From mRNA technology to T cell engagers, there were a number of advancements in cancer research in 2023.
PBS Member Stations rely on viewers like you. To support your local station, go to: http://to.pbs.org/DonateSPACE
↓ More info below ↓
Sign Up on Patreon to get access to the Space Time Discord!
/ pbsspacetime.
Check out the Space Time Merch Store.
https://pbsspacetime.com/
Sign up for the mailing list to get episode notifications and hear special announcements!
https://mailchi.mp/1a6eb8f2717d/space… we detected the very first gravitational wave, a new window was opened to the mysteries of the universe. We knew we’d see things previously thought impossible. And we just did — an object on the boundary between neutron stars and black holes, which promises to reveal the secrets of both. Hosted by Matt O’Dowd Written by Matt O’Dowd Graphics by Leonardo Scholzer, Yago Ballarini, & Pedro Osinski Directed by: Andrew Kornhaber Camera Operator: Bahaar Gholipour Executive Producers: Eric Brown & Andrew Kornhaber Previous Episodes Referenced: Ligo’s First Detection of Gravitational Waves: • LIGO’s First Detection of Gravitation… The Future of Gravitational Waves:
• The Future of Gravitational Waves How to build a black hole
• How to Build a Black Hole Strange Stars —
• Strange Stars | Space Time | PBS Digi… Special Thanks to Our Patreon Supporters Big Bang Supporters Robert Doxtator Ahmad Jodeh Caed Aldwych Radu Negulescu Alexander Tamas Morgan Hough Juan Benet Fabrice Eap David Nicklas Quasar Supporters Alec S-L Christina Oegren Mark Heising Vinnie Falco Hypernova Supporters william bryan Julian Tyacke Syed Ansar John R. Slavik Mathew Danton Spivey Donal Botkin John Pollock Edmund Fokschaner Joseph Salomone Hank S Matthew O’Connor chuck zegar Jordan Young John Hofmann Timothy McCulloch Gamma Ray Burst Supporters fieldsa eleanory Cody Lubinsky Peter Mertz Elliot Azizollahi Kevin O’Connell Bryan Dawley Richard Deighton Isaac Suttell Devon Rosenthal Oliver Flanagan Mikhail Klakotskiy Dawn M Fink Bleys Goodson Darryl J Lyle Robert Walter jechamt Bruce B Ismael Montecel M D Mark Daniel Cohen Andrew Richmond Simon Oliphant Mirik Gogri David Hughes Aria Ahmad Brandon Lattin Yannick Weyns Nickolas Andrew Freeman Protius Protius Brian Blanchard Shane Calimlim Tybie Fitzhugh Patrick Sutton Robert Ilardi Eric Kiebler Tatiana Vorovchenko Craig Stonaha Michael Conroy Graydon Goss Frederic Simon Greg Smith Sean Warniaha Tonyface John Robinson A G Kevin Lee Nick Wright Adrian Hatch Paul Rose Yurii Konovaliuk John Funai Cass Costello Geoffrey Short Bradley Jenkins Kyle Hofer Tim Stephani Luaan AlecZero Malte Ubl Nick Virtue Scott Gossett David Bethala Dan Warren John Griffith Daniel Lyons Josh Thomas DFaulk Kevin Warne Andreas Nautsch Brandon labonte.
When we detected the very first gravitational wave, a new window was opened to the mysteries of the universe. We knew we’d see things previously thought impossible. And we just did — an object on the boundary between neutron stars and black holes, which promises to reveal the secrets of both.
Hosted by Matt O’Dowd.
Check Out Rogue History On PBS Origins: https://youtu.be/xuT35ud41QQPBS Member Stations rely on viewers like you. To support your local station, go to: http:/…
The truck, based on an Aebi VT450 Transporter, featured a 320-horsepower electric drive system with a 90-kilowatt-hour battery.
The Taiwan Semiconductor Manufacturing Company’s (TSMC) advanced product costs could soar and hamper growth in A.I. chip supply.
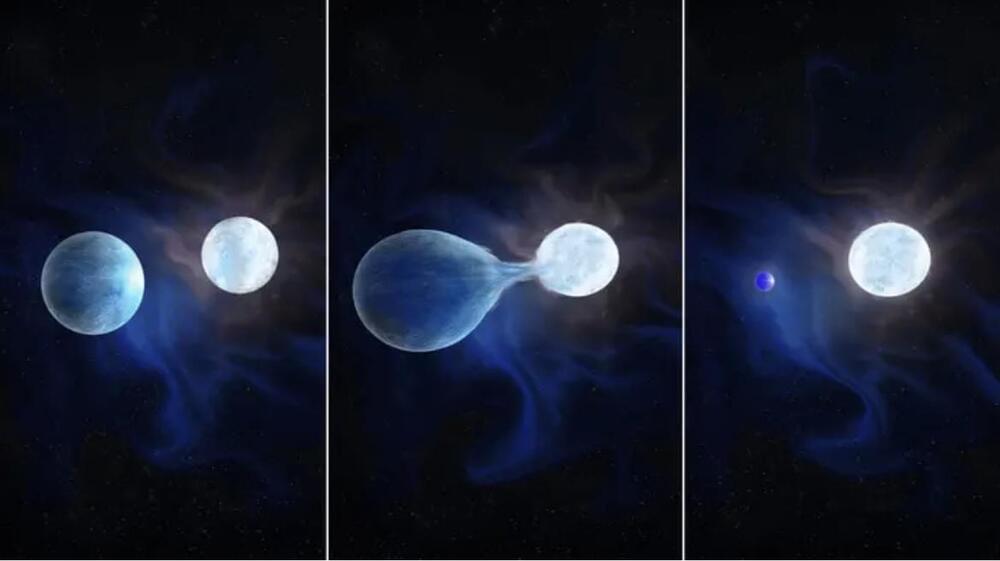
Observing these types of stars is rare; only one was previously identified. Now, researchers have found a whole population of these stars in the Large and Small Magellanic Clouds, relatively nearby satellite galaxies of the Milky Way. The finding may give insight into hot helium stars, which are thought to be the start of neutron star mergers and hydrogen-poor core-collapse supernovae. The study was published this month in Science.
“Our work sheds light on these fascinating relationships, revealing a universe that is far more interconnected and active than we previously imagined,” says Bethany Ludwig, a PhD candidate at the University of Toronto and coauthor of the study, in a press release. “Just as humans are social beings, stars too, especially the massive ones, are rarely alone.”
COPENHAGEN, Dec 28 (Reuters) — Denmark’s Maersk (MAERSKb. CO) will sail almost all container vessels travelling between Asia and Europe through the Suez Canal from now on while diverting only a handful around Africa, a Reuters breakdown of the group’s schedule showed on Thursday.
Major shipping companies, including container giants Maersk and Hapag-Lloyd (HLAG.DE), stopped using Red Sea routes and the Suez Canal earlier this month after Yemen’s Houthi militant group began targeting vessels, disrupting global trade.
Instead, they rerouted ships around Africa via the Cape of Good Hope to avoid attacks, charging customers extra fees and adding days or weeks to the time it takes to transport goods from Asia to Europe and to the east coast of North America.
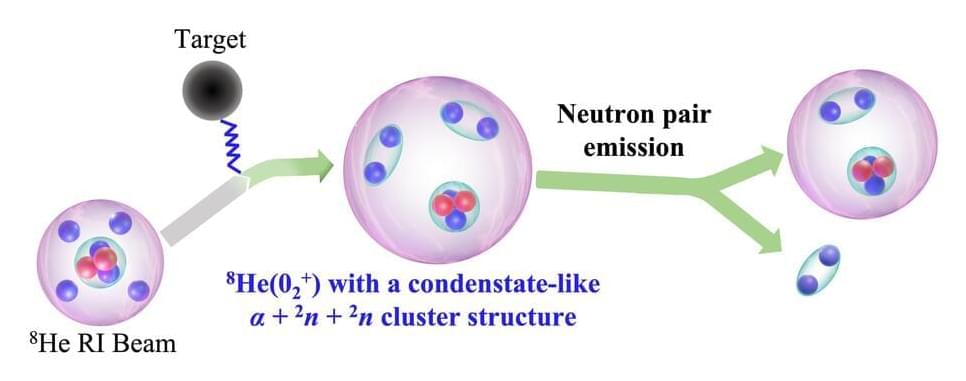
Researchers at Peking University in China have successfully observed the elusive 02+ state of 8 He, revealing a novel cluster structure with two strongly correlated neutron pairs. This finding provides insights into exotic nuclear structures and their potential implications for understanding neutron stars. The findings are published in Physical Review Letters.
The conventional nuclear model in physics posits a single-particle picture where nucleons, protons, and neutrons move independently within a nucleus, forming a well-defined shell structure. Governed by a mean potential created by nuclear forces, nucleons fill distinct energy levels or shells, leading to increased stability associated with magic numbers.
This model, rooted in quantum mechanics, successfully explains nuclear structure and stability but encounters limitations when addressing exotic nuclei, particularly those that are neutron-rich and unstable.
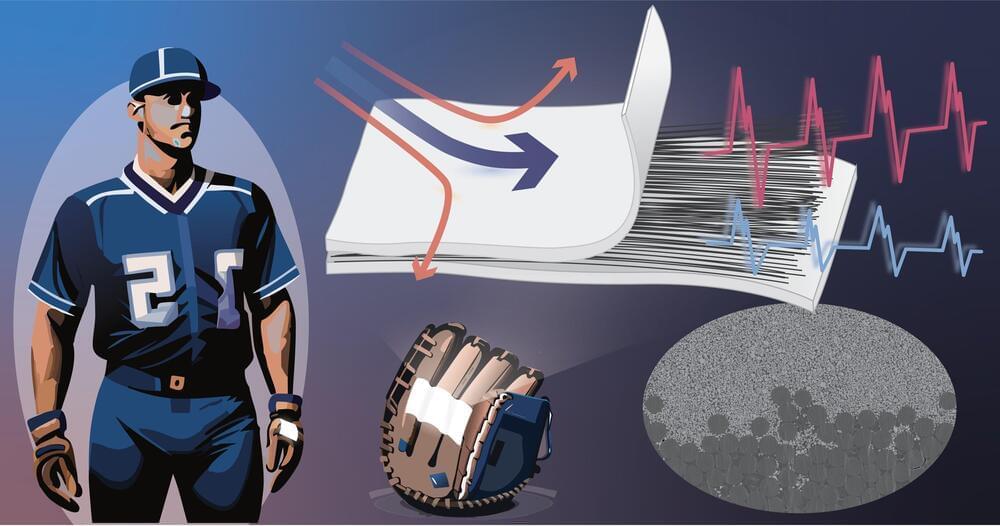
An international research group has engineered a novel, high-strength flexible device by combining piezoelectric composites with unidirectional carbon fiber (UDCF), an anisotropic material that provides strength only in the direction of the fibers. The new device transforms kinetic energy from human motion into electricity, providing an efficient and reliable means for high-strength and self-powered sensors.
Details of the group’s research were published in the journal Small on Dec.14, 2023.
Motion diction involves converting energy from human motion into measurable electrical signals and is something that may be crucial for ensuring a sustainable future.