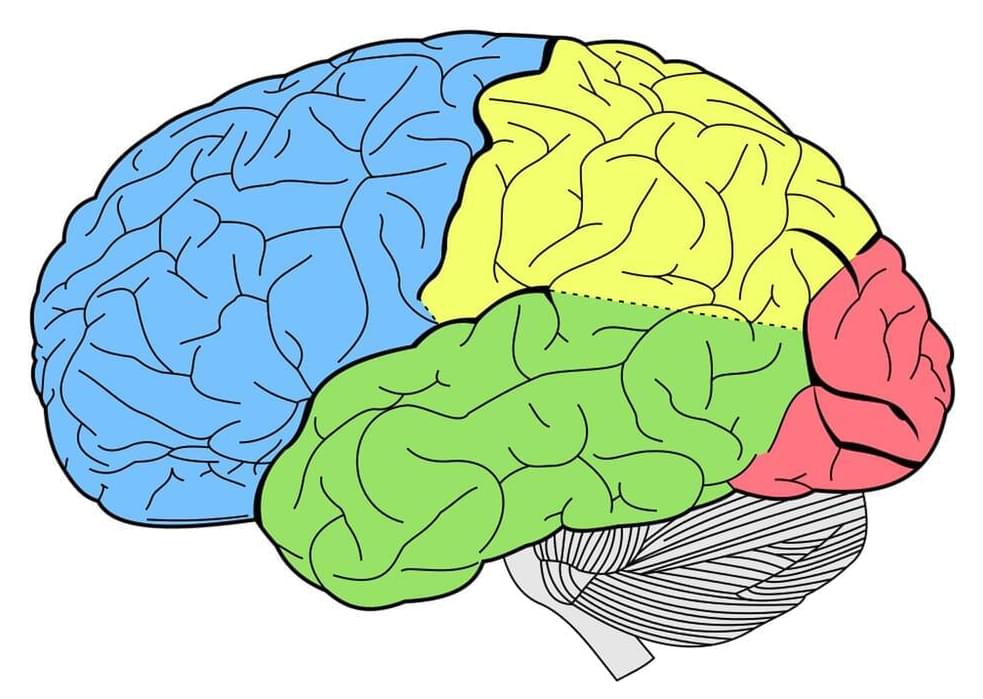
Preventative, predictive and personalized healthcare and longevity — dr. william kapp, MD — CEO, fountain life.
Dr. William Kapp, MD is Chief Executive Officer of Fountain Life (https://fountainlife.com/about/), a company focused on transforming the current healthcare system into one that is both proactive and data-driven, enabling enhanced longevity and catching and treating illnesses earlier than ever before, focusing on the detection and reversal of asymptomatic diseases and advancing an entirely new healthcare paradigm.
Dr. Kapp received his B.S. in Biochemistry from the University of Georgia and his M.S. in Immunology and M.D. at the Medical College of Georgia, where he graduated with honors and was inducted into Alpha Omega Alpha, the medical honor society. He attended the Baylor College of Medicine in Houston, Texas for residency in Orthopaedic Surgery and completed his specialty training in 1994.
Dr. Kapp is a board-certified orthopaedic surgeon and a Fellow in the American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons, has served on the Board of Directors of the Missouri Orthopaedic Association and has been chair of the Legislative Affairs Committee. Until 2005, he served as flight surgeon in the US Air Force Reserves with the rank of Major.
Dr. Kapp is a dynamic entrepreneur who has founded several healthcare start-ups, ranging from surgical centers and hospitals to electronic health record systems and medical real estate developments.