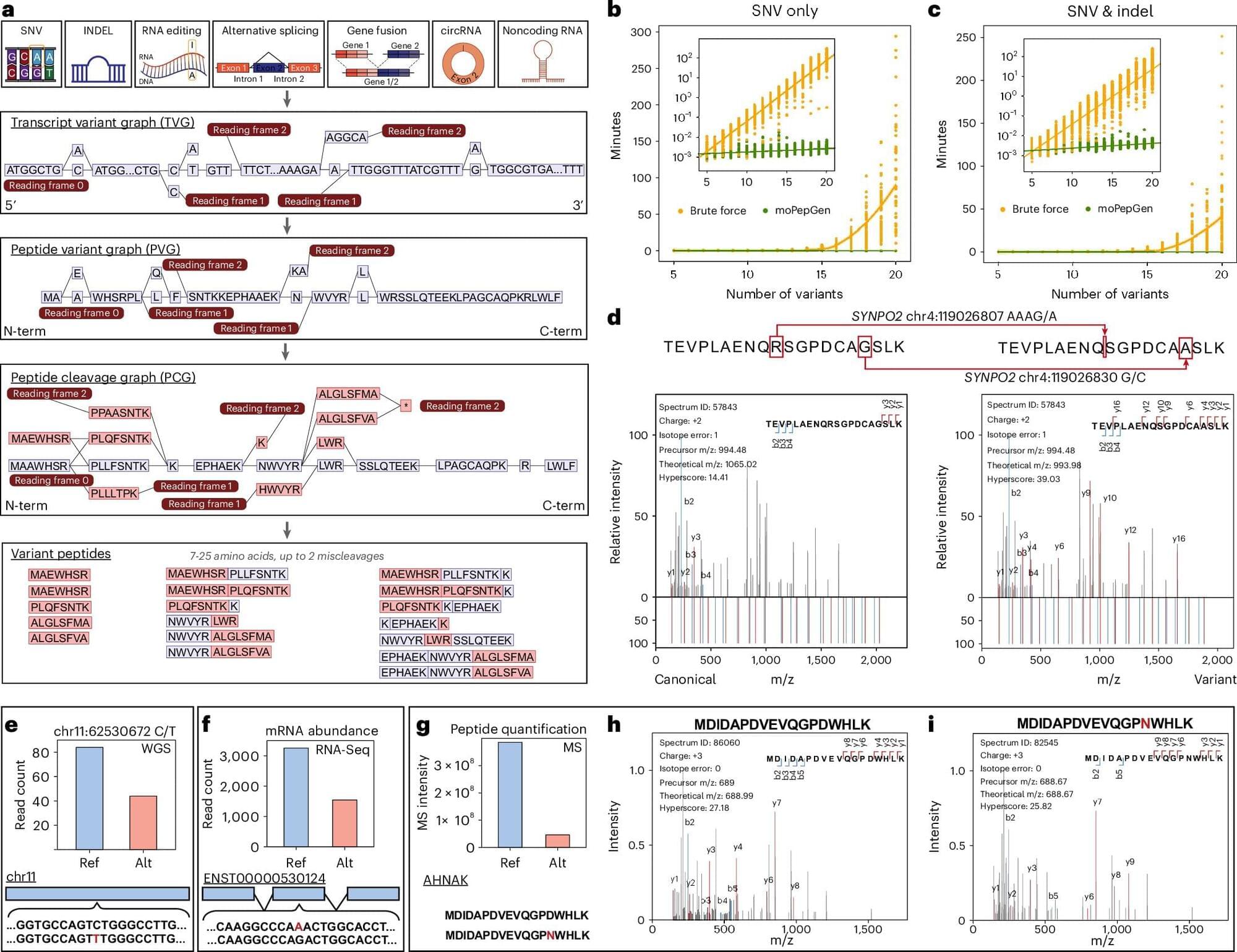
Scientists at UCLA and the University of Toronto have developed an advanced computational tool, called moPepGen, that helps identify previously invisible genetic mutations in proteins, unlocking new possibilities in cancer research and beyond.
The tool, described in Nature Biotechnology, will help understand how changes in our DNA affect proteins and ultimately contribute to cancer, neurodegenerative diseases, and other conditions. It provides a new way to create diagnostic tests and to find treatment targets previously invisible to researchers.
Proteogenomics combines the study of genomics and proteomics to provide a comprehensive molecular profile of diseases. However, a major challenge has been the inability to accurately detect variant peptides, limiting the ability to identify genetic mutations at the protein level. Existing proteomic tools often fail to capture the full diversity of protein variations.