Oh, and it’ll need the total current US power output.
Get the latest international news and world events from around the world.
More advanced civilizations might set aside our planet as a zoo wherein they can observe us, Zoo Hypothesis suggests
Could Earth be a cosmic sanctuary for observation? The Zoo Hypothesis suggests so.
In 1950, Italian-American physicist Enrico Fermi famously asked, “Where is everybody?” The question has since become the basis of the Fermi Paradox, addressing the conflict between the high probability of extraterrestrial life and the complete lack of evidence for its existence. Several hypotheses have been proposed to explain this, including the Zoo Hypothesis, first introduced in 1973 by Harvard astrophysicist John A. Ball. This theory posits that advanced alien civilizations may know of Earth and its inhabitants but choose to avoid contact, allowing humanity to develop naturally without interference.
Elon Musk Says Neuralink Should Make Brain Chips That Will Eliminate Neck And Back Pain
Billionaire entrepreneur Elon Musk said on Tuesday (October 29) that Neuralink, the company he co-founded, should look to develop a brain implant which would alleviate neck and back pain. Neuralink develops makes Brain-Computer Interfaces (BCIs) which can be implanted in human brain. Musk’s latest comment came in a post he made on X (formerly Twitter), the social media platform he owns.
I am increasingly convinced that @Neuralink should prioritize making an implant that can eliminate back & neck pain.
Would greatly improve people’s happiness while awake, as well as enhance quality of sleep.

Life Biosciences Is Bringing Reprogramming to the Clinic
Life Biosciences is a company co-founded by the celebrity geroscientist David Sinclair and is based on his Harvard team’s research into partial cellular reprogramming. In the heated race to translate this promising technology to the clinic, Life has emerged as one of the favorites, inching closer towards clinical trials in humans. Life is counting on its proprietary reprogramming technology that uses only three out of four classic reprogramming factors and on its strong team of scientists and managers. We talked to Dr. Sharon Rosenzweig-Lipson, Life’s Chief Scientific Officer, about the company’s journey, delving deep into the technology and its future.
I’ll start by saying that Life Biosciences is one of the most exciting companies in the longevity field. You might actually become the first company to have a partial reprogramming-based therapy approved.
At Life Biosciences, we’re focused on something that matters to everyone: helping people stay healthier as they age. We’re working on what we call cellular rejuvenation technologies, basically finding ways to turn back the clock in cells and make them more youthful. I came on board as Chief Scientific Officer about a year and a half ago, but I actually got to know the company pretty well before that. I consulted for them for a year, which gave me a chance to look under the hood, see the science they were doing, and I got really excited about what I saw.
Terrence Deacon — Philosophy of Biological Information
Donate to Closer To Truth and help us keep our content free and without paywalls: https://shorturl.at/OnyRq.
What is information in biology? information is essential for analyzing data and testing hypotheses. But what is information in evolution, population genetics, levels of selection, and molecular genetics? Is computational biology transformational?
Follow Closer To Truth on Instagram for news, announcements, and exciting updates: https://shorturl.at/p2IhM
Terrence William Deacon is an American neuroanthropologist. He taught at Harvard for eight years, relocated to Boston University in 1992, and is currently Professor of Anthropology and member of the Cognitive Science Faculty at the University of California, Berkeley.
Get member exclusives like early access to new content with a free Closer To Truth account: https://closertotruth.com/
Closer To Truth, hosted by Robert Lawrence Kuhn and directed by Peter Getzels, presents the world’s greatest thinkers exploring humanity’s deepest questions. Discover fundamental issues of existence. Engage new and diverse ways of thinking. Appreciate intense debates. Share your own opinions. Seek your own answers.
Cosmic Inflation Explained | Cosmology 101 Episode 6
In this episode of Cosmology 101, we learn how the detection of the Cosmic Microwave Background (CMB) validated the Big Bang Theory and led to the development of the concept of cosmic inflation.
Explore the challenges and ongoing debates in cosmology as scientists seek to uncover the true nature of the early universe and the origins of cosmic structure.
Join Katie Mack, Perimeter Institute’s Hawking Chair in Cosmology and Science Communication, on an incredible journey through the cosmos in our new series, Cosmology 101.
Sign up for our newsletter and download exclusive cosmology posters at: https://landing.perimeterinstitute.ca…
Follow the edge of theoretical physics on our social media:
/ pioutreach.
https://twitter.com/perimeter.
/ perimeterinstitute.
/ perimeter-institute.
Follow our host \.
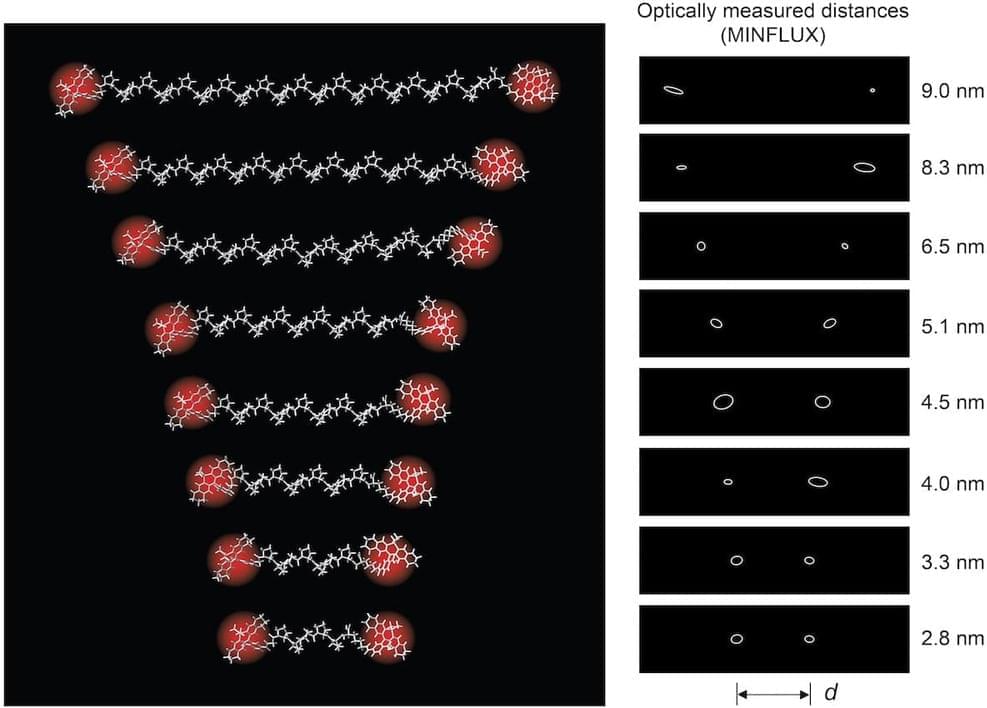
Optical technique measures intramolecular distances with angstrom precision
Physicists in Germany have used visible light to measure intramolecular distances smaller than 10 nm thanks to an advanced version of an optical fluorescence microscopy technique called MINFLUX. The technique, which has a precision of just 1 angstrom (0.1 nm), could be used to study biological processes such as interactions between proteins and other biomolecules inside cells.
In conventional microscopy, when two features of an object are separated by less than half the wavelength of the light used to image them, they will appear blurry and indistinguishable due to diffraction. Super-resolution microscopy techniques can, however, overcome this so-called Rayleigh limit by exciting individual fluorescent groups (fluorophores) on molecules while leaving neighbouring fluorophores alone, meaning they remain dark.
One such technique, known as nanoscopy with minimal photon fluxes, or MINFLUX, was invented by the physicist Stefan Hell. First reported in 2016 by Hell’s team at the Max Planck Institute (MPI) for Multidisciplinary Sciences in Göttingen, MINFLUX first “switches on” individual molecules, then determines their position by scanning a beam of light with a doughnut-shaped intensity profile across them.

Nvidia’s Huang Teams With Asia’s Richest Man on Blackwell AI Hub
Is AI going to take your job? Here’s what Nvidia CEO Jensen Huang told Bollywood star Akshay Kumar.
Read more on the chip giant’s partnerships with the biggest Indian corporates, including Ambani’s Reliance, announced at Nvidia’s AI summit in Mumbai.
Nvidia Corp.’s Jensen Huang struck a partnership with Asia’s richest man, Mukesh Ambani, to build out artificial intelligence infrastructure and spur the technology’s adoption in the world’s most populous country.

China has just launched the world’s first autonomous flying taxis
China has just launched the world’s first autonomous flying taxis, cutting a 1-hour drive down to just 7 minutes!
These eVTOL (electric Vertical Take-Off and Landing) aircraft feature 16 propellers and carry two passengers up to 30–40 km. They offer a thrilling glimpse into the future of urban transport. Each pilot-free flight is safely monitored from a high-tech command center.
What do you think about this? ☝️