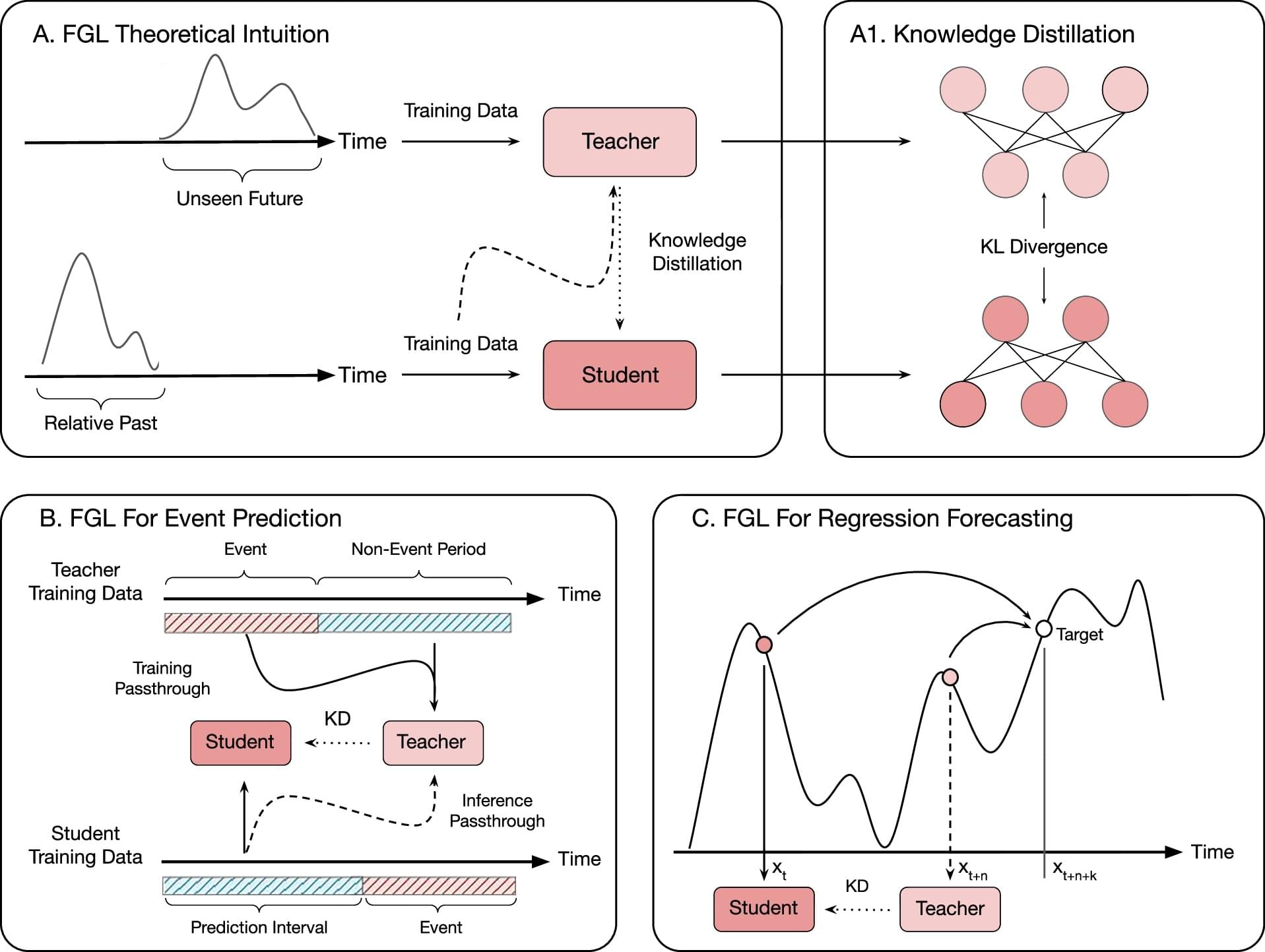
In the world around us, many things exist in the context of time: a bird’s path through the sky is understood as different positions over a period of time, and conversations as a series of words occurring one after another.
Computer scientists and statisticians call these sequences time series. Although statisticians have found ways to understand these patterns and make predictions about the future, modern deep learning AI models struggle to perform just as well, if not worse, than statistical models.
Engineers at the University of California, Santa Cruz, developed a new method for time series forecasting, powered by deep learning, that can improve its predictions based on data from the near future. When they applied this approach to the critical task of seizure prediction using brain wave data, they found that their strategy offers up to 44.8% improved performance for predicting seizures compared to baseline methods. While they focused on this critical health care application, the researchers’ method is designed to be relevant for a wide range of fields. A new study in Nature Communications reports their results.
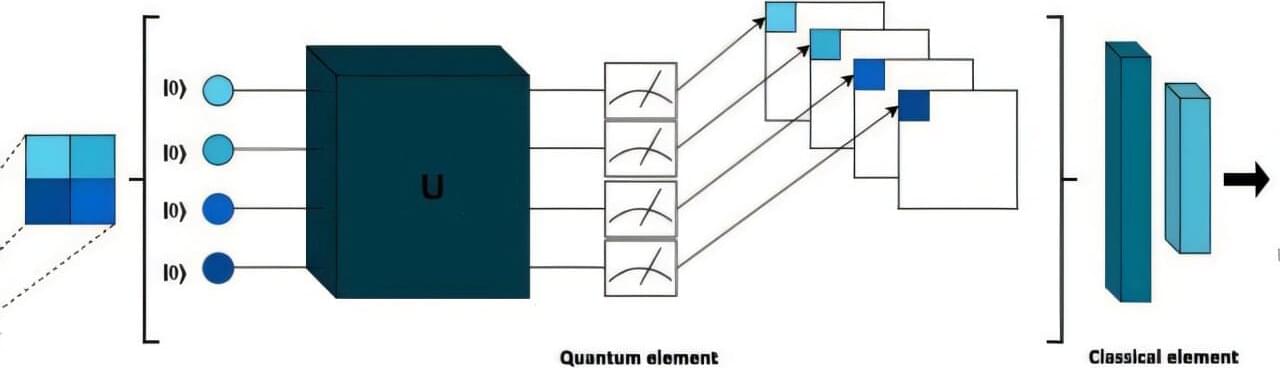
Quantum computing is still in its early stages of development, but researchers have extensively explored its potential uses. A recent study conducted at São Paulo State University (UNESP) in Brazil proposed a hybrid quantum-classical model to support breast cancer diagnosis from medical images.
The work was published as part of the 2025 IEEE 38th International Symposium on Computer-Based Medical Systems (CBMS), organized by the Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers (IEEE). In the publication, the authors describe a hybrid neural network that combines quantum and classical layers using an approach known as a quanvolutional neural network (QNN). They applied the model to mammography and ultrasound images to classify lesions as benign or malignant.
“What we wanted to bring to this work was a very basic architecture that used quantum computing but contained a minimum of quantum and classical devices,” says Yasmin Rodrigues, the first author of the study. The work is part of her scientific initiation project, supervised by João Paulo Papa, full professor in the Department of Computing at the Bauru campus of UNESP. Papa also co-authored the article.
A study from Rice University, published in PRX Quantum, has found that energy transfers more quickly between molecular sites when it starts in an entangled, delocalized quantum state instead of from a single site. The discovery could lead to the development of more efficient light-harvesting materials that enhance the conversion of energy from light into other forms of energy.
Many biochemical processes, including photosynthesis, depend on rapid and efficient energy transfer following absorption. Understanding how quantum mechanical effects like entanglement influence these processes at room temperature could significantly change our approach to creating artificial systems that mimic nature’s efficiency.
“Delocalizing the initial excitation across multiple sites accelerates the transfer in ways that starting from a single site cannot achieve,” said Guido Pagano, the study’s corresponding author and assistant professor of physics and astronomy.
Though it might seem like science fiction, scientists are working to build nanoscale molecular machines that can be designed for myriad applications, such as “smart” medicines and materials. But like all machines, these tiny devices need a source of power, the way electronic appliances use electricity or living cells use ATP (adenosine triphosphate, the universal biological energy source).
Researchers in the laboratory of Lulu Qian, Caltech professor of bioengineering, are developing nanoscale machines made out of synthetic DNA, taking advantage of DNA’s unique chemical bonding properties to build circuits that can process signals much like miniature computers. Operating at billionth-of-a-meter scales, these molecular machines can be designed to form DNA robots that sort cargos or to function like a neural network that can learn to recognize handwritten numerical digits.
One major challenge, however, has remained: how to design and power them for multiple uses.
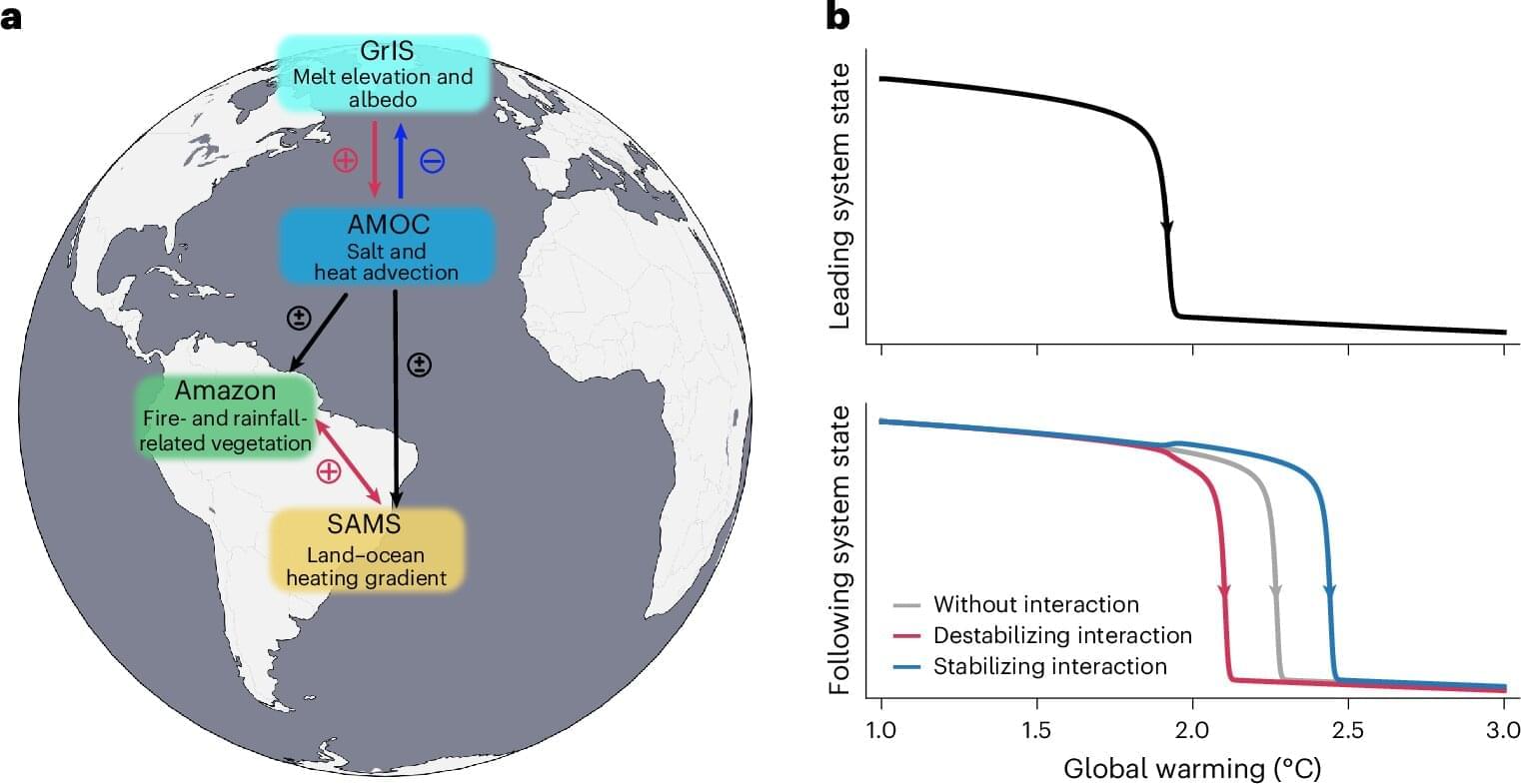
Four of the most important interconnected parts of the Earth’s climate system are losing stability, according to a review article based on observational data published in Nature Geoscience. The researchers succeeded in highlighting the warning signals for destabilization of the Greenland Ice Sheet, the Atlantic Meridional Overturning Circulation (AMOC), the Amazon rainforest, and the South American monsoon system.
A team of researchers from the University of Minnesota Twin Cities College of Science and Engineering and the University of Houston’s Cullen College of Engineering has discovered and measured the fraction of an electron that makes catalytic manufacturing possible.
This discovery, published in the journal ACS Central Science, explains the utility of precious metals such as gold, silver and platinum for this manufacturing, and provides insight for designing new breakthrough catalytic materials.
Industrial catalysts—substances that reduce the amount of energy required for a given chemical reaction—allow producers to increase the yield, speed or efficiency of a specific reaction in pursuit of other materials. Such catalysts are used in processes related to pharmaceutical and battery production as well as petrochemical efforts such as the refining of crude oil, allowing supply to keep pace with demand in ways it otherwise could not.
Imagine watching a favorite movie when suddenly the sound stops. The data representing the audio is missing. All that’s left are images. What if artificial intelligence (AI) could analyze each frame of the video and provide the audio automatically based on the pictures, reading lips and noting each time a foot hits the ground?
That’s the general concept behind a new AI that fills in missing data about plasma, the fuel of fusion, according to Azarakhsh Jalalvand of Princeton University. Jalalvand is the lead author on a paper about the AI, known as Diag2Diag, that was recently published in Nature Communications.
“We have found a way to take the data from a bunch of sensors in a system and generate a synthetic version of the data for a different kind of sensor in that system,” he said. The synthetic data aligns with real-world data and is more detailed than what an actual sensor could provide. This could increase the robustness of control while reducing the complexity and cost of future fusion systems. “Diag2Diag could also have applications in other systems such as spacecraft and robotic surgery by enhancing detail and recovering data from failing or degraded sensors, ensuring reliability in critical environments.”