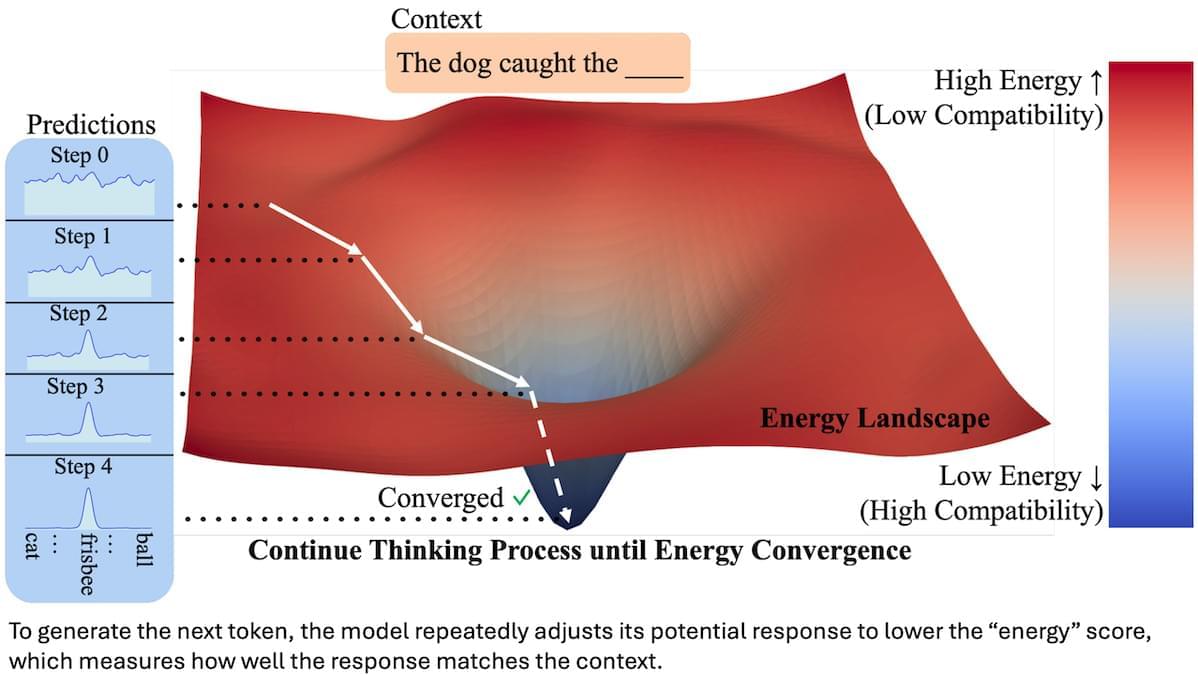
A new study reveals a missing area of brain activity in the minds of people with schizophrenia who hear voices.
The analysis of brain wave data suggests a combination of two neurological functions could trigger auditory verbal hallucinations.
Researchers from China found evidence of a breakdown in the ability to prepare the senses for specific words to be spoken. This on its own, however, isn’t enough; another area that filters our brain’s internal chatter is also enhanced in those with schizophrenia who experience unsettling auditory hallucinations.