Scientists have developed a more stable platform for Majorana zero modes, exotic particles that could revolutionize quantum computing. Using a carefully engineered three-site Kitaev chain composed of quantum dots and superconducting links, the team achieved greater separation of MZMs, boosting th
For the first time, scientists have characterized a promethium coordination complex, advancing the understanding of challenging lanthanide elements. Promethium, a rare earth element, is unique in that it lacks stable isotopes. As a result, it constantly decays, making it challenging to study. In
In a significant breakthrough that could accelerate the progress of quantum technologies, researchers from the USC
<span class=””>Founded in 1880, the <em>University of Southern California</em> is one of the world’s leading private research universities. It is located in the heart of Los Angeles.</span>
New experiments on thallium decay have helped determine the Sun formed over 10–20 million years, improving stellar nucleosynthesis models. Have you ever wondered how long it took our Sun to form in the stellar nursery where it was born? An international team of scientists has just brought us clos
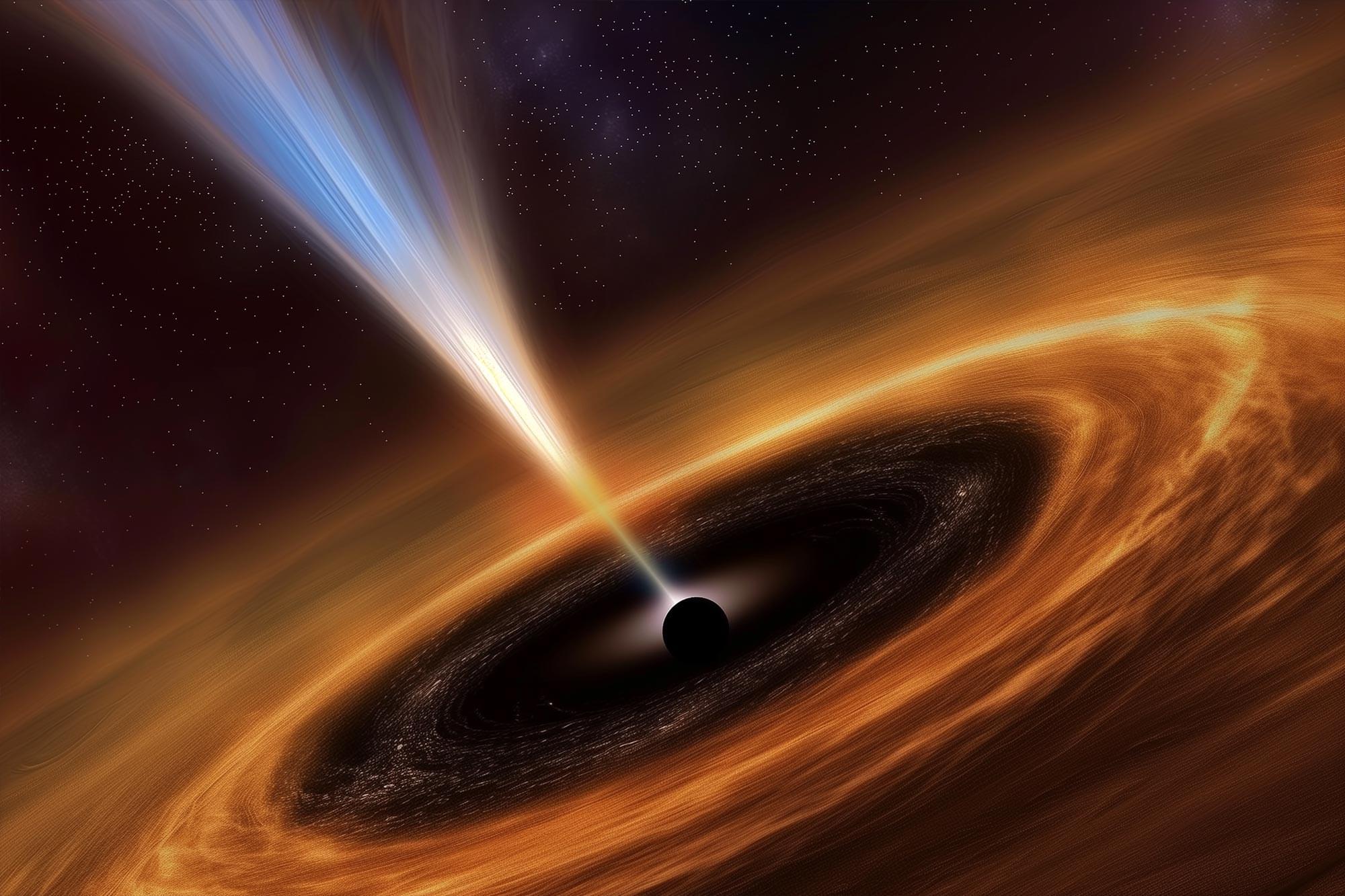
Astronomers have found compelling evidence for the closest known supermassive black hole outside the Milky Way. This enormous black hole resides in the Large Magellanic Cloud (LMC), one of our galaxy’s nearest neighbors.
The discovery was made by precisely tracking the motion of 21 stars located on the outskirts of the Milky Way. These stars are moving so rapidly that they will eventually escape the gravitational pull of the Milky Way and any nearby galaxies. Such stars are known as “hypervelocity” stars.
By analyzing their trajectories, much like forensic scientists tracing a bullet’s path, researchers were able to determine their origins. About half of the stars were found to have been ejected by the supermassive black hole at the center of the Milky Way. The rest, however, appear to have been flung out by a different source: a previously undetected supermassive black hole in the Large Magellanic Cloud.
A new paper explains how signals oscillating at complex-valued frequencies could transform sensing, imaging, and communication technologies. Researchers from the Advanced Science Research Center at the CUNY Graduate Center (CUNY ASRC) and Florida International University have published new findin
Some stars in our galaxy pulse like musical instruments, and scientists have found a way to listen in. These rhythmic starquakes, like vibrations in a string or drum, reveal vital clues about a star’s age, composition, and life cycle.
By studying these “melodies” in a star cluster called M67—whose stars are like solar siblings—researchers uncovered a strange pause in stellar evolution called the “plateau.” This discovery helps pinpoint stellar ages with remarkable precision, bringing us closer to understanding how stars, and ultimately our galaxy, have evolved.
Celestial Music: Listening to Starquakes.
Fragments of a rare Merlin manuscript from the 1200s discovered and digitised in a ground-breaking three-year project at Cambridge University Library.
Lariocidin was efficient against strains of E. coli, including drug-resistant ones, according to the new study.
Researchers say they have discovered a new class of antibiotics that could treat drug-resistant bacteria, the first to reach the market in nearly three decades.
The new molecule, called lariocidin, works by targeting a part of a bacteria’s cell called the ribosome and can disrupt the cell’s functions.
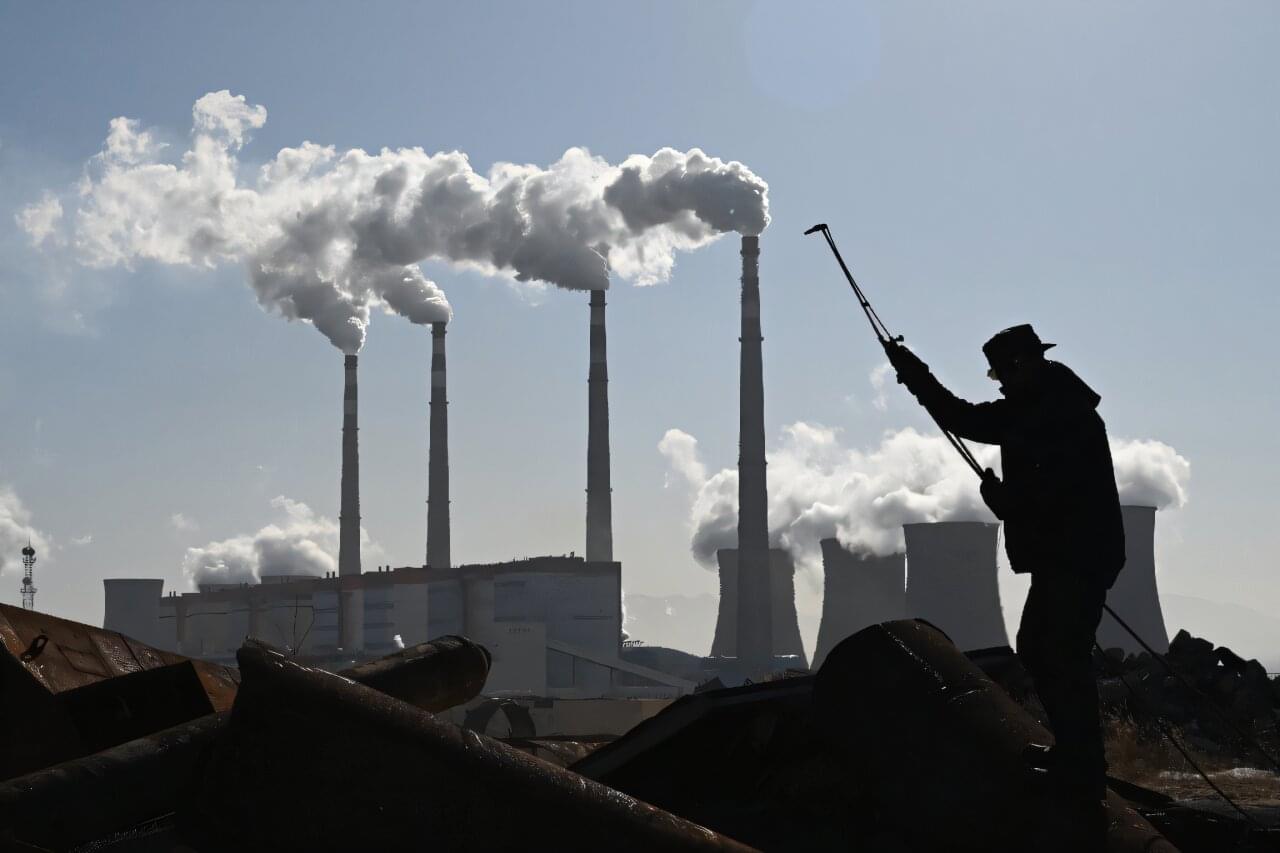
The world added the smallest amount of new coal capacity in two decades last year, a report said Thursday, but use of the fossil fuel is still surging in China and India.
Coal accounts for just over a third of global electricity production and phasing it out is fundamental to meeting climate change goals.
Just 44 gigawatts (GW) of new coal power capacity was produced globally last year, the lowest figure since 2004, according to the report by a group of energy-and environment-focused research organizations and NGOs.