More on rapamycin.
Get the latest international news and world events from around the world.
Huge Problem with Modern GPUs. New Breakthrough Technology Explained
39,785 views • Jul 12, 2024 • #ASUSCopilotPlusPC #ASUS #Vivobook
A Big Wreck Is About To Happen At The Intersection Of Artificial Intelligence Boulevard And Net Zero Avenue
To put the forecasted demand into context, consider this: A recent MIT study found that a single data center consumes electricity equivalent to 50,000 homes. Estimates indicate that Microsoft, Amazon, and Google operate about 600 data centers in the U.S. today…
Arguments exist that by 2030, 80% of renewable power sources will fulfill electricity demand. For reference, the U.S. generated roughly 240 billion kilowatt hours of solar and 425 billion kilowatt hours of wind, totaling 665 billion kilowatt hours in 2023. Assuming a 50/50 split between wind and solar, that scenario implies that, to satisfy the U.S. electricity demand that adequately facilitates AI competitiveness, wind and solar will have to generate approximately 3.4 trillion kilowatt hours of electricity each. That is more than a ten-fold increase over the next five years. The EIA highlights that the U.S. planned utility-scale electric-generating capacity addition in 2023 included 29 million kilowatts of solar (54% of the total) and 6 million kilowatts of wind (11% of the total), which pales in comparison to the estimated amount required.
It just doesn’t get much more clear; renewables cannot begin to supply the energy needed for AI data centers. Only fossil fuels and nuclear can get the job done. It’s that simple. AI is not something global elites are going to let slide by. They’ve had a good run with the Big Green Grift but those days are going to gradually (maybe not so gradually) come to an end, as the demand for energy to power AI forces a reconsideration.
Scientists Identify a Speech Trait That Foreshadows Cognitive Decline
Can you pass me the whatchamacallit? It’s right over there next to the thingamajig.
Many of us will experience “lethologica”, or difficulty finding words, in everyday life. And it usually becomes more prominent with age.
Frequent difficulty finding the right word can signal changes in the brain consistent with the early (“preclinical”) stages of Alzheimer’s disease – before more obvious symptoms emerge.

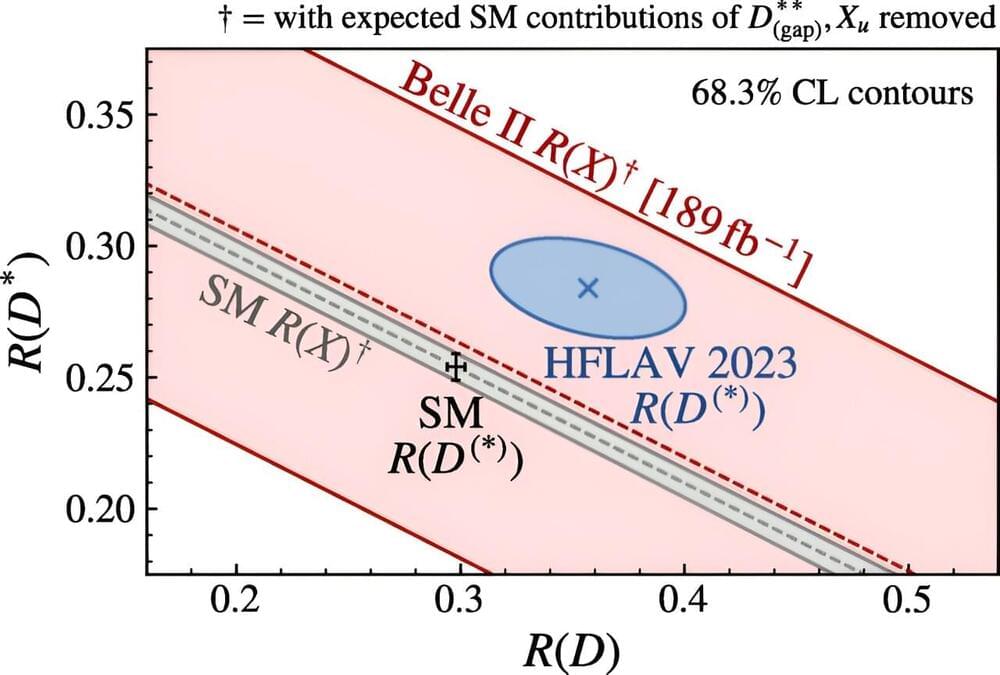
Belle II experiment reports the first direct measurement of tau-to-light-lepton ratio
The Belle II experiment is a large research effort aimed at precisely measuring weak-interaction parameters, studying exotic hadrons (i.e., a class of subatomic particles) and searching for new physical phenomena. This effort primarily relies on the analysis of data collected by the Belle II detector (i.e., a general purpose spectrometer) and delivered by the SuperKEKB, a particle collider, both located at the High Energy Accelerator Research Organization (KEK) in Tsukuba, Japan.

Neural networks made of light can make machine learning more sustainable
Scientists propose a new way of implementing a neural network with an optical system which could make machine learning more sustainable in the future. The researchers at the Max Planck Institute for the Science of Light have published their new method in Nature Physics, demonstrating a method that is much simpler than previous approaches.
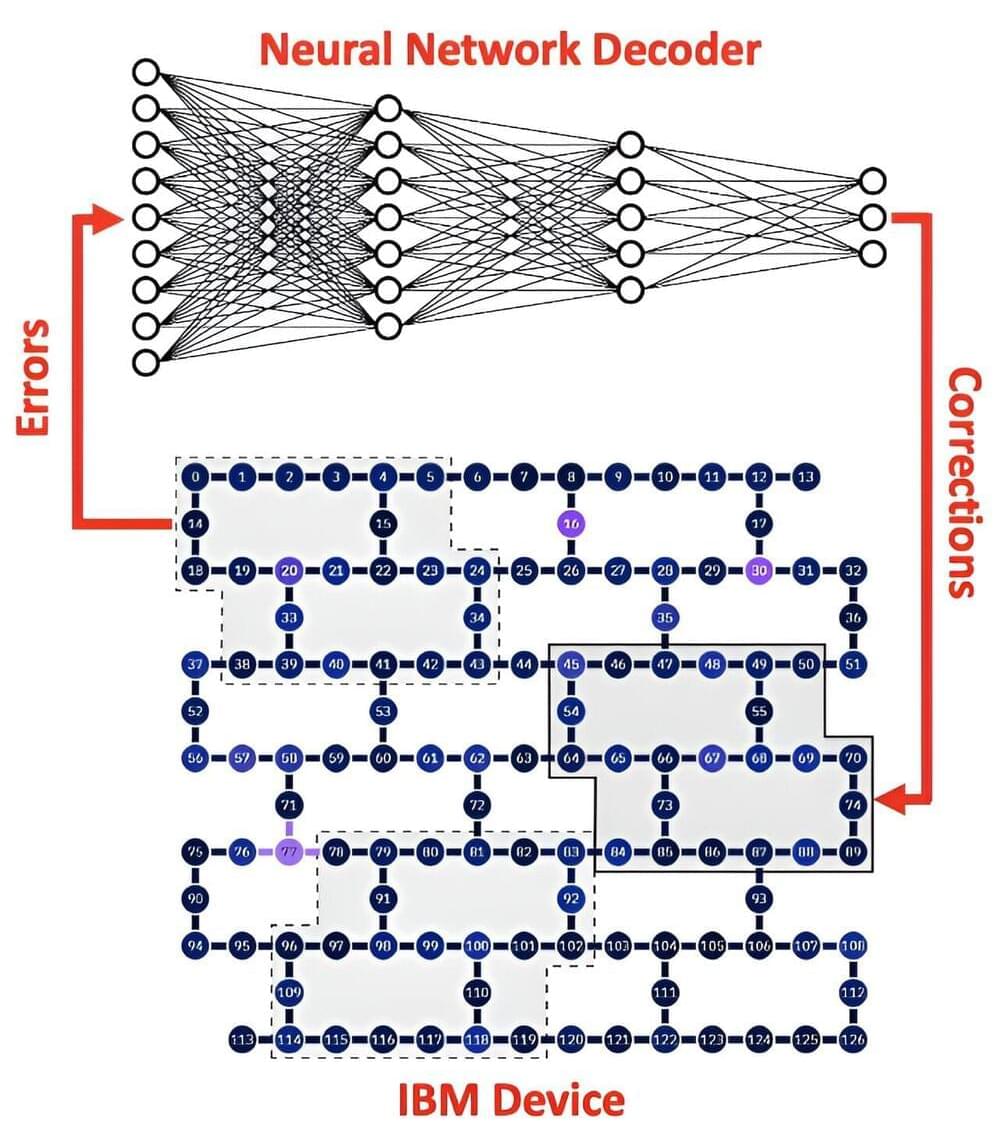
Artificial intelligence could help make quantum computers a reality
CSIRO research, published as a letter in Physical Review Research journal, found for the first time that AI could help process and resolve quantum errors known as qubit noise, which are generated by the nature of quantum physics.
Overcoming these errors is widely considered the largest barrier to advanced quantum computers moving from experiment to tool.
In conventional computers, information is stored and processed in “bits,” which work on the principles of binary numbers. Each bit can represent either 0 or 1. But quantum computing devices are made up of quantum bits, or “qubits.”
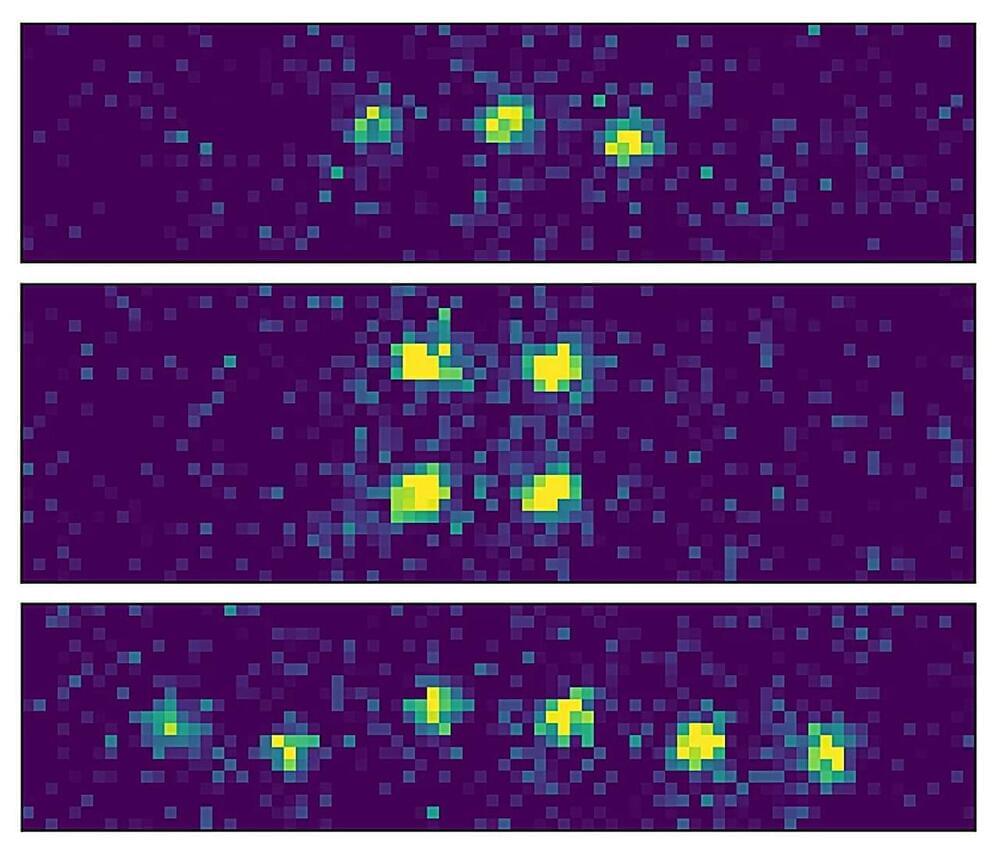
Securely propagating entanglement at the push of a button
Entanglement, Einstein’s “spooky action at a distance,” today is THE tool of quantum information science. It is the essential resource for quantum computers and used to transmit quantum information in a future quantum network. But it is highly sensitive. It is therefore an enormous challenge to entangle resting quantum bits (qubits) with flying qubits in the form of photons “at the push of a button.”
A life of the mind — with Daniel Dennett
Join the late, renowned philosopher and cognitive scientist Daniel C Dennett on a captivating journey of intellectual exploration through his own life.
Sign up as a member to watch the Q\&A here: • Q\&A: A life of the mind — Daniel Dennett.
Buy Daniel’s book here: https://geni.us/K3Ja.
This lecture was recorded on 3 October 2023 at the Ri.
We had some difficulties with the internet connection at the beginning of this video, but it improves after that, so keep watching!
00:00 Introduction.
2:30 The importance of making mistakes.
7:30 Tools of the mind.
11:20 How can you get the right knowledge?
14:24 Douglas Hofstadter and Joosting.
19:46 Richard Dawkins and memes.
22:57 Ruth Millikan and language.
24:20 Giulio Tononi and the IIT controversy.
31:50 Descartes’ mistakes.
35:50 Daniel’s biggest mistake.
40:43 Helping philosophers and scientists to imagine.
43:07 Julian Jaynes, consciousness and dualism.
48:22 More iconoclasts of philosophy.
52:46 Karl Pribram and James Gibson.
From his formative years in Beirut to his academic pursuits at Harvard, and from the vibrant jazz clubs of Paris to his introspective musings on his tractor in Maine, discover the stories behind some of his most influential books, such as ‘Consciousness Explained’ and ‘Darwin’s Dangerous Idea’. Whose contents have reshaped our understanding of the mind, consciousness and the nature of the human experience.