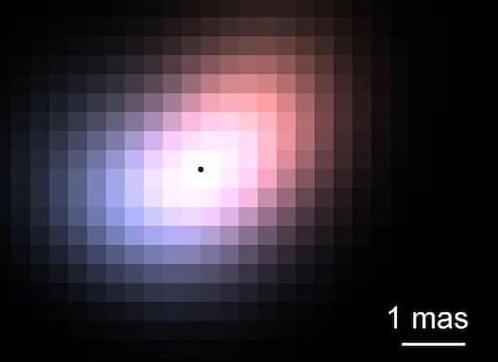
Astronomers have discovered a clever way to make a single telescope capture sharper details than should be physically possible. The technique involves feeding starlight through a special optical fibre called a photonic lantern. Anyone else thinking of a certain glowing green lantern from a movie? Alas not, instead of special powers, it splits light according to its spatial patterns like separating a musical chords into individual notes. The researchers achieved resolution that has never been achieved before without linking multiple telescopes together. When they tested the technique on a star 162 light-years away, they not only proved it works but stumbled upon an unexpected discovery, that the star’s surrounding gas disc is mysteriously lopsided.