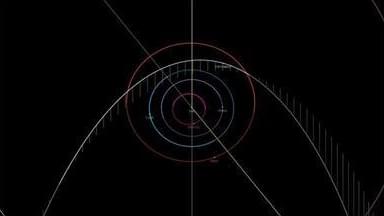
Astronomy lovers, a comet will be visible in the night sky this summer! Although you may need binoculars or a telescope to view it, it’ll be the first time this comet has been visible since 1956, according to Star Walk.
Comet 13P/Olbers will make its return to the night sky this July, marking the first time in 69 years that it’s been able to be seen from Earth. According to experts at Star Walk, while faint, its sky placement and distance to the sun will allow it to be best visible around June 30, which is this Sunday.
Those interested in seeing the comet will have to look west about two hours after sunset.