The world’s biggest octopus aggregation is made up of thousands of these usually solitary creatures
Get the latest international news and world events from around the world.

Scientists discover hidden geometry that bends electrons like gravity
Researchers have discovered a hidden quantum geometry inside materials that subtly steers electrons, echoing how gravity warps light in space. Once thought to exist only on paper, this effect has now been observed experimentally in a popular quantum material. The finding reveals a new way to understand and control how materials conduct electricity and interact with light. It could help power future ultra-fast electronics and quantum technologies.

In its second-largest ever acquisition, US tech giant acquires Q.ai amid effort to break into wearables market; 30% of firm’s staff were called up to reserve duty on Oct. 7…
…Q.ai is tight-lipped in public about its technology, but patents it filed show tech being used in headphones or glasses using ‘facial skin micro movements’ for nonverbal communication, according to the FT.
Apple’s vice president of hardware, Johnny Srouji, said in a statement that the startup is ‘pioneering new and creative ways to use imaging and machine learning.’
The move may be a component of Apple’s strategy for ‘wearable’ products, such as smart glasses. Software that reads facial expressions could potentially make way for a hands-free user interface that doesn’t require talking out loud, reports noted.

Spaceflight causes astronauts’ brains to shift, stretch and compress in microgravity
Spaceflight takes a physical toll on astronauts, causing muscles to atrophy, bones to thin and bodily fluids to shift. According to a new study published in the journal PNAS, we can now add another major change to that list. Being in microgravity causes the brain to change shape.
Here on Earth, gravity helps to keep the brain anchored in place while the cerebrospinal fluid that surrounds it acts as a cushion. Scientists already knew that, without gravity’s steady pull, the brain moves upward, but this new research showed that it is also stretched and compressed in several areas.
Brains on the move Researchers led by Rachel Seidler at the University of Florida reached this conclusion after studying MRI scans of 26 astronauts taken before and after their missions to the International Space Station. These were compared with scans from 24 volunteers who participated in a head-down tilt bed rest experiment. They spent 60 days lying at a six-degree downward angle to mimic how weightlessness causes bodily fluids and organs to move toward the head.
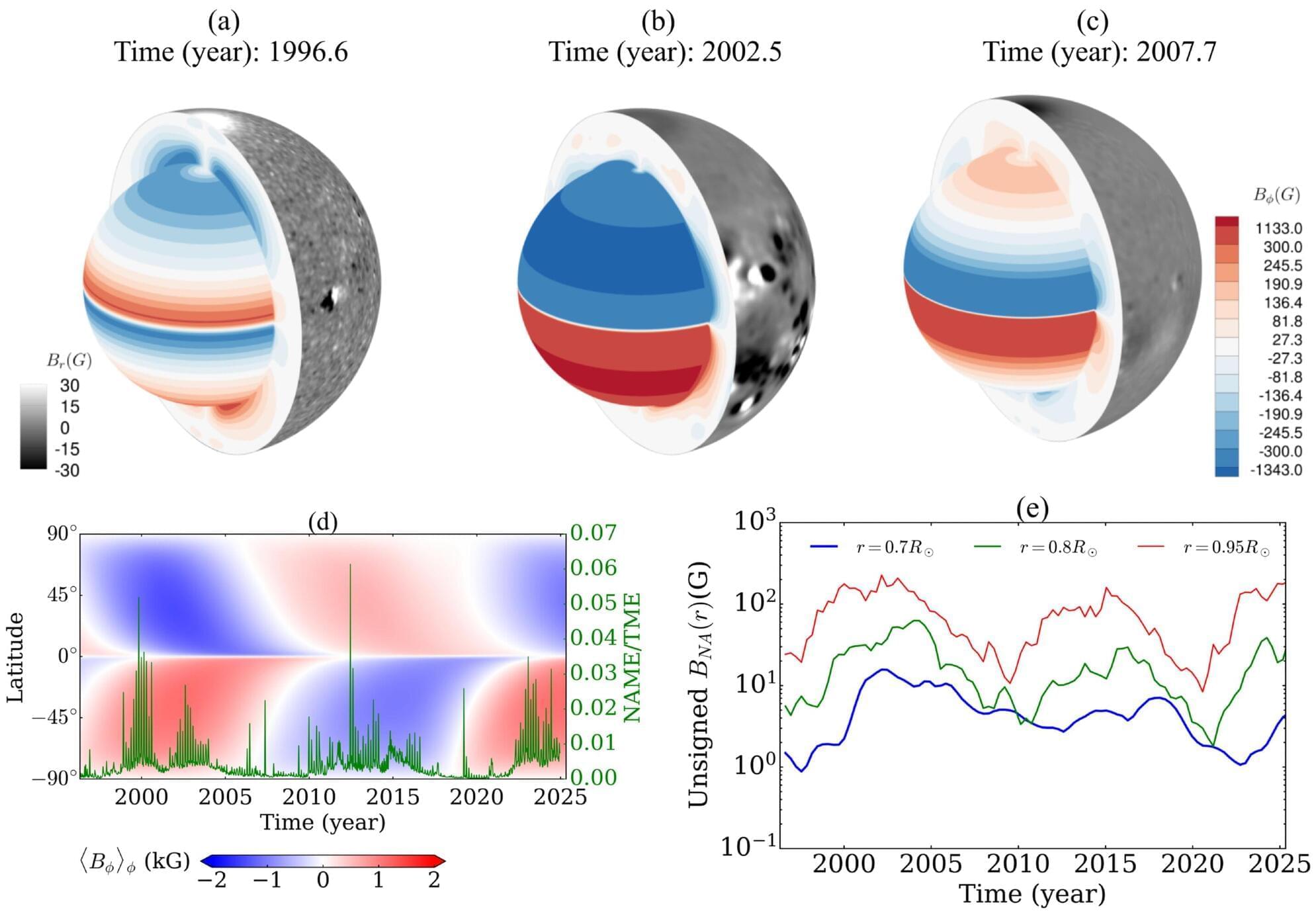
New 3D map of the sun’s magnetic interior could improve predictions of disruptive solar flares
For the first time, scientists have used satellite data to create a 3D map of the sun’s interior magnetic field, the fundamental driver of solar activity. The research, published in The Astrophysical Journal Letters, should enable more accurate predictions of solar cycles and space weather that affects satellites and power grids.
The sun is more than just a fiery hot ball of hydrogen and helium gas. It is a giant magnetic star. Beneath the surface is a magnetic layer that is responsible for everything from the dark spots we see on its face to violent flares that erupt into space. Because of the disruption caused by solar storms, we need to know what is going on inside. We can’t directly observe the interior, so to date we have relied on models that depend on simplified assumptions. But these can be inaccurate.
To get a better idea of what is going on inside the sun, researchers from India fed 30 years of daily magnetic maps from satellites (from 1996 to 2025) into a sophisticated 3D model of the solar dynamo, the physical process that generates the sun’s magnetic field. By using this real-world data, they could track how magnetic fields move deep beneath the surface, where satellites cannot penetrate.
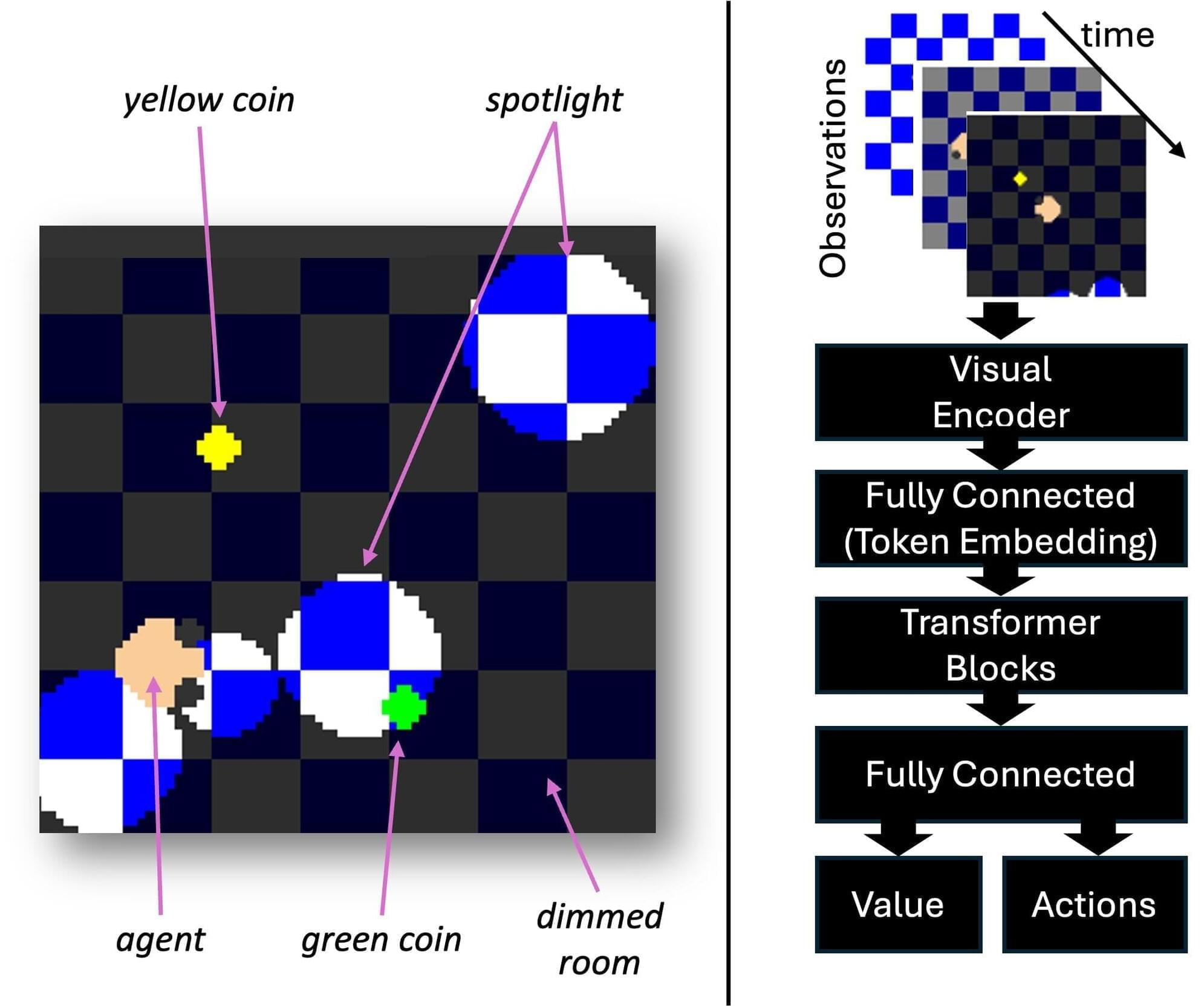
Geometry behind how AI agents learn revealed
A new study from the University at Albany shows that artificial intelligence systems may organize information in far more intricate ways than previously thought. The study, “Exploring the Stratified Space Structure of an RL Game with the Volume Growth Transform,” has been published online through arXiv.
For decades, scientists assumed that neural networks encoded data on smooth, low-dimensional surfaces known as manifolds. But UAlbany researchers found that a transformer-based reinforcement-learning model instead organizes its internal representations in stratified spaces—geometric structures composed of multiple interconnected regions with different dimensions. Their findings mirror recent results in large language models, suggesting that stratified geometry might be a fundamental feature of modern AI systems.
“These models are not living on simple surfaces,” said Justin Curry, associate professor in the Department of Mathematics and Statistics in the College of Arts and Sciences. “What we see instead is a patchwork of geometric layers, each with its own dimensionality. It’s a much richer and more complex picture of how AI understands the world.”
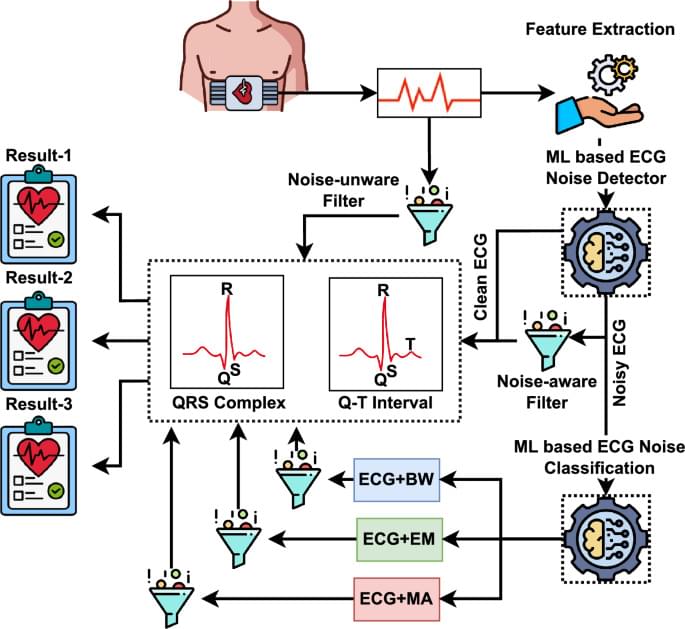
Design and evaluation of a knowledge-based ECG noise filtering framework
Rahman, S., Yearwood, J. & Karmakar, C. Design and evaluation of a knowledge-based ECG noise filtering framework. Sci Rep 16, 2,429 (2026). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-025-32249-7
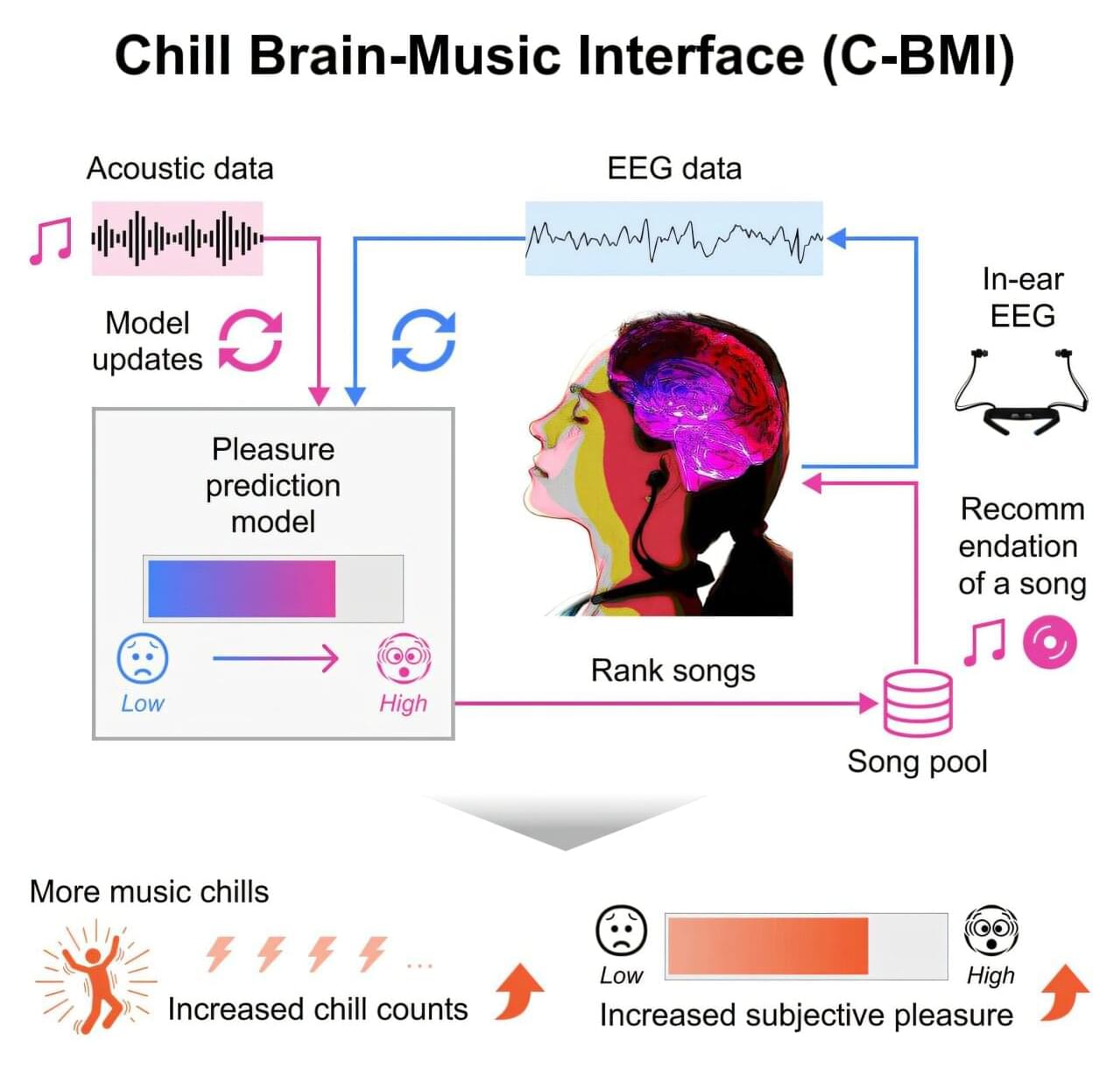
Chill brain-music interface: Using brain signals to enhance the emotional power of music
Musical chills are pleasurable shivers or goosebump sensations that people feel when they resonate with the music they’re listening to. They reduce stress and have beneficial side effects, but they are difficult to induce reliably. Now, researchers from Japan have developed a practical system that uses in-ear electroencephalography sensors to measure the brain’s response to music in real time and provide music suggestions that enhance chills.
Most people are familiar with “musical chills”—a sudden, involuntary shiver or goosebump sensation that occurs when a song resonates perfectly with one’s emotions. These chills are not just a surface-level feeling, but a profound neurological event. When we experience intense musical pleasure, parts of the brain’s reward system activate in a manner similar to how they would respond to life-affirming stimuli, such as beloved foods or positive social connections.
However, despite the universal nature of the experience, musical chills are difficult to trigger reliably. This limits our ability to harness their psychological and physiological benefits, even with today’s on-demand access to vast libraries of music.
Dr. Chris Oswald — Precision Nutrition, Epigenetics & Practitioner-Led Longevity Care
Precision Nutrition, Epigenetics & Practitioner-Led Longevity Care — Dr. Chris Oswald — Head of Medical Affairs, Pure Encapsulations, Nestlé Health Science.
Dr. Chris Oswald, DC, CNS, is Head of Medical Affairs for Pure Encapsulations (https://www.pureencapsulations.com/), part of Nestlé Health Science family. He is a chiropractor, certified nutrition specialist and certified functional medicine practitioner and has been treating patients since 2007.
At Pure Encapsulations, Dr. Oswald leads medical education, scientific strategy, and innovation across well-known professional brands including Pure Encapsulations, Douglas Labs, Klean Athlete, Genestra, and others. In this role, he sits at the intersection of clinical science, practitioner education, and product innovation — translating complex evidence into practical tools that help healthcare professionals practice more confident, personalized nutritional medicine.
Dr. Oswald’s clinical work, in combination with his work in professional dietary supplement companies, gives him unique insight into the creation of clinically useful tools and education to support the unique needs of clinicians and patients in functional, integrative and natural health.
Before joining Pure Encapsulations, Dr. Oswald held senior leadership roles across the nutraceutical and health tech landscape, including Chief Science Officer, Head of Product Innovation and R&D, Head of Operations, Interim Head of Sales, and VP of Nutraceuticals at companies like January AI and Further Food. Across those roles, he’s led everything from supply chain and regulatory strategy to product development, claims substantiation, and national practitioner education.