Two space agencies say we need filter systems for drinking moon water, and they need the public’s help with the AquaLunar challenge.
Enlarged Prostate
Posted in futurism
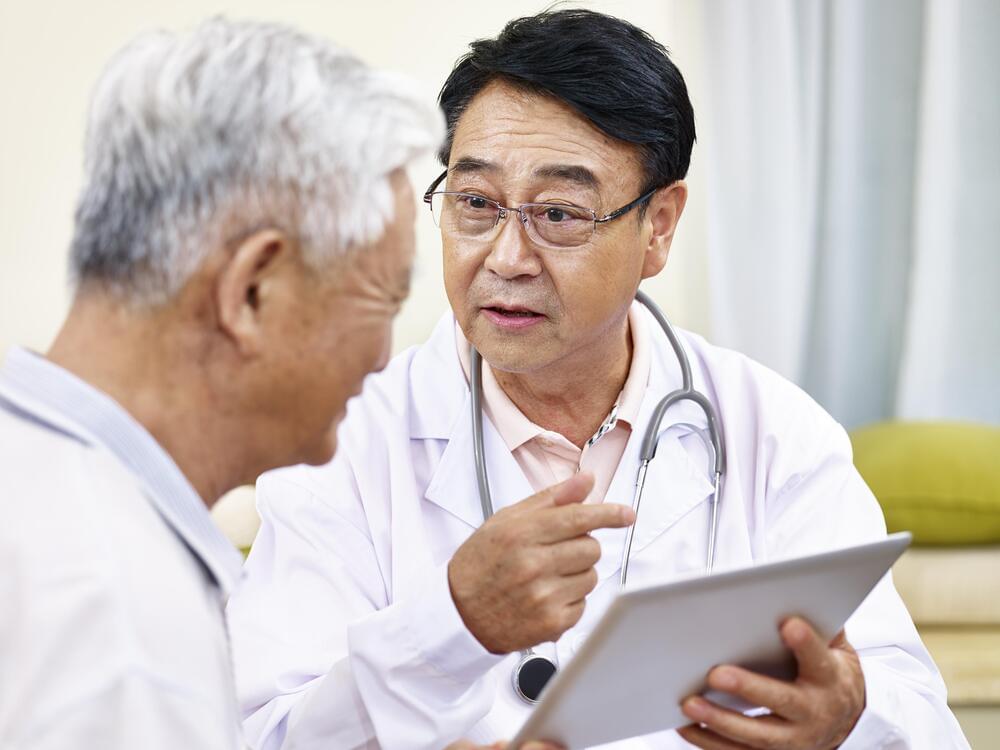
An enlarged prostate is when the prostate gland becomes larger than normal causing symptoms that can slow or block the flow of urine out of the bladder. It is also called benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH). Learn more about symptoms, diagnosis and treatment:
Enlarged prostate, or benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH), is a common problem in men over 50. Learn about the symptoms and treatments.
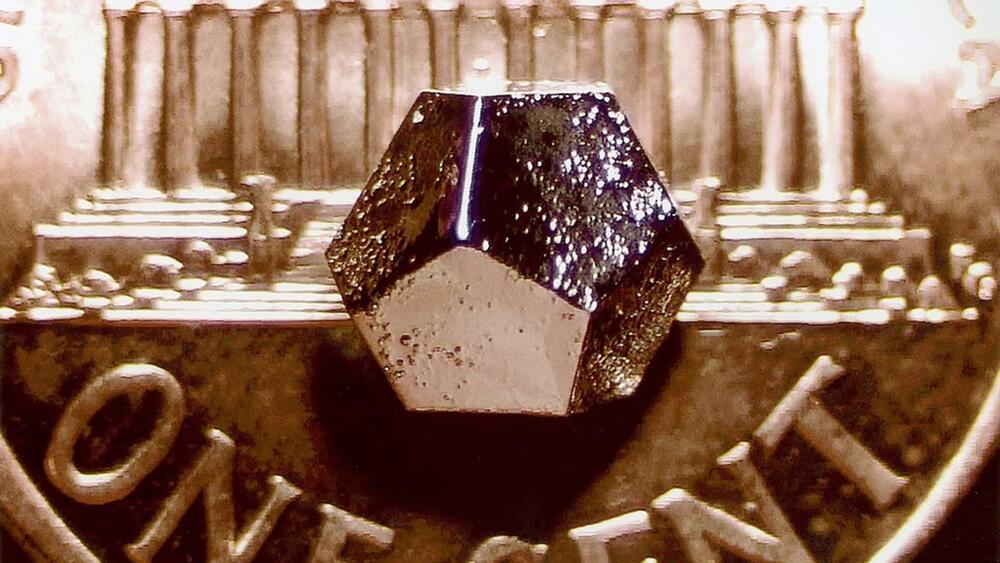
Research reveals the secrets of non-Heisenberg Tsai-type crystals that could open doors to applications in spintronics and magnetic refrigeration.
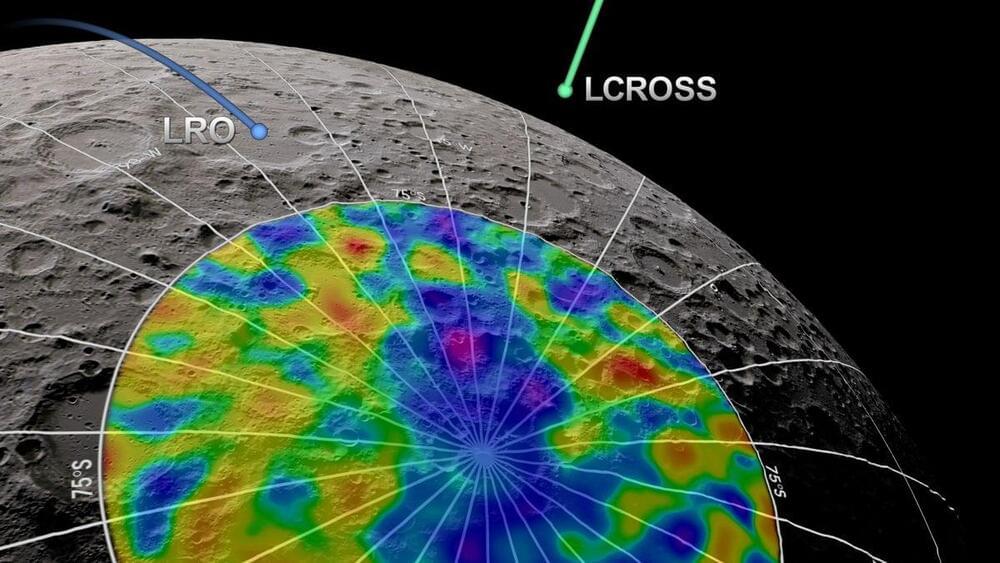
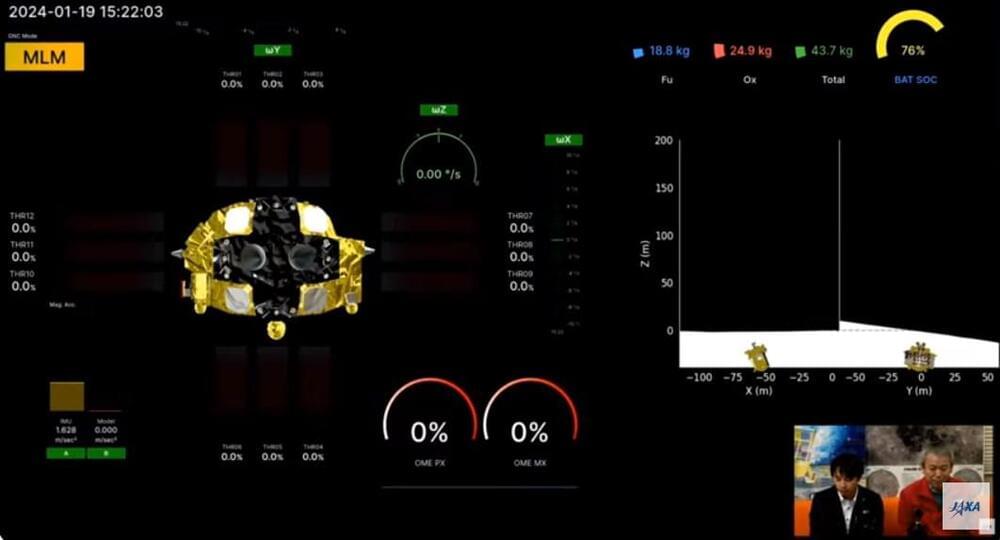
HELSINKI — Japan’s SLIM “Moon Sniper” spacecraft made a successful lunar landing Friday, making the country just the fifth to robotically land on the moon.
The Smart Lander for Investigating Moon (SLIM) spacecraft began its descent from a 15-kilometer perilune shortly after 10:00 a.m. Eastern, Jan. 19 (1500 UTC), decelerating from a speed of around 1,700 meters per second.
SLIM appeared to have successfully touched down at 10:20 a.m. (1520 UTC), during a Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency (JAXA) livestream of the event. It was not however immediately clear if the landing was successful, with the livestream ending inconclusively. A wait of more than an hour followed for clarification and confirmation.
Melanoma cancer vaccine with minimal side effects nearing Phase 3 in clinical trials, according to experts.
The full recording of Parnia’s Lab’s premiere film, Rethinking Death: Exploring What Happens When We Die. In Rethinking Death, scientists, physicians, and survivors of cardiac arrest explore the liminal space between life and death, breaking down these stunning scientific breakthroughs to tell the remarkable, scientific story of what happens after we die.
Special thank you to Stellaris Productions, New York University Grossman School of Medicine, and of course, the researchers and survivors without whom this story could not be told:
Dr. Robert Montgomery.
Dr. Sam Parnia.
Dr. Lance Becker.
Dr. Tom Aufderheide.
Dr. Stephan Mayer.
Dr. Samuel Tisherman.
Alysson Muotri.
Dr. Lindsay Gurin.
Dr. Bruce Greyson.
Dr. Mary Neal.
Jeffery Olsen.
Rachel Finch.
Dr. Anthony Bossis.
Dr. Megan Craig.
Dr. Donald Hoffman.
Dr. Joseph Lowy
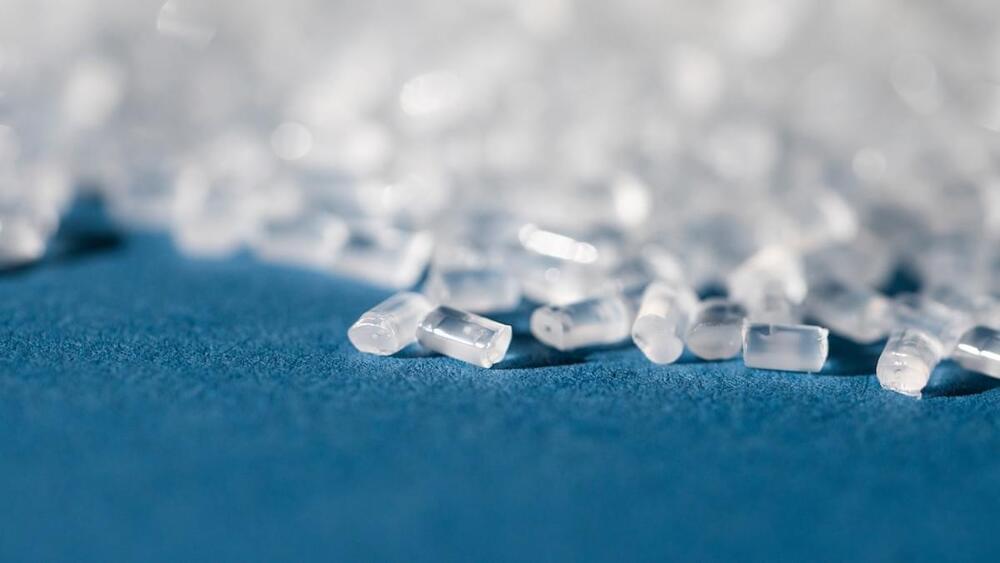
Innovations in recycling
Posted in innovation, sustainability
Scientists are looking for new ways to recycle plastic in an endless loop, so it never becomes waste. Now, revolutionary technology is advancing the movement.
Ultimate computing and biomolecular consciousness and nanotechnology.
Shared with Dropbox.