The world’s first commercial space walk, performed by billionaire Jared Isaacman and SpaceX engineer Sarah Gillis, tested new technology and was practically flawless.
By Lee Billings
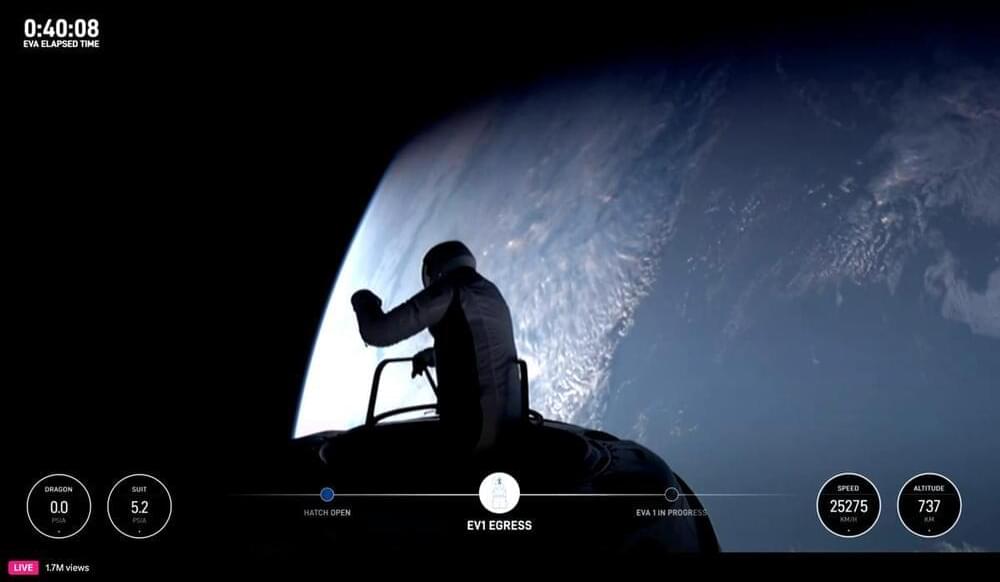
The world’s first commercial space walk, performed by billionaire Jared Isaacman and SpaceX engineer Sarah Gillis, tested new technology and was practically flawless.
By Lee Billings

Elon Musk is not smiling: Oracle and Elon Musk’s AI startup xAI recently ended talks on a potential $10 billion cloud computing deal, with xAI opting to build its own data center in Memphis, Tennessee.
At the time, Musk emphasised the need for speed and control over its own infrastructure. “Our fundamental competitiveness depends on being faster than any other AI company. This is the only way to catch up,” he added.
XAI is constructing its own AI data center with 100,000 NVIDIA chips. It claimed that it will be the world’s most powerful AI training cluster, marking a significant shift in strategy from cloud reliance to full infrastructure ownership.
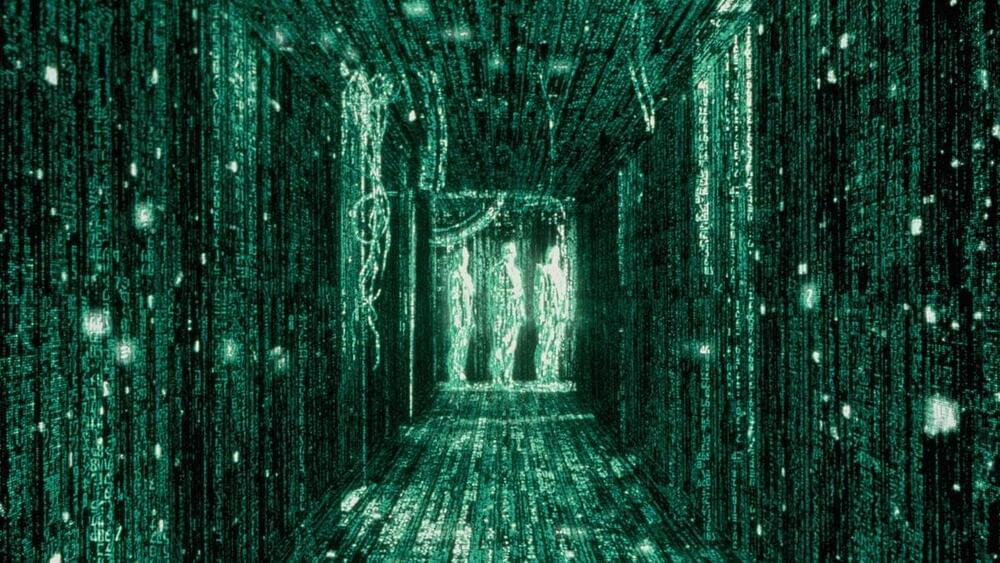


“The Matrix” may have been right all along. The idea that we are all living in a virtual simulation of reality formed the basis of the 1999 cult film, and now some philosophers and an increasing number of scientists are coming round to the idea it might actually be true.
Simulation theory, as it is known, is a “theoretical hypothesis that says what people perceive as reality is actually an advanced, hyper-realistic computer simulation, possibly overseen by a higher being”, said BuiltIn.
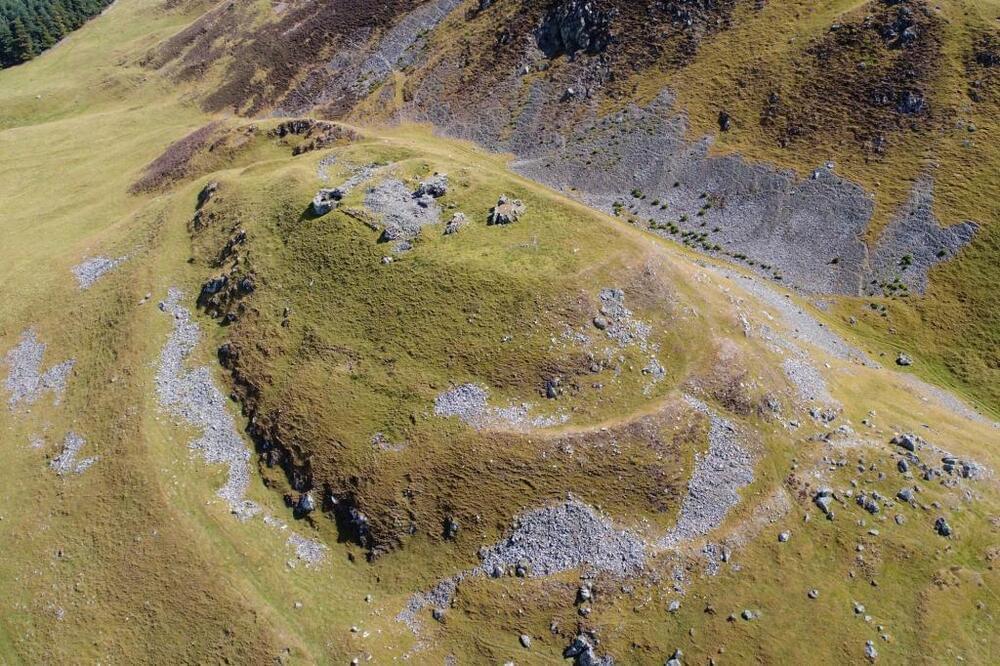

There may be some truth to the myth of Merlin.
On Tuesday, archeologists in Scotland revealed evidence of the legendary wizard’s death in Drumelzier between the 6th and 7th centuries — and the findings could change the way we tell Merlin’s tale.
Merlin was said to have been a loyal advisor to King Arthur amid the Dark Ages before being imprisoned, killed and buried along the river Tweed, according to Vita Merlini Sylvestris (the Life of Merlin of the Forest), a medieval manuscript of his life which is currently held at the British Library.
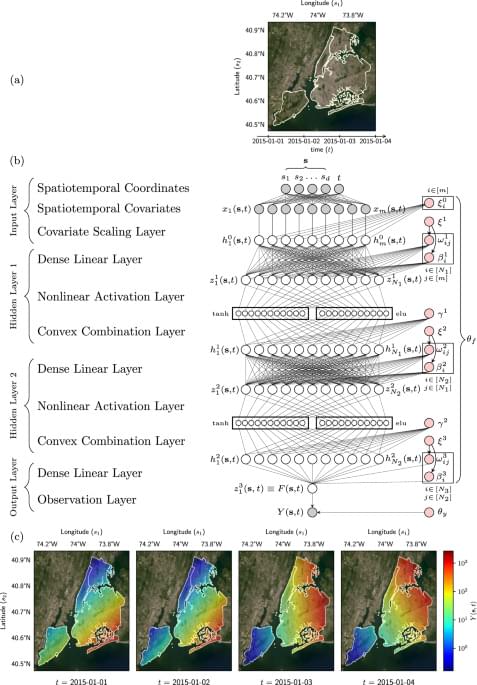
Spatiotemporal data consisting of measurements gathered at different times and locations is challenging to analyse due to variability and noise impact across different scales. The authors propose a statistical approach that delivers models of large-scale spatiotemporal datasets applicable to data-analysis tasks of forecasting and interpolation.

The principles of thermodynamics are cornerstones of our understanding of physics. But they were discovered in the era of steam-driven technology, long before anyone dreamed of quantum mechanics. In this episode, the theoretical physicist Nicole Yunger Halpern talks to host Steven Strogatz about how physicists today are reinterpreting concepts such as work, energy and information for a quantum world.
Listen on Apple Podcasts, Spotify, TuneIn or your favorite podcasting app, or you can stream it from Quanta.