Focusing on sound production instead of word choice makes for a flexible system.
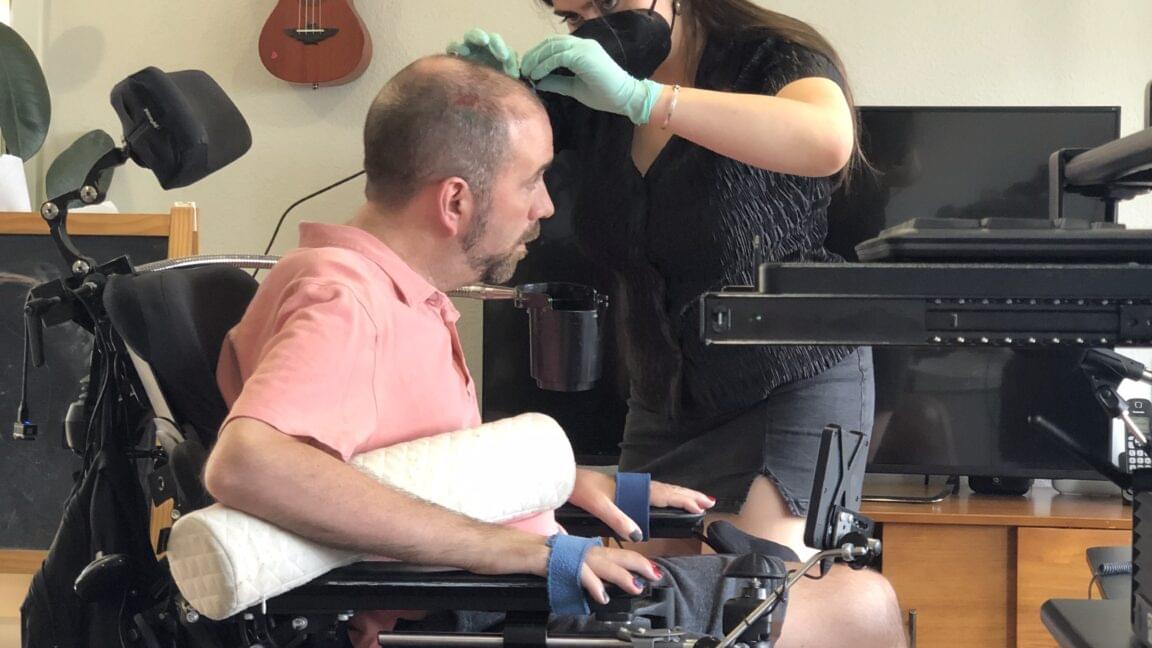



ImageimagePoorly energized mitochondria trap a subpopulation of mitochondrial precursor proteins in the intermembrane space. This article introduces ‘mitochondrial triage of precursor proteins’ (MitoTraP) as a mechanism that prevents the mistargeting of non-imported proteins to the nucleus and reduces proteotoxic effects.

The Princeton researchers built their devices with great care. Along with former postdoctoral fellow Qi Zhang, they created ultra-clean samples and chilled them using liquid helium. They measured how the material reacted when exposed to circularly polarized mid-infrared light, at wavelengths around 10.6 microns. They observed a strong response when the light’s spin matched the material’s internal chiral state—a sign of a phenomenon called the circular photogalvanic effect (CPGE).
The CPGE has become a powerful tool in recent years. It works by measuring how electric currents change depending on the direction of light spin. In this case, the presence of a CPGE signal directly proved that the material’s internal structure was chiral. Even more, the direction and pattern of the signal revealed which symmetries had been broken.
The discovery puts to rest years of debate among physicists. Since 2021, there’s been disagreement over whether the charge-ordered state in KV₃Sb₅ actually breaks key symmetries or if those effects were caused by noise or imperfections. Earlier tools like scanning tunneling microscopes and electrical measurements had shown hints of chirality, but results were unclear and often contradicted each other.
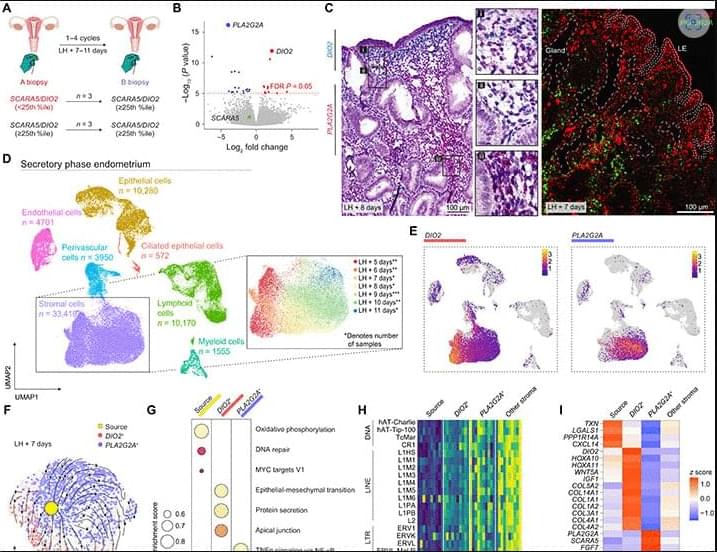
Miscarriage denotes the loss of a pregnancy before viability (1). Approximately one in three embryos perishes following implantation in healthy women, although often before routine detection of pregnancy (2, 3). This attrition rate reflects the high prevalence of chromosomal errors in preimplantation human embryos (4) and the physiological role of the endometrium in selecting against low-fitness embryos (2, 3, 5, 6). The pooled miscarriage risk in all clinically recognized pregnancies is an estimated 15% (1), with most losses (~90%) occurring before the onset of uteroplacental perfusion at the end of the first trimester (7). Epidemiological studies consistently highlight that two factors, maternal age and the number of preceding pregnancy losses, disproportionally affect miscarriage rates (7–9). The age-dependent risk reflects the increase in aneuploid pregnancies in women aged 35 years and older, mirroring the incidence of meiotic chromosome errors in oocytes and embryos (10, 11). Each prior pregnancy loss further compounds the risk stepwise by 5 to 10% (7–9), but the underlying mechanism is unknown. A plausible but untested hypothesis is that the recurrence risk of miscarriage reflects the frequency of menstrual cycles culminating in an endometrial environment permissive of embryo implantation but inadequately prepared for decidual transformation (3), that is, the formation of a robust immunotolerant matrix that anchors and supports the semiallogenic placenta throughout pregnancy (2, 5).
Each menstrual cycle starts with the shedding of the superficial endometrial layer, bleeding, and reepithelization of the basal layer. Following menstruation, estradiol-dependent regeneration of the superficial layer, on average, quadruples the thickness and volume of the uterine mucosa before ovulation (12). Local morphogen and cytokine gradients regulate epithelial and stromal cell proliferation, resulting in tissue stratification and positional cell specification. After ovulation, progesterone acting on this spatial template triggers a decidual reaction, an endogenous inflammatory tissue response that heralds the start of the 4-day midluteal implantation window (2, 13). Histologically, the implantation window coincides with the onset of glandular secretion, marked oedema, and proliferative expansion and differentiation of uterine natural killer (uNK) cells (14, 15).
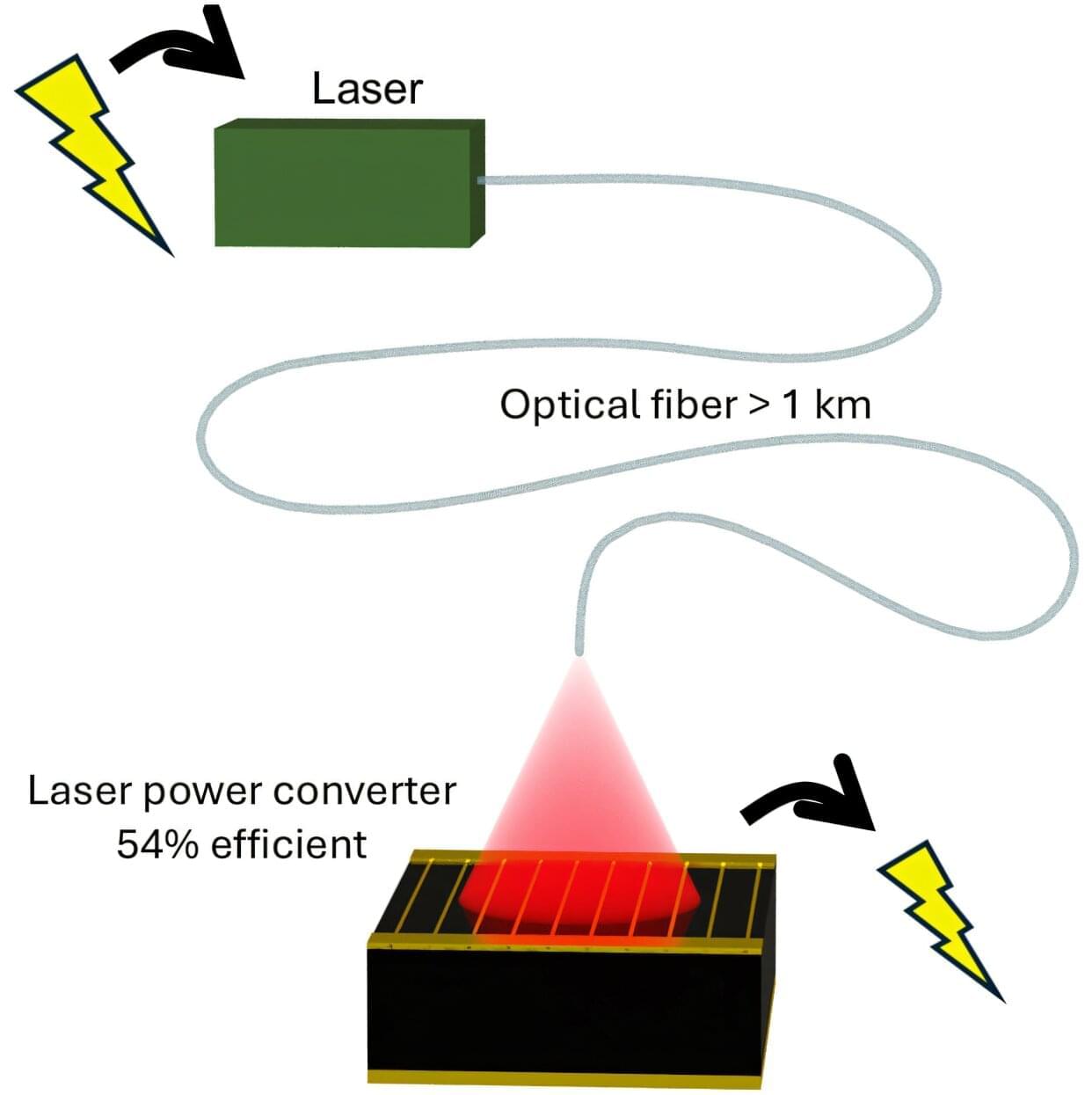
From smart grids to the internet of things, the modern world is increasingly reliant on connectivity between electronic devices. Thanks to University of Ottawa researchers, these devices can now be simultaneously connected and powered with a simple optical fiber over long distances, even in the harshest environments.
This significant step forward in the development of photonic power converters—devices that turn laser light into electrical power —could integrate laser-driven, remote power solutions into existing fiber optic infrastructure. This, in turn, could pave the way for improved connectivity and more reliable communication in remote locations and extreme situations.
“In traditional power over fiber systems, most of the laser light is lost,” explains Professor Karin Hinzer of the University of Ottawa’s SUNLAB, which collaborated with Germany’s Fraunhofer Institute for Solar Energy Systems on the study. “With these new devices, the fiber can be much longer.”
Questions to inspire discussion.
🚕 Q: How reliable is Tesla’s robotaxi service based on recent experiences? A: Tesla’s robotaxi service has perfect rides in 9 out of 10 experiences, with one incident of phantom braking due to sun glare.
📱 Q: How do users access and pay for Tesla’s robotaxi service? A: Users access the service through a separate app from the Tesla app, requiring Tesla sign-in and linked credit card information for payment.
Tesla Model Updates and Pricing.
🔋 Q: What changes were made to the refreshed Model S and X? A: The refresh includes new hardware for improved autonomy, new color options, wheel design, and ambient lighting, with a $5,000 price increase and 5–7% range increase.
🛡️ Q: What does Tesla’s new extended warranty plan offer? A: Tesla’s plan extends coverage for 4 years or 100,000 miles at $50–150 per month depending on the model, covering most manufactured parts except the high-voltage battery, tires, and glass.