Cloudflare mitigates a record-breaking 3.8 Tbps DDoS attack, marking a surge in global cyber threats.




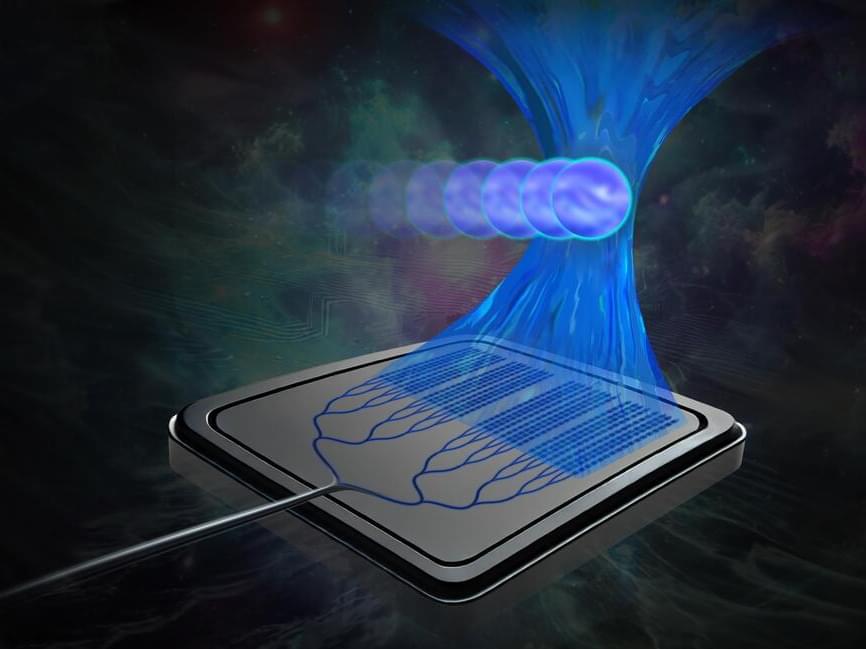
MIT researchers have developed a miniature, chip-based “tractor beam,” like the one that captures the Millennium Falcon in the film “Star Wars,” that could someday help biologists and clinicians study DNA, classify cells, and investigate the mechanisms of disease.
Small enough to fit in the palm of your hand, the device uses a beam of light emitted by a silicon-photonics chip to manipulate particles millimeters away from the chip surface. The light can penetrate the glass cover slips that protect samples used in biological experiments, enabling cells to remain in a sterile environment.
Traditional optical tweezers, which trap and manipulate particles using light, usually require bulky microscope setups, but chip-based optical tweezers could offer a more compact, mass manufacturable, broadly accessible, and high-throughput solution for optical manipulation in biological experiments.
The Hubbard model is a studied model in condensed matter theory and a formidable quantum problem. A team of physicists used deep learning to condense this problem, which previously required 100,000 equations, into just four equations without sacrificing accuracy. The study, titled “Deep Learning the Functional Renormalization Group,” was published on September 21 in Physical Review Letters.
Dominique Di Sante is the lead author of this study. Since 2021, he holds the position of Assistant Professor (tenure track) at the Department of Physics and Astronomy, University of Bologna. At the same time, he is a Visiting Professor at the Center for Computational Quantum Physics (CCQ) at the Flatiron Institute, New York, as part of a Marie Sklodowska-Curie Actions (MSCA) grant that encourages, among other things, the mobility of researchers.
He and colleagues at the Flatiron Institute and other international researchers conducted the study, which has the potential to revolutionize the way scientists study systems containing many interacting electrons. In addition, if they can adapt the method to other problems, the approach could help design materials with desirable properties, such as superconductivity, or contribute to clean energy production.
🌏 Get NordVPN 2Y plan + 4 months extra here ➼ https://NordVPN.com/sabine It’s risk-free with Nord’s 30-day money-back guarantee! ✌
A collaboration of a neurologist, a computer scientist, and a philosopher has just put forward a new theory of consciousness. It is based on the idea of causal models. The authors claim boldly that their idea solves the hard problem of consciousness and explains why zombies don’t exist in nature. Really? I’ve had a look.
Paper: https://osf.io/preprints/osf/mtgn7
🤓 Check out my new quiz app ➜ http://quizwithit.com/
💌 Support me on Donorbox ➜ https://donorbox.org/swtg.
📝 Transcripts and written news on Substack ➜ https://sciencewtg.substack.com/
👉 Transcript with links to references on Patreon ➜ / sabine.
📩 Free weekly science newsletter ➜ https://sabinehossenfelder.com/newsle…
👂 Audio only podcast ➜ https://open.spotify.com/show/0MkNfXl…
🔗 Join this channel to get access to perks ➜
/ @sabinehossenfelder.
🖼️ On instagram ➜ / sciencewtg.
#science #sciencenews #consciousness

We tackle the hard problem of consciousness taking the naturally-selected, self-organising, embodied organism as our starting point. We provide a mathematical formalism describing how biological systems self-organise to hierarchically interpret unlabelled sensory information according to valence and specific needs. Such interpretations imply behavioural policies which can only be differentiated from each other by the qualitative aspect of information processing. Selection pressures favour systems that can intervene in the world to achieve homeostatic and reproductive goals. Quality is a property arising in such systems to link cause to affect to motivate real world interventions. This produces a range of qualitative classifiers (interoceptive and exteroceptive) that motivate specific actions and determine priorities and preferences.
Planck length and Planck time and quantum foam.
Space Emerging from Quantum.
The other day I was amused to find a quote from Einstein, in 1936, about how hard it would be to quantize gravity: “like an attempt to breathe in empty space.” Eight decades later, I think we can still agree that it’s hard.
So here is a possibility worth considering: rather than quantizing gravity, maybe we should try to gravitize quantum mechanics. Or, more accurately but less evocatively, “find gravity inside quantum mechanics.” Rather than starting with some essentially classical view of gravity and “quantizing” it, we might imagine starting with a quantum view of reality from the start, and find the ordinary three-dimensional space in which we live somehow emerging from quantum information. That’s the project that ChunJun (Charles) Cao, Spyridon (Spiros) Michalakis, and I take a few tentative steps toward in a new paper.
We human beings, even those who have been studying quantum mechanics for a long time, still think in terms of a classical concepts. Positions, momenta, particles, fields, space itself. Quantum mechanics tells a different story. The quantum state of the universe is not a collection of things distributed through space, but something called a wave function. The wave function gives us a way of calculating the outcomes of measurements: whenever we measure an observable quantity like the position or momentum or spin of a particle, the wave function has a value for every possible outcome, and the probability of obtaining that outcome is given by the wave function squared. Indeed, that’s typically how we construct wave functions in practice. Start with some classical-sounding notion like “the position of a particle” or “the amplitude of a field,” and to each possible value we attach a complex number.