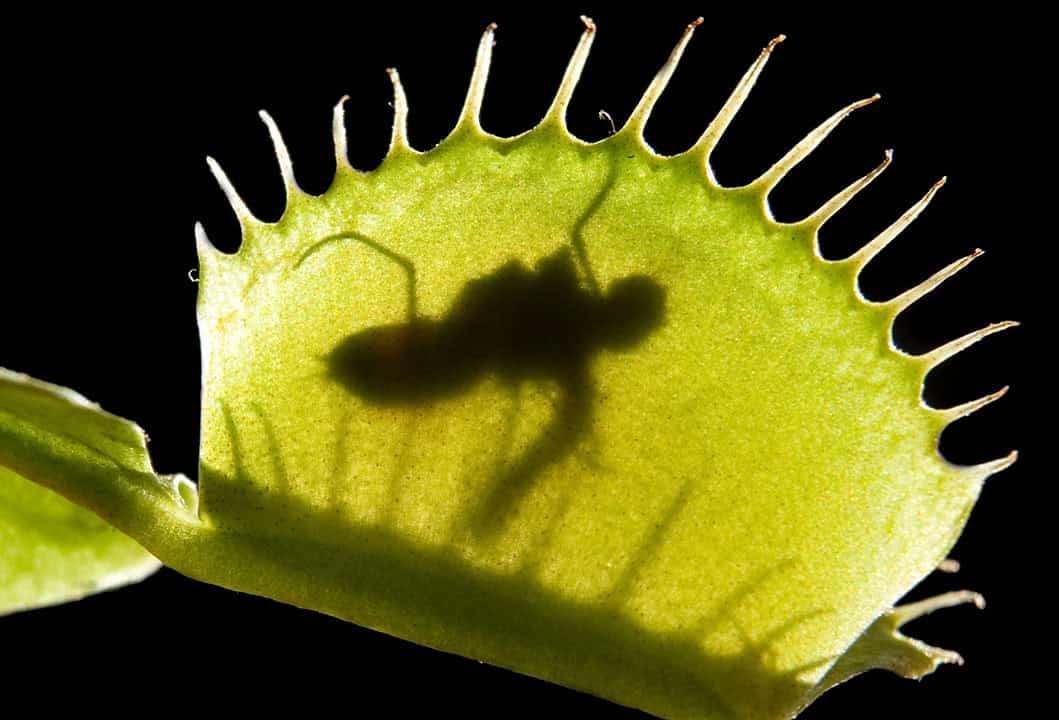
Japanese scientists discover the molecular switch that lets the Venus flytrap sense touch.
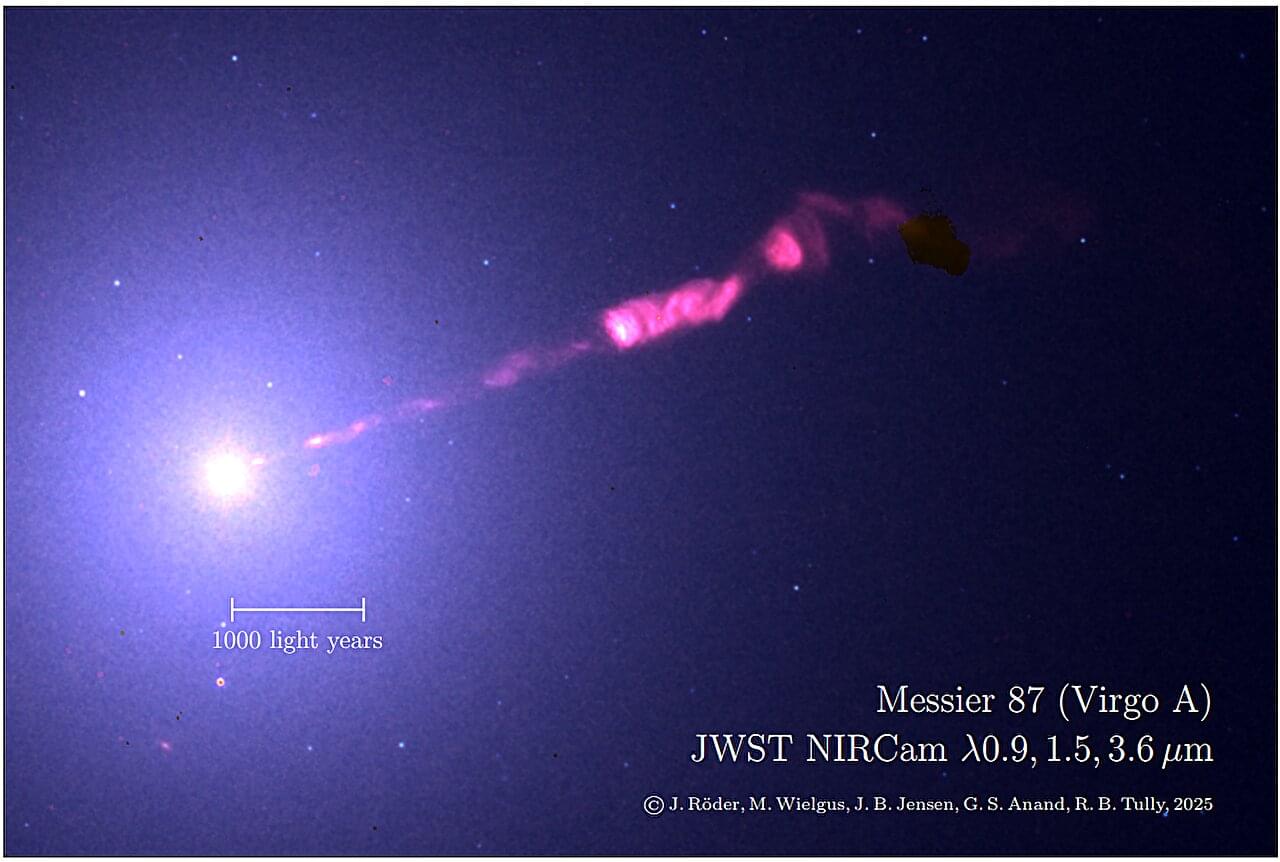



Scientists have long been aware of the massive elliptical galaxy, M87. The galaxy was first observed in the late 18th century by Charles Messier, who cataloged objects in the sky specifically to avoid them when looking for comets. However, numerous later observations in the radio, X-ray, optical, UV, and gamma-ray bands revealed that the object is a galaxy with a prominent jet emerging from a supermassive black hole at its core. This jet is now well known for its synchrotron emission in the radio to optical wavelengths.
Although many observations have been made on M87, data had been somewhat lacking in the infrared spectrum. But now, a group of scientists have utilized new data from the James Webb Space Telescope (JWST) and its near infrared cameras (NIRCam) to resolve some previously fuzzy details about M87’s jet. The work is now published in the journal Astronomy & Astrophysics.
The JWST+NIRCam images were taken in four infrared bands at 0.90, 1.50, 2.77, and 3.56 µm. In order to isolate the light coming from the actual jet, the team used background subtraction methods, calibration, and galaxy modeling to remove light from stars, galactic dust, background galaxies, and globular clusters. This revealed a detailed infrared picture of the main jet, as well as the counter-jet, which points in the opposite direction coming out from the black hole.
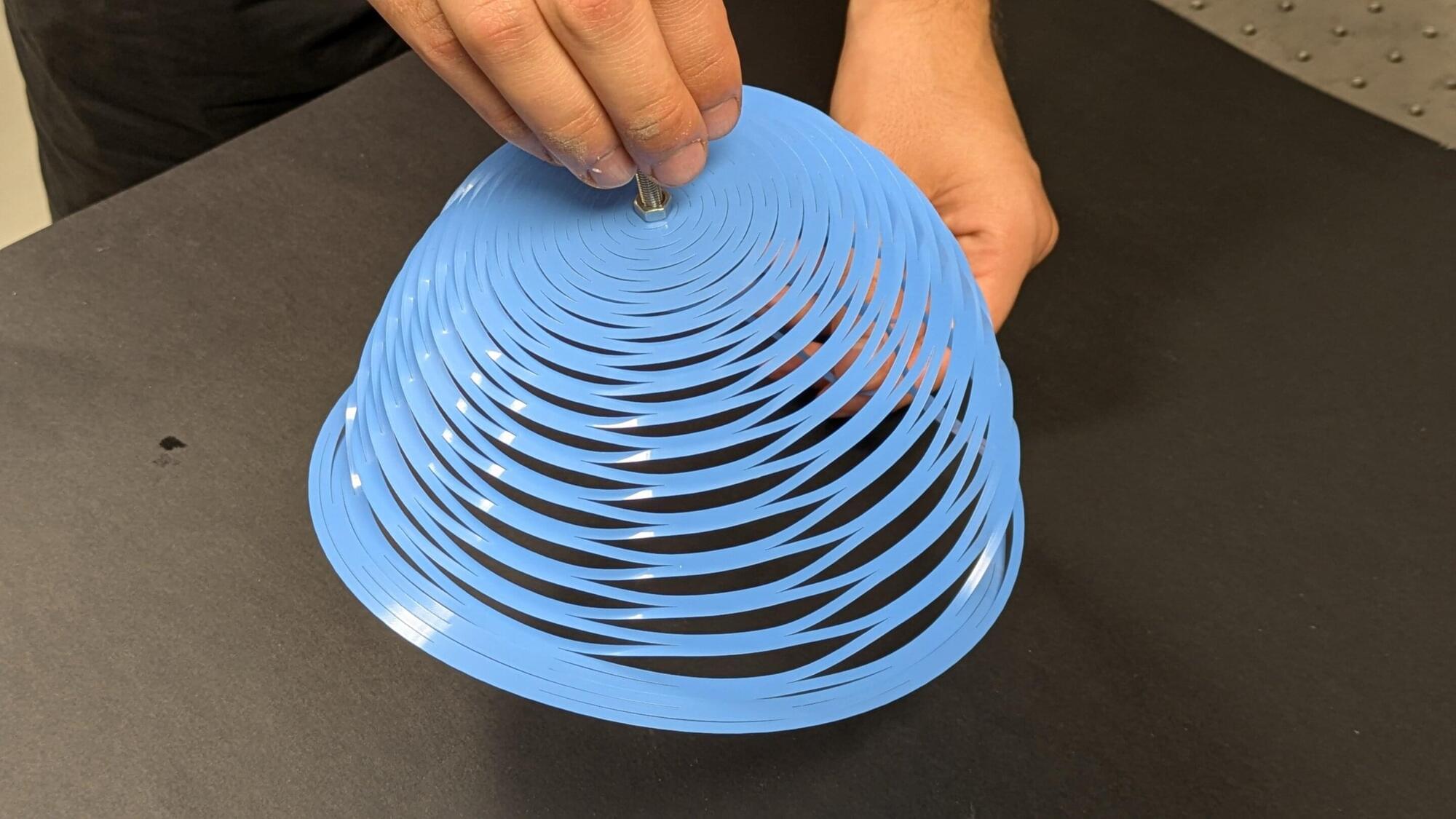
A team of engineers from Polytechnique Montréal report a new and unique parachute concept inspired by the Japanese art of kirigami today in Nature. This simple, robust and low-cost approach has a wide variety of potential applications ranging from humanitarian aid to space exploration.
Kirigami is a technique that modifies the mechanical properties of a sheet of material by making precise folds and cuts to it. Children use it to make snowflakes out of paper, and engineers have used it to create extensible structures, flexible medical devices and deployable spatial structures. However, kirigami techniques have never been applied to parachute production.
The Polytechnique Montréal research team has now changed all that.

Autism spectrum disorder (ASD) is a neurodevelopmental disorder that is estimated to be experienced by roughly 1 in 127 people worldwide. It is characterized by atypical patterns in brain development, which manifest in differences in communication, social interactions, behavior and responses to sensory information.
Past neuroscientific and genetic studies suggest that a variety of factors contribute to the development of ASD. These can include genetic factors, chemical alterations that influence the expressions of genes (i.e., epigenetic factors), differences in the structure of specific brain regions or neural circuits, and environmental factors, such as early life events or infections or immune responses during pregnancy.
Researchers at the Korea Brain Research Institute and University of Fukui in Japan recently carried out a study aimed at further exploring these different dimensions of ASD, focusing on brain structure, the communication between brain regions, epigenetic changes and behavioral patterns. Their findings, published in Translational Psychiatry, paint a clearer picture of the intricate underpinnings of the disorder and could inform the development of more precise tools for diagnosing it.
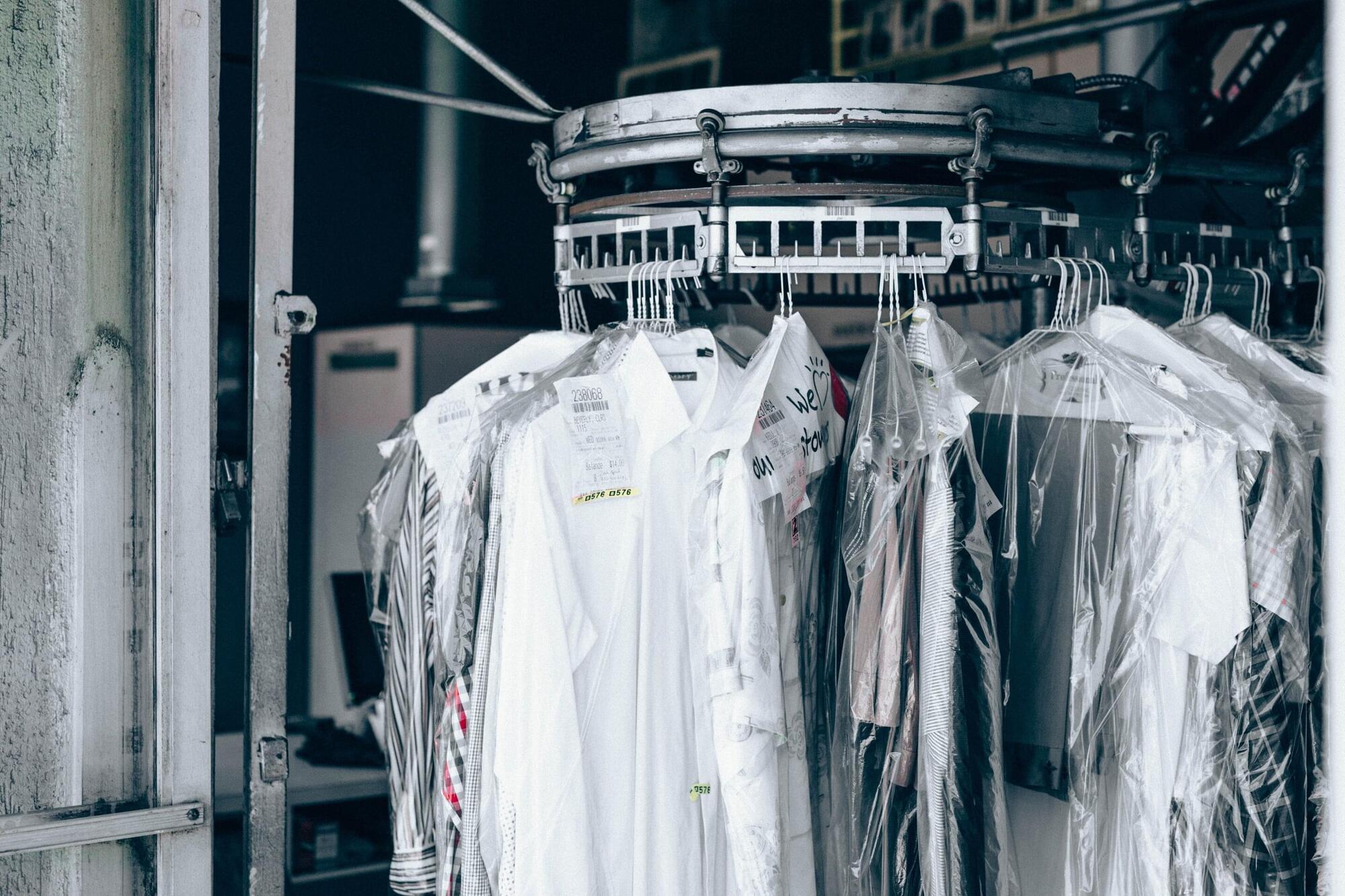

Long-term exposure to the industrial solvent trichloroethylene (TCE) outdoors may be linked to an increased risk of Parkinson’s disease, according to a large nationwide study published in Neurology.
TCE is a chemical used in metal degreasing, dry cleaning and other industrial applications. Although TCE has been banned for certain uses, it remains in use today as an industrial solvent and is a persistent environmental pollutant in air, water and soil across the United States. The study does not prove that TCE exposure causes Parkinson’s disease, it only shows an association.
“In this nationwide study of older adults, long-term exposure to trichloroethylene in outdoor air was associated with a small but measurable increase in Parkinson’s risk,” said study author Brittany Krzyzanowski, Ph.D., of Barrow Neurological Institute in Phoenix. “These findings add to a growing body of evidence that environmental exposures may contribute to Parkinson’s disease.”

The universe is approaching the midpoint of its 33-billion-year lifespan, a Cornell physicist calculates with new data from dark-energy observatories. After expanding to its peak size about 11 billion years from now, it will begin to contract—snapping back like a rubber band to a single point at the end.
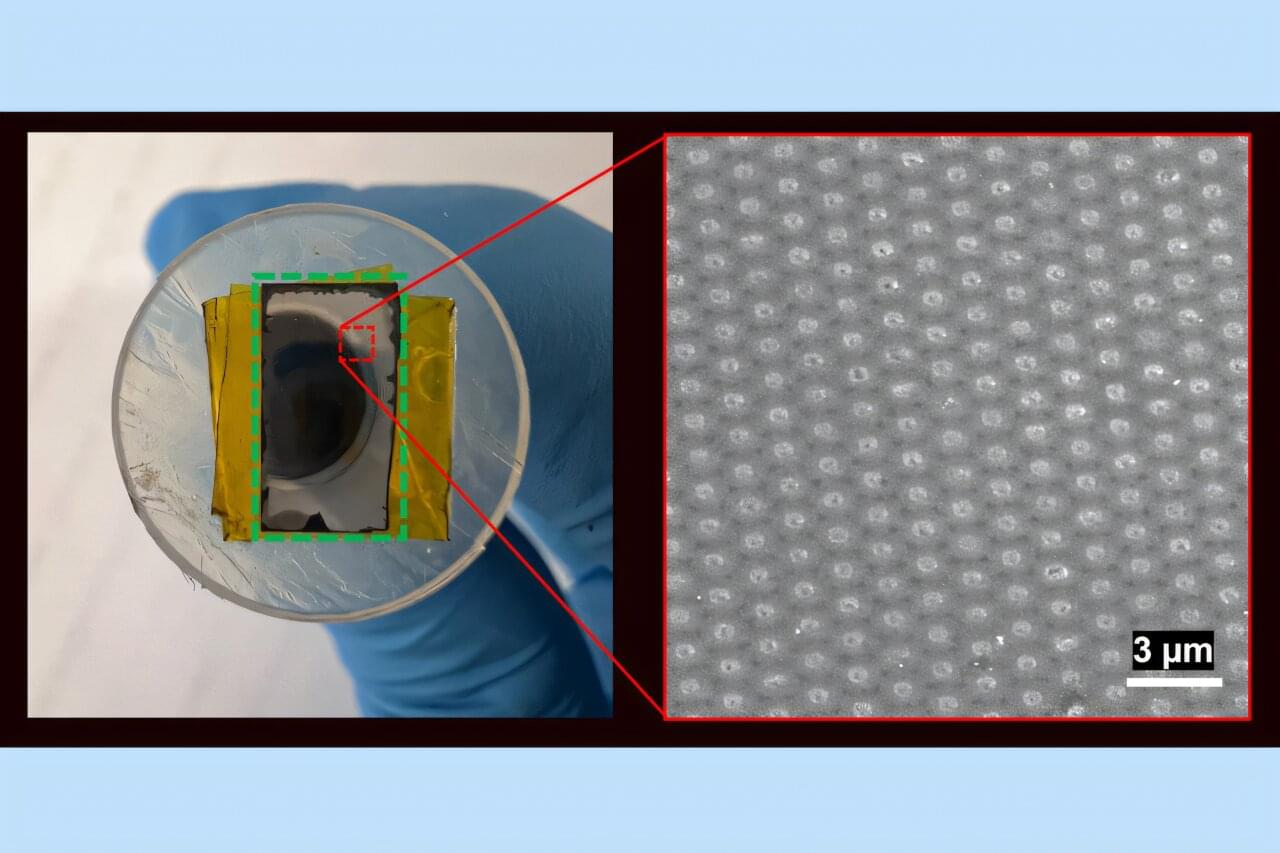
Palladium is one of the keys to jump-starting a hydrogen-based energy economy. The silvery metal is a natural gatekeeper against every gas except hydrogen, which it readily lets through. For its exceptional selectivity, palladium is considered one of the most effective materials at filtering gas mixtures to produce pure hydrogen.
Today, palladium-based membranes are used at commercial scale to provide pure hydrogen for semiconductor manufacturing, food processing, and fertilizer production, among other applications in which the membranes operate at modest temperatures. If palladium membranes get much hotter than around 800 Kelvin, they can break down.
Now, MIT engineers have developed a new palladium membrane that remains resilient at much higher temperatures. Rather than being made as a continuous film, as most membranes are, the new design is made from palladium that is deposited as “plugs” into the pores of an underlying supporting material. At high temperatures, the snug-fitting plugs remain stable and continue separating out hydrogen, rather than degrading as a surface film would.
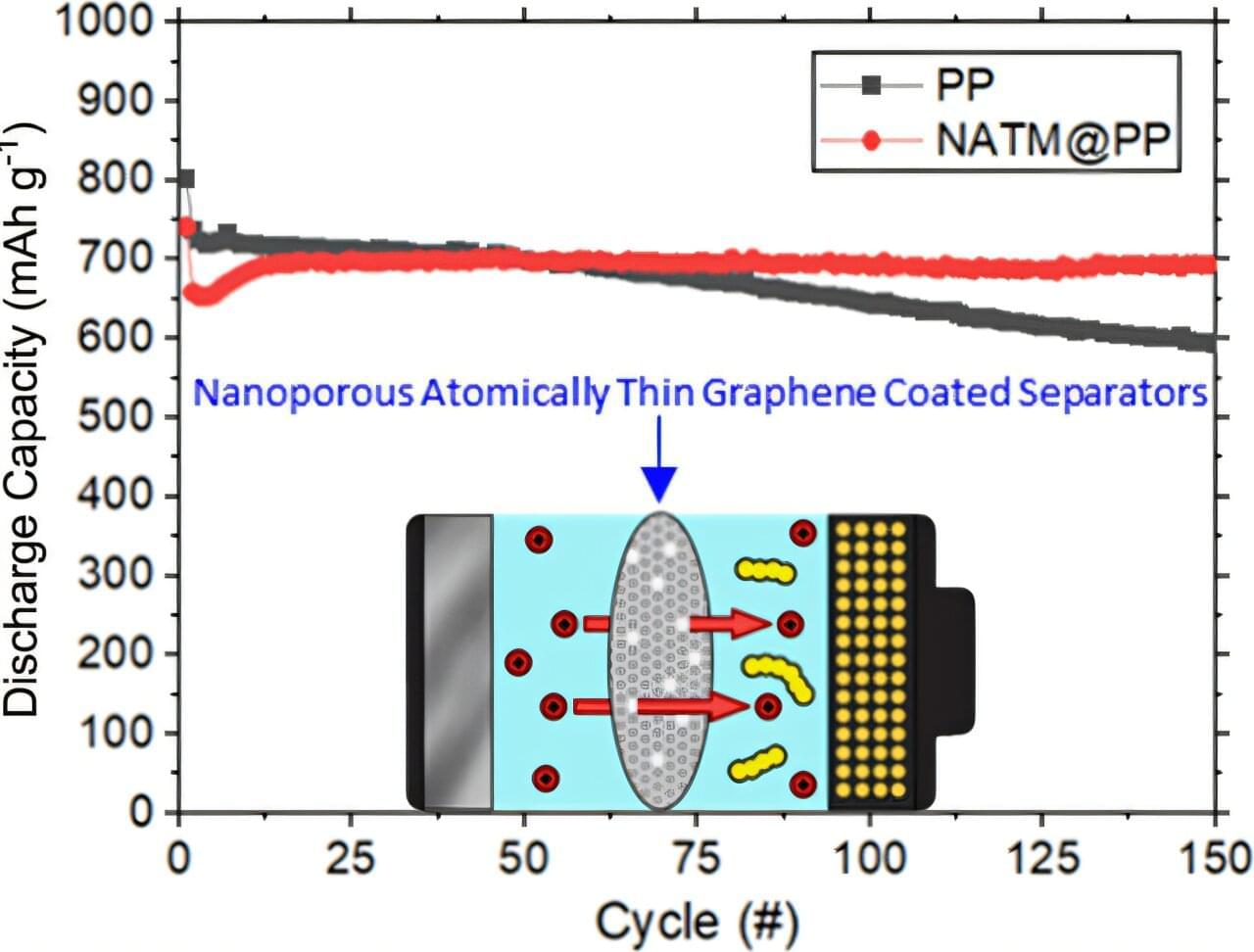
Longer-lasting phones, lighter drones, electric cars that drive farther. These are just some of the possibilities thanks to a new battery separator design from University of Florida researchers and their partners.
Think of a tiny coffee filter, but this one works inside a battery. The team recently showed that a one-atom-thick filter can block sulfur chains from shuttling within the battery, potentially unlocking the long-awaited promise of lithium–sulfur batteries.
While lithium–sulfur batteries are lighter and pack more power in a lighter package compared to the more conventional lithium-ion batteries, their fatal flaw is the sulfur doesn’t cooperate well inside the system. It clumps into long chains that clog up the works, draining the battery’s power and cutting its lifespan.
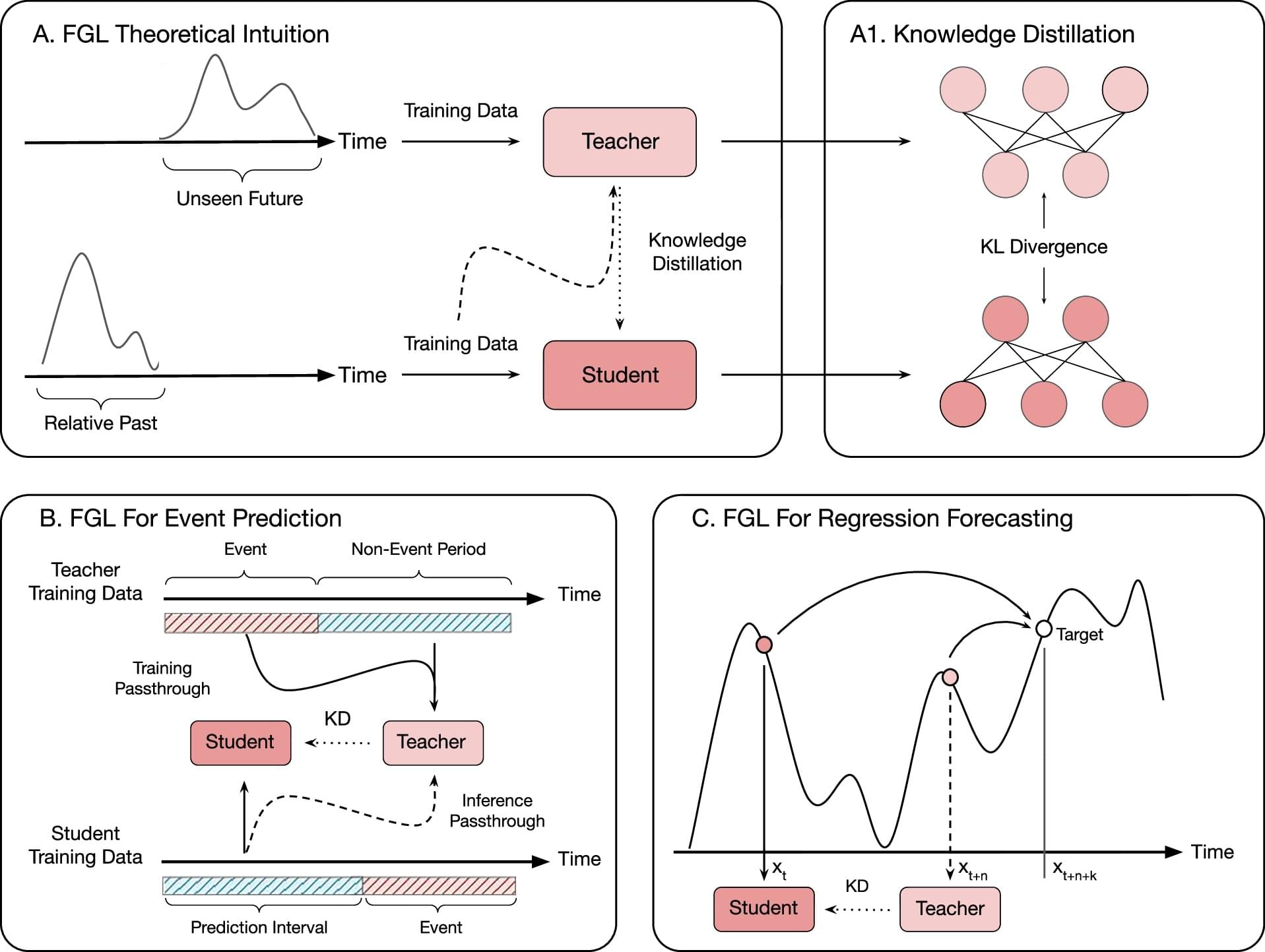
In the world around us, many things exist in the context of time: a bird’s path through the sky is understood as different positions over a period of time, and conversations as a series of words occurring one after another.
Computer scientists and statisticians call these sequences time series. Although statisticians have found ways to understand these patterns and make predictions about the future, modern deep learning AI models struggle to perform just as well, if not worse, than statistical models.
Engineers at the University of California, Santa Cruz, developed a new method for time series forecasting, powered by deep learning, that can improve its predictions based on data from the near future. When they applied this approach to the critical task of seizure prediction using brain wave data, they found that their strategy offers up to 44.8% improved performance for predicting seizures compared to baseline methods. While they focused on this critical health care application, the researchers’ method is designed to be relevant for a wide range of fields. A new study in Nature Communications reports their results.