The brain’s astounding cellular diversity and networked complexity could show how to make AI better.



The potential role of vitamin D in preventing and treating colorectal cancer (CRC) has attracted growing research interest – especially as CRC rates are rising, particularly among younger adults. This isn’t a new area of study. Low vitamin D levels have long been linked to a higher risk of developing colorectal cancer.
One large study involving over 12,000 participants found that people with low blood levels of vitamin D had a 31 per cent greater risk of developing CRC compared to those with higher levels. Similarly, another study reported a 25 per cent lower CRC risk among individuals with high dietary vitamin D intake.
Data from the Nurses’ Health Study – a long-term investigation of American nurses – showed that women with the highest vitamin D intake had a 58 per cent lower risk of developing colorectal cancer compared to those with the lowest intake.

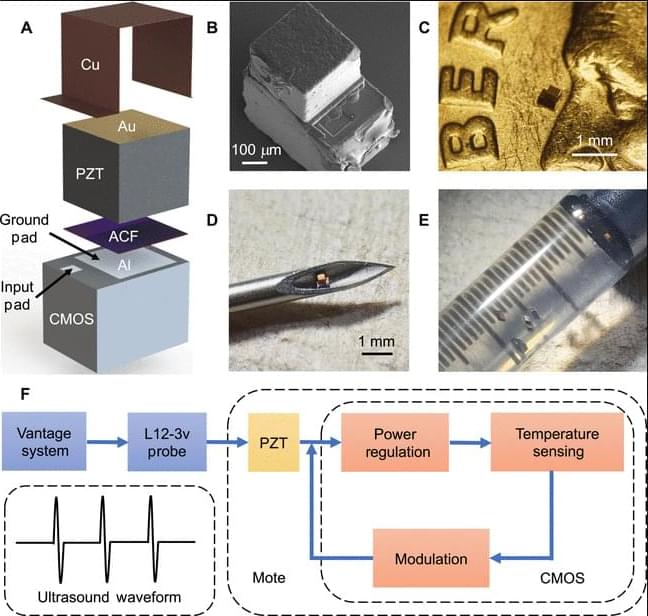
In a new demonstration, a U.S. researcher showcased that a quantum computer outperforms supercomputers in approximate optimization tasks.
The University of Southern California-led (USC) study demonstrated the first quantum scaling advantage for approximate optimization problem-solving using a quantum annealer.
Quantum annealing is a specific type of quantum computing that can use quantum physics principles to find high-quality solutions to difficult optimization problems. Rather than requiring exact optimal solutions, the study focused on finding solutions within a certain percentage (≥1%) of the optimal value, according to researchers.



The common cold sore virus, which is often caught in childhood, usually stays in the body for life—quietly dormant in the nerves. Now and then, things like stress, illness or injury can trigger it, bringing on a cold sore in some people. But this same virus—called herpes simplex virus type 1—may also play an important role in something far more serious: Alzheimer’s disease.
Over 30 years ago, my colleagues and I made a surprising discovery. We found that this cold sore virus can be present in the brains of older people. It was the first clear sign that a virus could be quietly living in the brain, which was long thought to be completely germ-free—protected by the so-called “blood-brain barrier.”
Then we discovered something even more striking. People who have a certain version of a gene (called APOE-e4) that increases their risk of Alzheimer’s, and who have been infected with this virus, have a risk that is many times greater.

A groundbreaking cement developed by Chinese scientists can now generate electricity from heat—thanks to a bio-inspired design that mimics plant stems. By combining hydrogel layers with traditional cement, this innovation enhances ion flow and delivers record-high thermoelectric efficiency. This breakthrough could power smart infrastructure, allowing buildings, roads, and bridges to self-generate electricity for sensors, lighting, and more—ushering in a new era of energy-smart cities.
