Adding PARP inhibitor niraparib to standard prostate cancer treatment delays disease progression in men with certain DNA repair gene mutations. | Drug Discovery And Development

The team wanted to understand how immune cells of the brain, called microglia, contribute to Alzheimer’s disease (AD) pathology. It’s known that subtle changes, or mutations, in genes expressed in microglia are associated with an increased risk for developing late-onset AD.
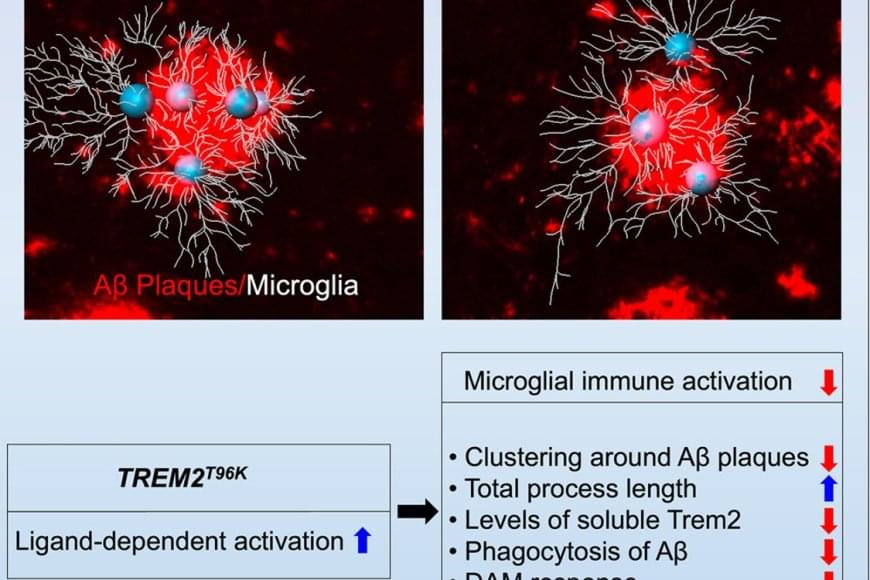
The study focused on one such mutation in the microglial gene TREM2, an essential switch that activates microglia to clean up toxic amyloid plaques (abnormal protein deposits) that build up between nerve cells in the brain. This mutation, called T96K, is a “gain-of-function” mutation in TREM2, meaning it increases TREM2 activation and allows the gene to remain super active.
They explored how this mutation impacts microglial function to increase risk for AD. The authors generated a mutant mouse model carrying the mutation, which was bred with a mouse model of AD to have brain changes consistent with AD. They found that in female AD mice exclusively, the mutation strongly reduced the capability of microglia to respond to toxic amyloid plaques, making these cells less protective against brain aging.
Scientists have developed a chromium-molybdenum-silicon alloy that withstands extreme heat while remaining ductile and oxidation-resistant. It could replace nickel-based superalloys, which are limited to about 1,100°C. The new material might make turbines and engines significantly more efficient, marking a major step toward cleaner, more powerful energy systems.


Discover the hidden brain of the Saturn V — the Instrument Unit’s gyroscopes. Learn how these precision-spinning machines guided humanity’s most powerful rocket with unmatched accuracy, keeping Apollo on course to the Moon.
🚀 Every like, comment, and share helps keep Apollo’s engineering story alive.
If you liked this video, please share it with a friend and leave a comment below — it really helps the channel grow.
🚀 New Apollo episodes every week!
📘 Recommended Reading for Space Enthusiasts.
Explore the real stories, engineering, and people behind the Apollo Program — these are the best books to deepen your knowledge:
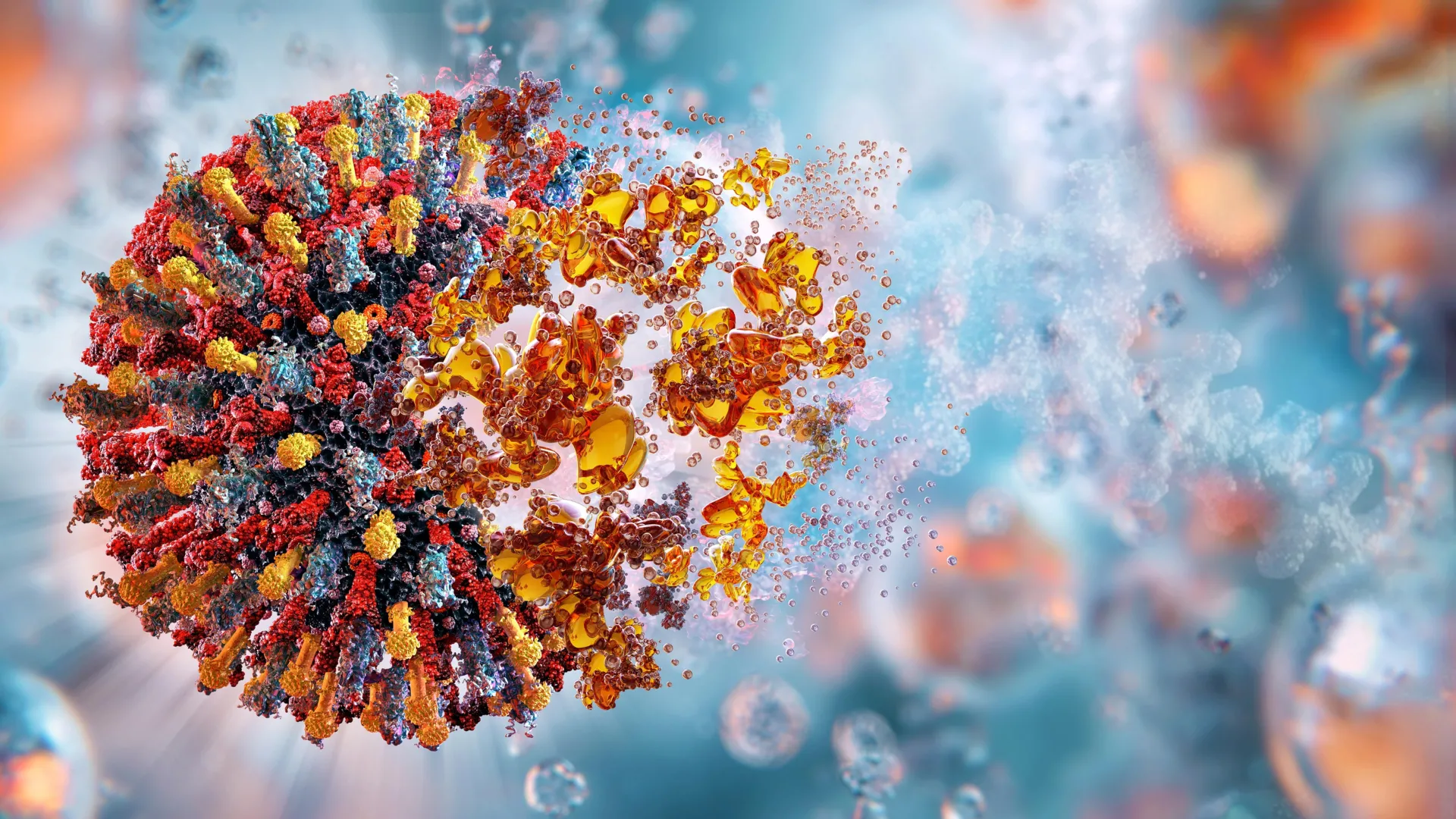
Researchers at the University of Massachusetts Amherst have shown that their nanoparticle-based vaccine can successfully prevent several aggressive cancers in mice, including melanoma, pancreatic cancer, and triple-negative breast cancer. Depending on the cancer type, up to 88% of vaccinated mice stayed tumor-free (depending on the cancer), and the vaccine also reduced — and in some cases completely prevented — the spread of cancer throughout the body.
“By engineering these nanoparticles to activate the immune system via multi-pathway activation that combines with cancer-specific antigens, we can prevent tumor growth with remarkable survival rates,” says Prabhani Atukorale, assistant professor of biomedical engineering in the Riccio College of Engineering at UMass Amherst and corresponding author on the paper.
Atukorale had previously shown that her nanoparticle-based drug design could shrink or eliminate tumors in mice. The new findings reveal that this approach can also prevent cancer from forming in the first place.
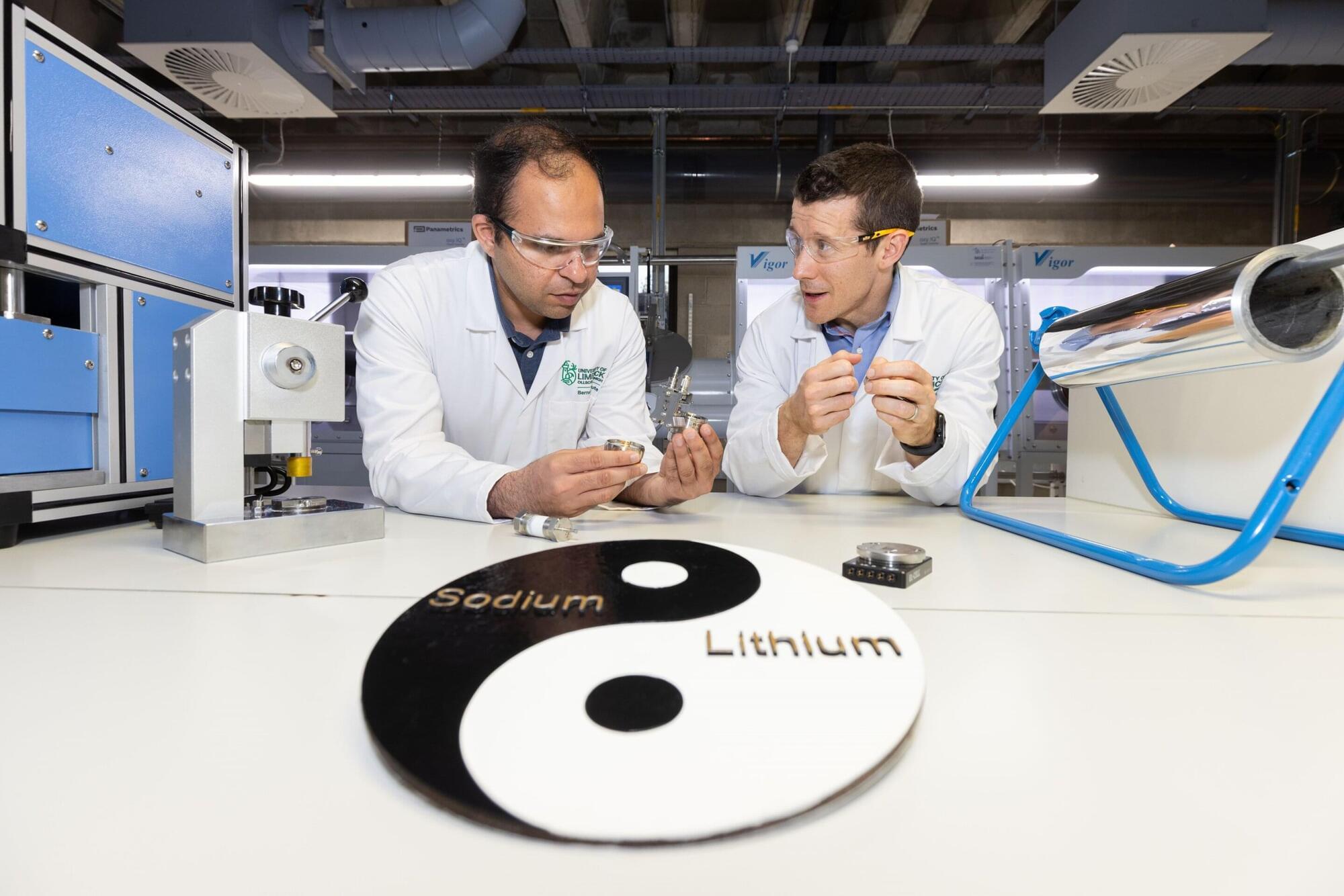

Researchers at University of Limerick (UL) have developed a battery that could reshape the future of electric vehicles and portable electronics. Their breakthrough in energy storage technology has seen the development of the world’s first full-cell dual-cation battery.
This innovative system combines lithium and sodium ions to significantly enhance both battery capacity and stability, marking a new frontier in sustainable energy research.
The work, published in Nano Energy, was led by Hugh Geaney, Associate Professor of Chemistry at UL’s Department of Chemical Sciences and Principal Investigator at UL’s Bernal Institute, and Government of Ireland postdoctoral fellow, Dr. Syed Abdul Ahad, his colleague at the Department and the Bernal Institute.