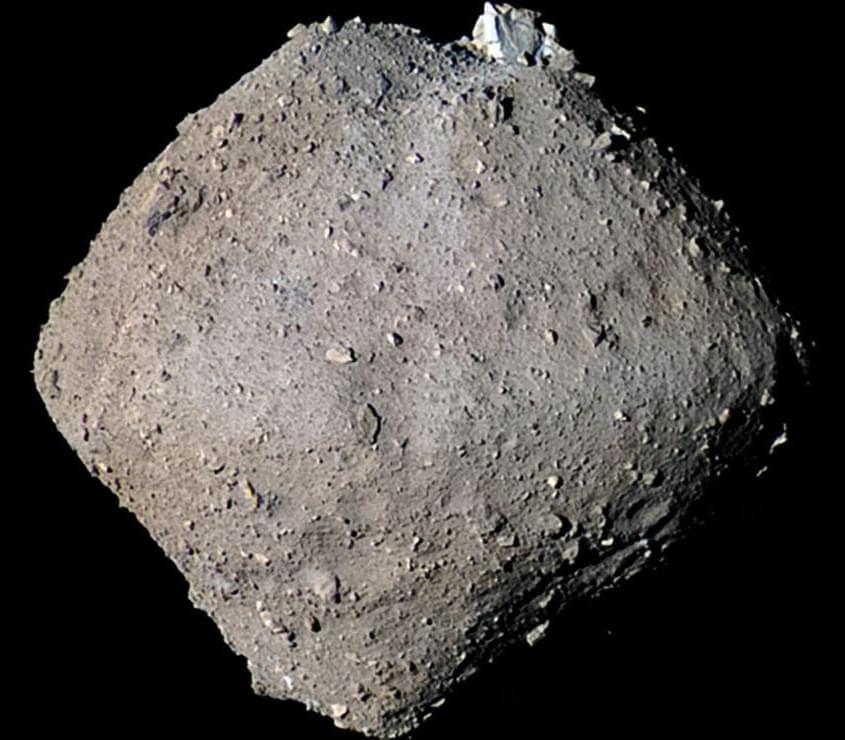
Scientists studying the chemical makeup of asteroid Ryugu and the Murchison meteorite find intriguing differences in their organic molecules.
Renowned journalist and science fiction author Cory Doctorow is convinced that the AI is doomed to drop off a cliff.
“Of course AI is a bubble,” he wrote in a recent piece for sci-fi magazine Locus. “It has all the hallmarks of a classic tech bubble.”
Doctorow likens the AI bubble to the dotcom crisis of the early 2000s, when Silicon Valley firms started dropping like flies when venture capital dried up. It’s a compelling parallel to the current AI landscape, marked by sky-high expectations and even loftier promises that stand in stark contrast to reality.
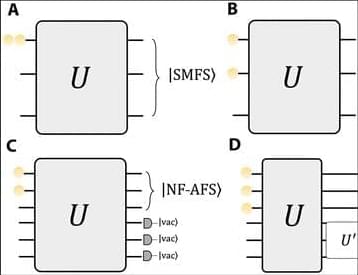
The generation of an intrinsic non-Fock state beyond the linear optics limit is confirmed using conditional coherence.
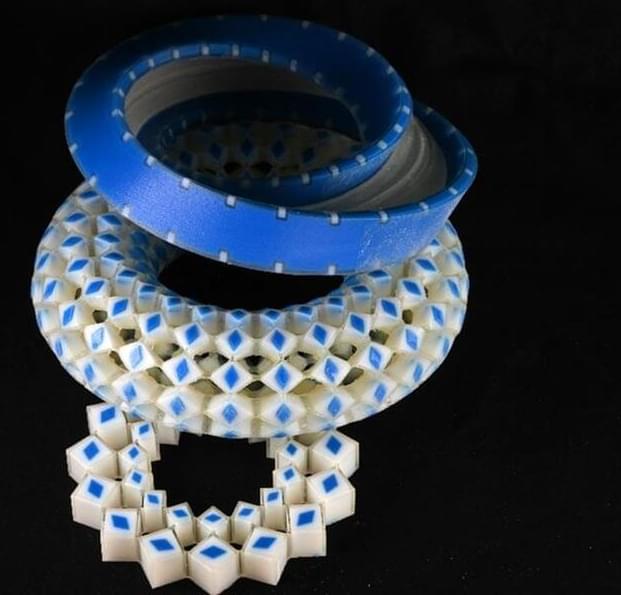
A groundbreaking discovery in metamaterial design reveals materials with built-in deformation resistance and mechanical memory, promising advancements in robotics and computing.
Researchers from the University of Amsterdam Institute of Physics and ENS de Lyon have discovered how to design materials that necessarily have a point or line where the material doesn’t deform under stress, and that even remember how they have been poked or squeezed in the past. These results could be used in robotics and mechanical computers, while similar design principles could be used in quantum computers.
The outcome is a breakthrough in the field of metamaterials: designer materials whose responses are determined by their structure rather than their chemical composition. To construct a metamaterial with mechanical memory, physicists Xiaofei Guo, Marcelo Guzmán, David Carpentier, Denis Bartolo, and Corentin Coulais realized that its design needs to be “frustrated,” and that this frustration corresponds to a new type of order, which they call non-orientable order.
In this new episode Steven sits down with the physician and longevity expert, Dr Peter Attia. 0:00 Intro 03:26 What is your mission? 06:52 Medicine 3.0 14:51 When should we really think about diseases? 23:14 What role does trauma play in longevity? 47:24 The 5 health deterioration 50:16 Proof exercise is important 01:04:48 Body deterioration can be slowed down 01:08:38 How much exercise should we be doing? 01:14:03 The importance of stability 01:20:59 We’ve engineered discomfort out of our lives 01:26:29 Sugar 01:34:16 Misconceptions about weight loss 01:45:13 Alcohol 01:49:13 Sleep 01:52:35 Hormone replacement therapy 01:57:07 Hair loss 01:59:48 The last guests question You can purchase Dr Attia’s new book, ‘Outlive: The Science and Art of Longevity’, here — https://amzn.to/3FUD6ok Follow Dr Attia: Instagram: https://bit.ly/3rBMyJ7 Twitter: https://bit.ly/44DkrYF YouTube: https://bit.
Rice University scientists and collaborators at Texas A&M University and University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center have found a new way to kill cancer cells by using near-infrared light to make a small dye molecule attached to their membrane vibrate strongly. It is the first time this kind of mechanical molecular action has been used as a potential therapy.
UCLA department of integrative biology and physiologyluskin endowment for leadership symposiumpushing the boundaries: neuroscience, cognition, and lifemarta…
A special form of molecule has been found to “tear apart” the membranes of cancer cells once activated, a promising new study by scientists at Rice University in Texas has revealed.
Known as aminocyanine molecules – and commonly used as synthetic dyes in medical imaging – their atoms can vibrate in unison and form a “plasmon” when hit with near-infrared light, causing cancer cells’ membranes to rupture.
And this treatment – through the use of what researchers are calling “molecular jackhammers” – is unbelievably effective, going by the study’s results.
OpenAI recently topped $1.6 billion in annualized revenue on strong growth from its ChatGPT product, up from $1.3 billion as of mid-October, according to two people with knowledge of the figure.
The 20% growth over two months represented in that figure—a measure of the prior month’s revenue multiplied by 12—suggests that the company was able to hold onto its business momentum in selling artificial intelligence to enterprises despite a leadership crisis in November that provided an opening for rivals to go after its customers.