Subscribe: http://bit.ly/1Wq6gwm.
Connect with Singularity University:
Website: http://singularityu.org.
Singularity HUB: http://singularityhub.com.
Facebook: https://www.facebook.com/singularityu.
Twitter: https://twitter.com/singularityu.
Linkedin: https://www.linkedin.com/company/singularity-university.
Google+: https://plus.google.com/+singularityu.
About Singularity University:
Singularity University is a benefit corporation headquartered at NASA’s research campus in Silicon Valley. We provide educational programs, innovative partnerships and a startup accelerator to help individuals, businesses, institutions, investors, NGOs and governments understand cutting-edge technologies, and how to utilize these technologies to positively impact billions of people.
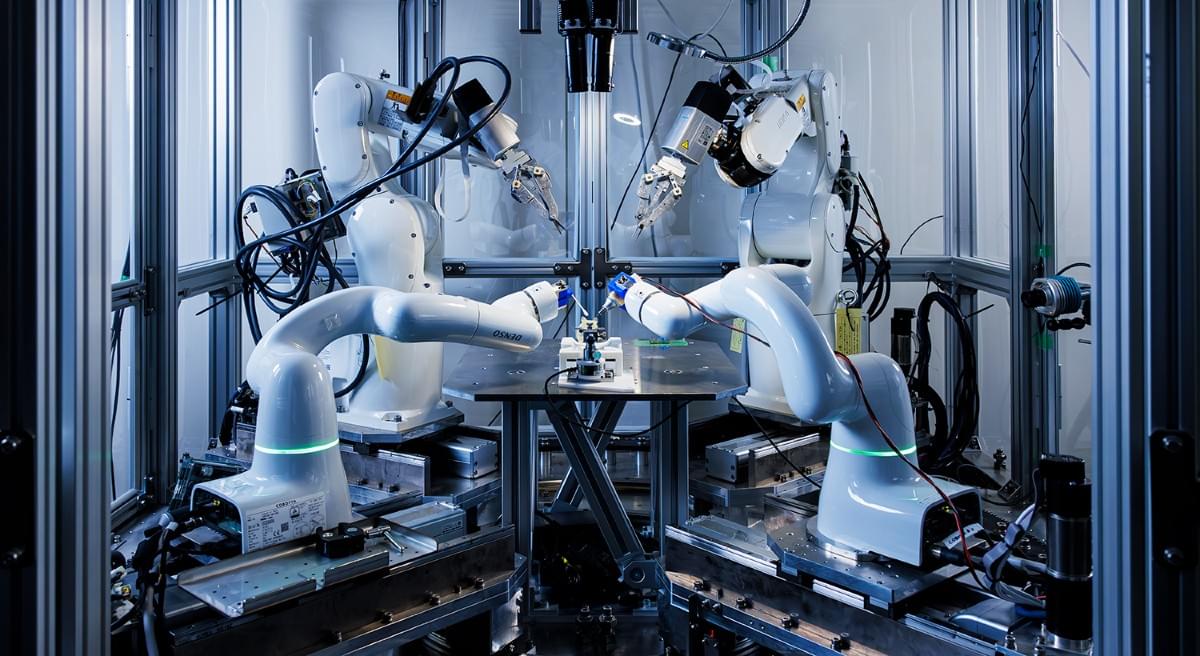
Intro to Nanotechnology with Ralph Merkle | Singularity University.
https://www.youtube.com/user/SingularityU