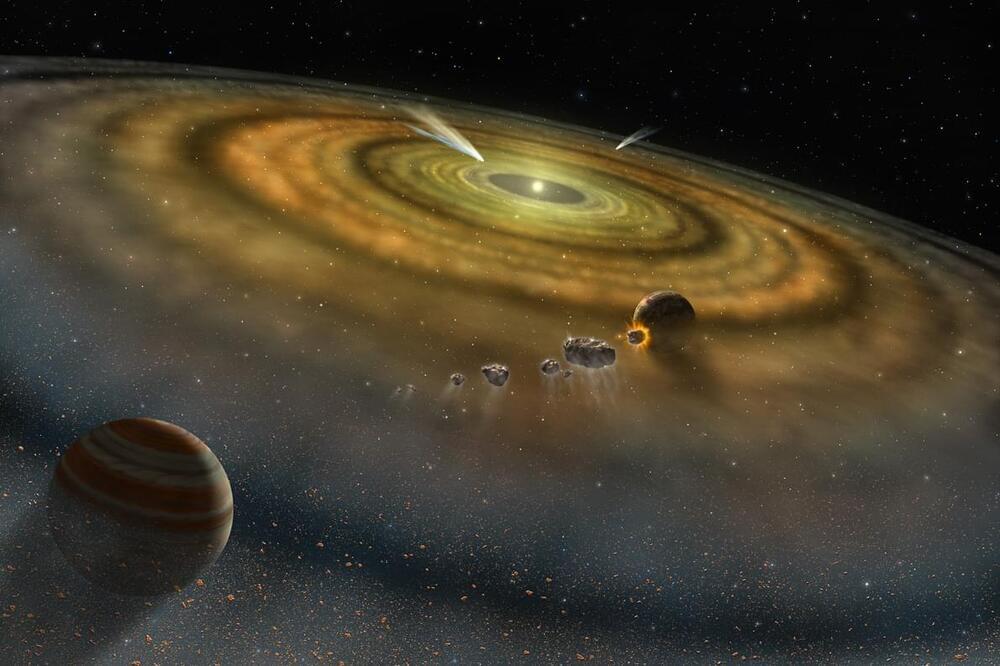
How do giant planets form and is this process slow or fast based on the amount of available dust used to build those planets? This is what a recent study published in Astronomy & Astrophysics hopes to address as a team of researchers from Germany investigated how sub-micron-sized dust kicks off the planetary formation process within a protoplanetary disc. This study holds the potential to help scientists better understand the formation and evolution of planets throughout our solar system and exoplanetary systems, as well.
For the study, the researchers developed first-of-its-kind model to involve all constituents responsible for the physical processes that from planets. Focusing on sub-micron-sized dust, they included factors such as pebble accumulation, planetary gas buildup, planetary migration, and dust buildup, among others. In the end, they found that ring-shaped disturbances in the protoplanetary disk, which they refer to as substructures, can result in multiple gas giants’ formation in rapid sequence.
Dr. Til Birnstiel, who is a professor of theoretical astrophysics at Ludwig-Maximilians-Universität München and a co-author on the study, said: “When a planet gets large enough to influence the gas disk, this leads to renewed dust enrichment farther out in the disk. In the process, the planet drives the dust – like a sheepdog chasing its herd – into the area outside its own orbit.”