Sign Up on Patreon to get access to the Space Time Discord!https://www.patreon.com/pbsspacetimeCheck out the Space Time Merch Store https://www.pbsspacetime.c…
Get the latest international news and world events from around the world.
Two Scientists Are Building a Real Star Trek ‘Impulse Engine’
Space may be the final frontier, but we can’t go far on rocket fuel. Now, two scientists are working on a device that may one day make the \.
Neil deGrasse Tyson Explains Dimensions
What’s up with the fourth dimension? Neil deGrasse Tyson and Chuck Nice explore the dimensions, worldlines, and what it would mean to be 4D.
Learn about time and space and how we navigate through both. What would a 2D world be like for two-dimensional people? We break down what it’s like for 3D beings to interact with the second dimension and what it would be like for 4D beings to interact with the third dimension. Plus, we discuss flying cars and whether we already have them.
Get the NEW StarTalk book, ‘To Infinity and Beyond: A Journey of Cosmic Discovery’ on Amazon: https://amzn.to/3PL0NFn.
Come check out our brand-new channel! / @startalkplus.
Support us on Patreon: / startalkradio.
FOLLOW or SUBSCRIBE to StarTalk:
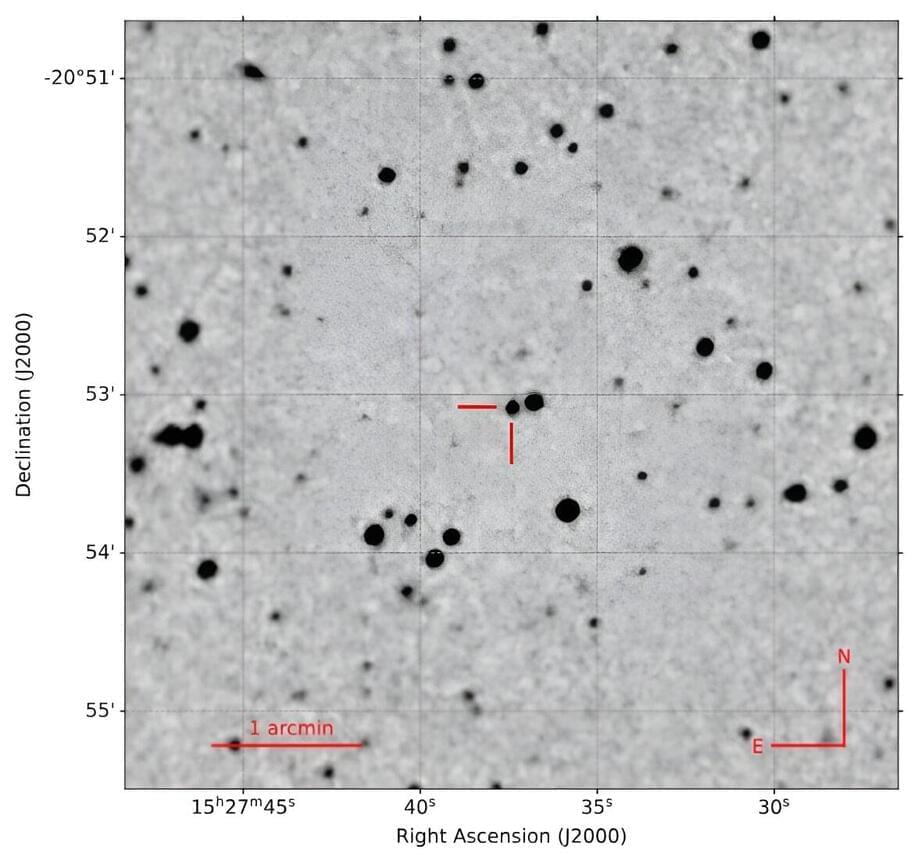
New cataclysmic variable discovered by astronomers
By analyzing the data from ESA’s XMM-Newton and Gaia satellites, astronomers from the Leibniz Institute for Astrophysics Potsdam (AIP) in Germany and elsewhere have detected a new magnetic cataclysmic variable system, most likely of the polar type. The finding was reported in a research paper published March 21 on the pre-print server arXiv.


Scientists discover a key quality-control mechanism in DNA replication
“Trillions of cells in our body divide every single day, and this requires accurate replication of our genomes. Our work describes a new mechanism that regulates protein stability in replicating DNA. We now know a bit more about an important step in this complex biological process.”
An enduring mystery of ‘lagging strand’ DNA replication
The DNA replication process is carried out by multiple protein complexes with highly specialized functions, including the unwinding of DNA and the copying of the two unwound DNA strands. The process is akin to a factory assembly line where balls made up of massive, crumpled strings of data are unraveled, allowing specific pieces to be trimmed and copied. Biologists know a good deal about how this process starts and proceeds, but know less about how it is stopped or paused.
Chickadees have unique neural ‘barcodes’ for memories of stashing away food
Black-capped chickadees have extraordinary memories that can recall the locations of thousands of morsels of food to help them survive the winter. Now scientists at Columbia’s Zuckerman Institute have discovered how the chickadees can remember so many details: they memorize each food location using brain cell activity akin to a barcode. These new findings may shed light on how the brain creates memories for the events that make up our lives.
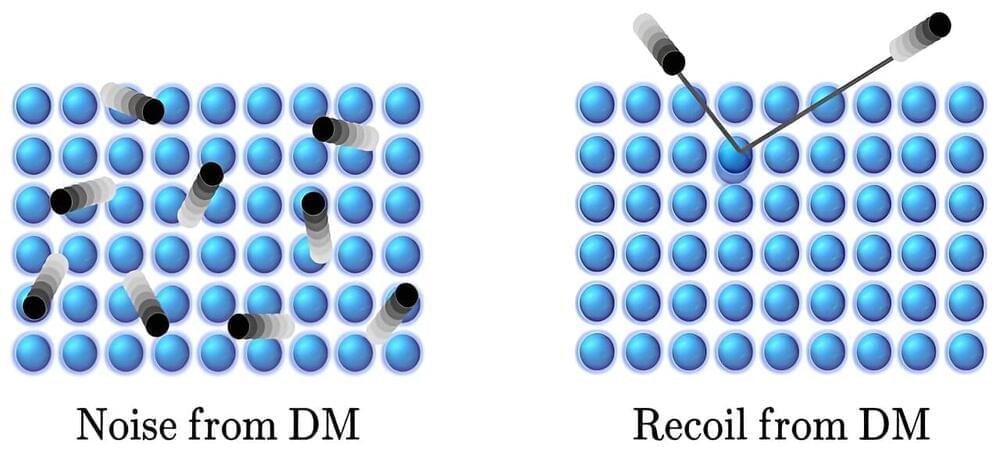
Physicists propose new way to search for dark matter: Small-scale solution could be key to solving large-scale mystery
Ever since its discovery, dark matter has remained invisible to scientists despite the launch of multiple ultra-sensitive particle detector experiments around the world over several decades.
Now, physicists at the Department of Energy’s (DOE) SLAC National Accelerator Laboratory are proposing a new way to look for dark matter using quantum devices, which might be naturally tuned to detect what researchers call thermalized dark matter.
Most dark matter experiments hunt for galactic dark matter, which rockets into Earth directly from space, but another kind might have been hanging around Earth for years, said SLAC physicist Rebecca Leane, who was an author of the new study.
A method to compute the Rényi entanglement entropy in auxiliary-field quantum Monte Carlo simulations
Entanglement is a widely studied quantum physics phenomenon, in which two particles become linked in such a way that the state of one affects the state of another, irrespective of the distance between them. When studying systems comprised of several strongly interacting particles (i.e., many body systems) in two or more dimensions, numerically predicting the amount of information shared between these particles, a measure known as entanglement entropy (EE), becomes highly challenging.
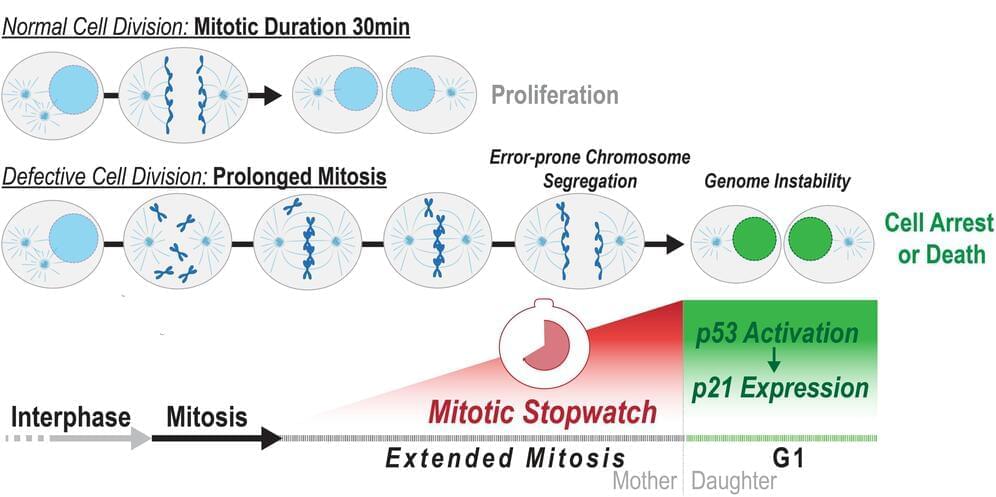
Memories of mitosis: Molecular mechanism that detects defects during cell division could aid cancer treatment
Every day, our cells are hard at work multiplying. Cell division is a precise process, but sometimes this process is impaired and diseases like cancer occur. Mitosis is one of the most important phases in the cell cycle. During this phase, a cell’s DNA is split into two equal sets of chromosomes and it divides into two genetically identical daughter cells.