In the U.S., one in five of the 37 million adults who has diabetes doesn’t know it. Current methods of diagnosing diabetes and prediabetes usually require a visit to a doctor’s office or lab work, both of which can be expensive and time-consuming. Now, diagnosing diabetes and prediabetes may be as simple as breathing.
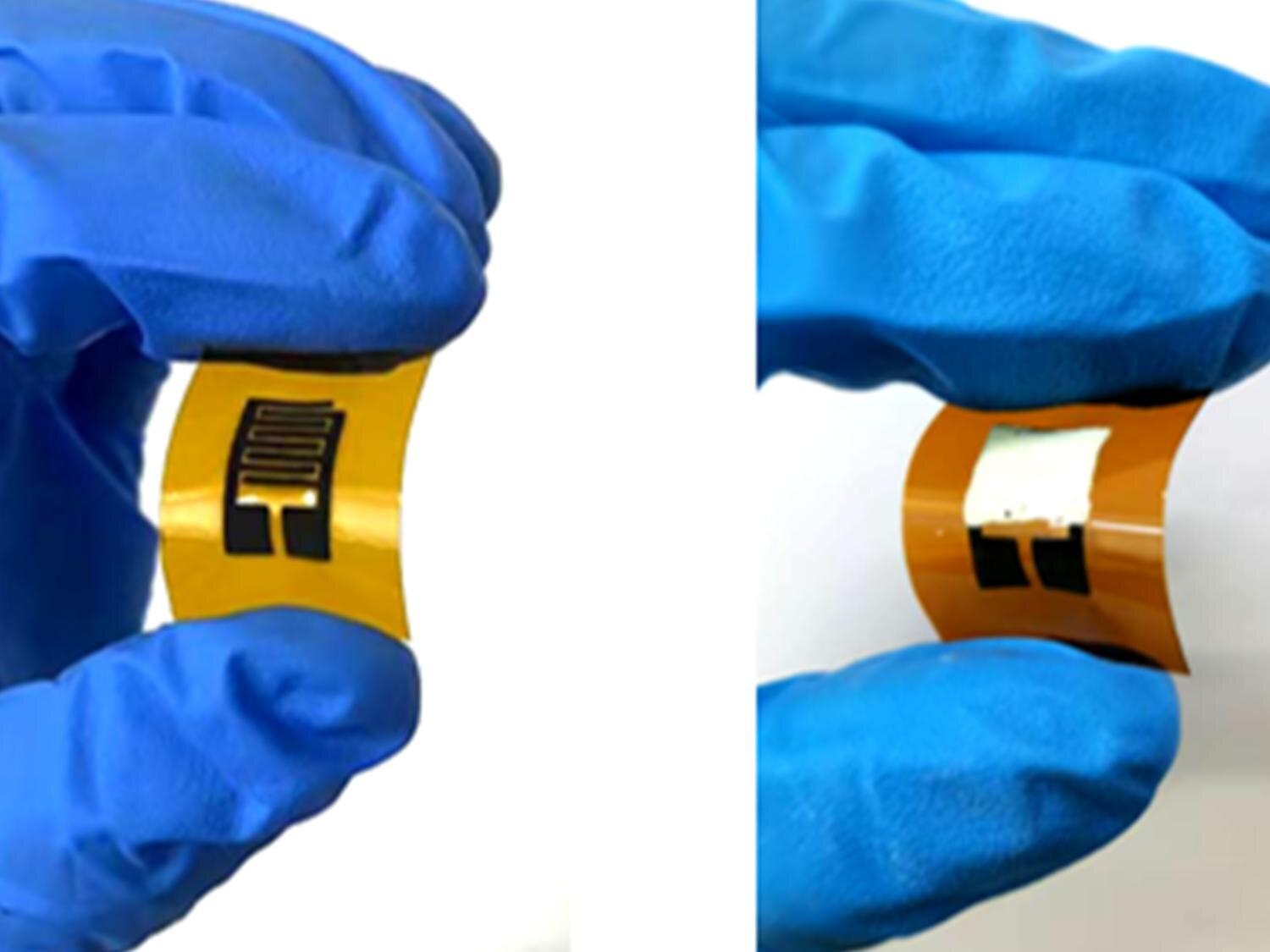
A research team led by Huanyu “Larry” Cheng, James L. Henderson, Jr. Memorial Associate Professor of Engineering Science and Mechanics at Penn State, has developed a sensor that can help diagnose diabetes and prediabetes on-site in a few minutes using just a breath sample. Their results are published in the Chemical Engineering Journal.
Previous diagnostic methods often used glucose found in blood or sweat, but this sensor detects acetone levels in the breath. While everyone’s breath contains acetone as a byproduct of burning fat, acetone levels above a threshold of about 1.8 parts per million indicate diabetes.