Oral squamous cell carcinoma (OSCC) is a painful disease that severely impairs eating, drinking, and talking (1–5). Patients with OSCC are less opioid responsive and develop opioid tolerance quicker than patients with other chronic pain conditions (6, 7). Escalating doses of opioids are required as tolerance develops, causing not only severe adverse effects (6) such as addiction but also prolonged hospitalizations and increased readmission rate in patients (8). The mechanisms underlying oral cancer pain and opioid tolerance are not well understood.
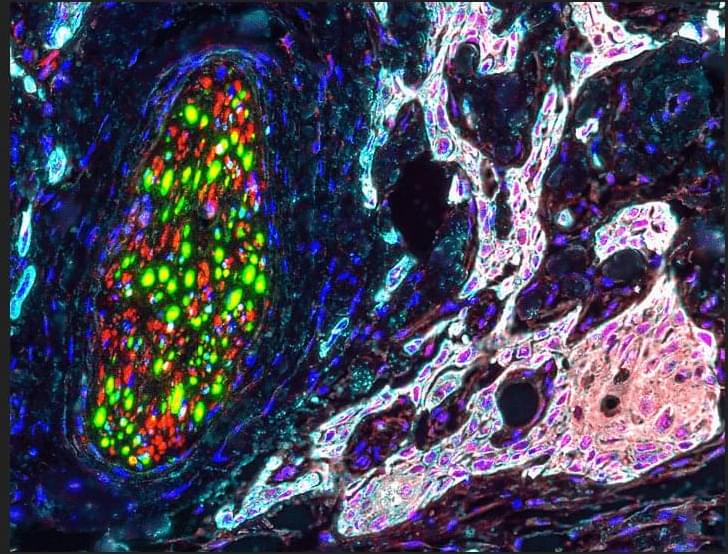
Epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) is a member of the receptor tyrosine kinases (RTKs) subfamily named HER/ERBB that is aberrantly expressed in 80 to 100% of the OSCC cases (9–11). EGFR antagonism including antibodies and tyrosine kinase inhibitors (TKIs) are US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) approved to treat many cancers, including OSCC (12–14). Clinical studies report pain relief in patients with neuropathic pain, including those associated with cancer after treatment with EGFR inhibitors (15, 16). Human genetic studies find associations between painful disease conditions and EGFR and its ligands, such as epiregulin, heparin-binding EGF (HB-EGF), and transforming growth factor–α (TGFα) (17–19). In animal models, HB-EGF directly causes dorsal root ganglion (DRG) cell excitation and elicits pain-like behaviors, whereas epiregulin mainly works in conjunction with underlying inflammation or tissue injury to generate pain (17, 19, 20). EGFR has also been implicated in opioid tolerance in human (21) and animal studies (20, 22, 23). Although elegant mechanistic studies suggest that EGFR can activate various pathways—through the ion channel transient receptor potential vanilloid 1 (TRPV1), the kinase cascade phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase (PI3K)–AKT–mammalian target of rapamycin (mTOR), the protease matrix metalloproteinase–9 (MMP-9), or the oncogene KRAS [to tetrahydrobiopterin (BH4)]—to increase pain sensitivities in mice (17, 24), these studies were done at the spinal level of noncancer pain models. It has been shown that EGFR involvement in pain is ligand and disease dependent (17, 25, 26), which warrants the investigation of EGFR signaling both in the setting of oral cancer pain that involves the trigeminal system and in opioid analgesic tolerance.
In this study, we aimed to determine how EGFR signaling contributes to oral cancer pain and opioid tolerance. We found that EGFR activation sensitizes trigeminal ganglion (TG) neurons and enhances glutamate N-methyl-d-aspartate receptor (NMDAR) signaling, resulting in heightened cancer pain and diminished opioid analgesic efficacy. EGFR ligands abundant in the OSCC tumor microenvironment trigger calcium influx, NMDAR phosphorylation, and protein kinase C (PKC) up-regulation in TG neurons. Last, we showed that EGFR activation induces presynaptic and postsynaptic hypersensitivity of NMDARs in the trigeminal nucleus caudalis (TNc) of the brainstem. Together, these findings establish EGFR-mediated NMDAR sensitization as a central mechanism underlying oral cancer pain and opioid tolerance and highlight EGFR as a promising therapeutic target.