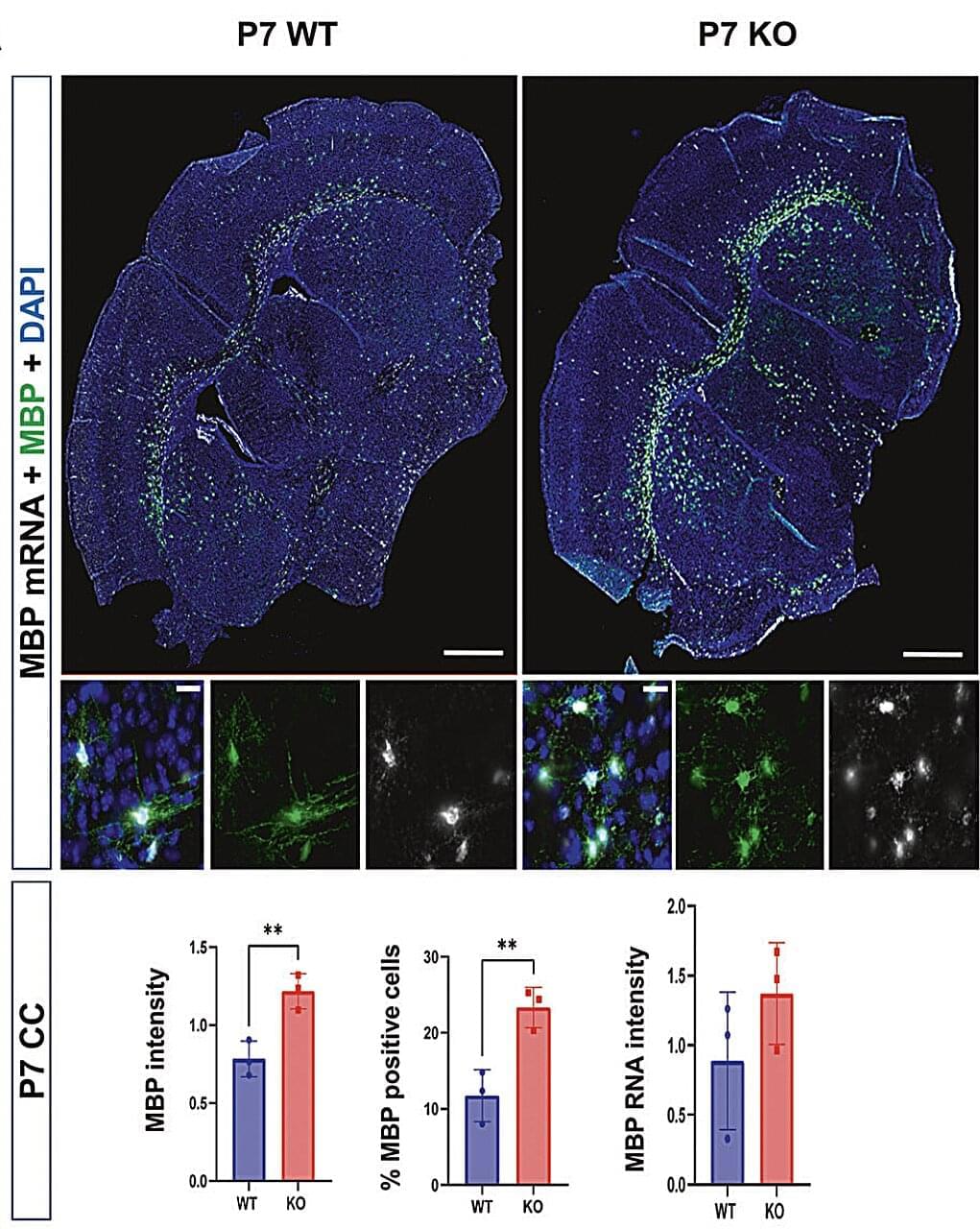
Autism spectrum disorder (ASD) is a neurodevelopmental condition characterized by differences in communication, behavior and the processing of sensory information. Past research has shown that some individuals diagnosed with ASD exhibit specific genetic variants or differences in the regulation of genes.
In some patients, the Shank3 gene was found to be mutated, partially or fully deleted, or not expressed as much. This gene is known to support the creation of junctions at which connected neurons communicate with each other, known as synapses.
Past findings suggest that people diagnosed with ASD who exhibit variants in Shank3 also present abnormalities in the volume, structure and function of white matter. White matter is a brain region filled with a fatty substance known as myelin, which insulates nerves and allows signals to travel faster within the nervous system.