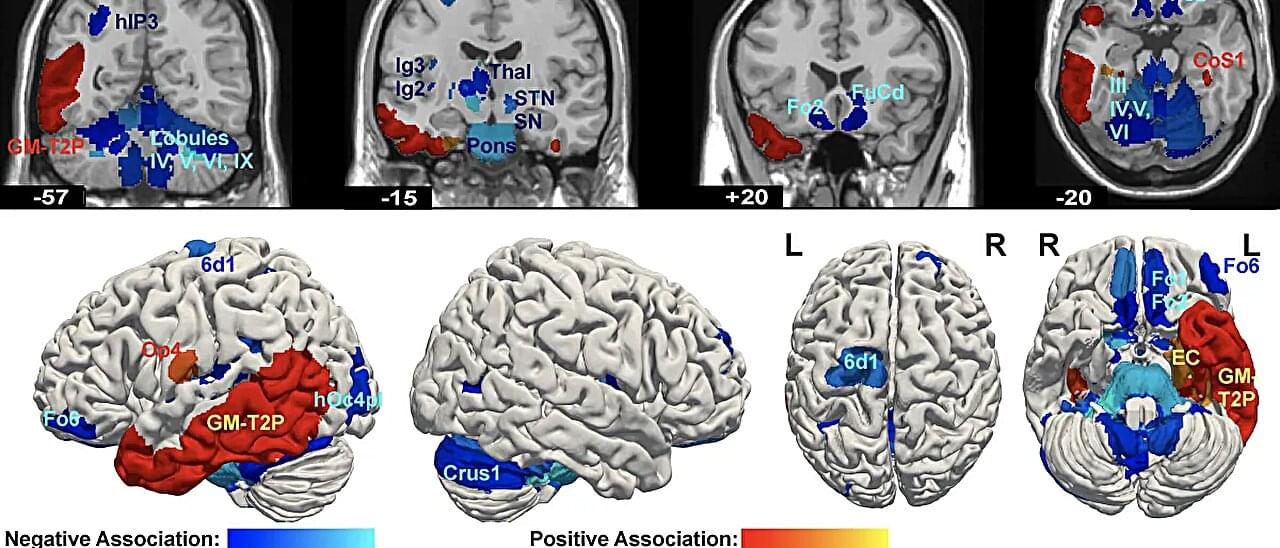
A recent study has shed light on the brain structure differences associated with psychopathy—a condition known to be one of the strongest predictors of persistent violent behavior.
The findings are published in the journal European Archives of Psychiatry and Clinical Neuroscience.
Using advanced neuroimaging and the Julich-Brain Atlas, researchers from Forschungszentrum Jülich, RWTH Aachen University, Heinrich-Heine-University Düsseldorf, Georg August University, (Germany) and University of Pennsylvania (U.S.) have identified specific brain networks that appear to be structurally altered in individuals exhibiting psychopathic traits. The Atlas can be freely accessed via the EBRAINS Research Infrastructure.