“The Moon’s South Pole is a completely different environment than where we landed during the Apollo missions,” said Dr. Sarah Noble. “It offers access to some of the Moon’s oldest terrain, as well as cold, shadowed regions that may contain water and other compounds.”
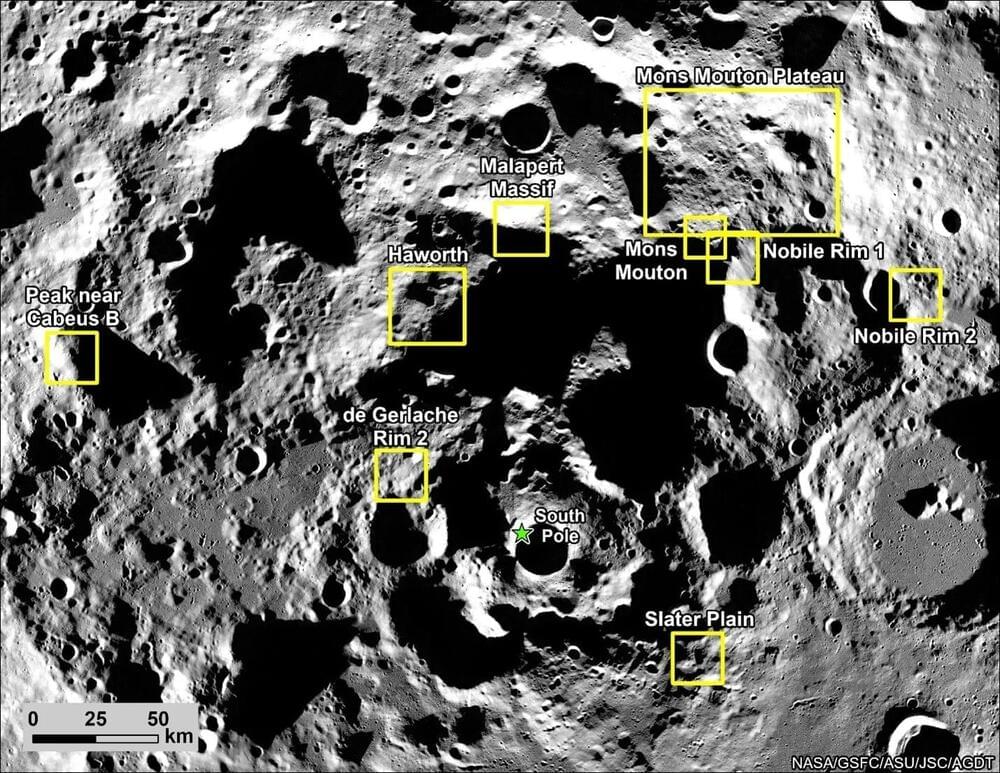
Where will NASA’s Artemis Program precisely land astronauts near the lunar south pole? This is what the famed space agency hopes to figure out as they recently narrowed the list of potential landing regions from 13 to 9, underscoring NASA’s ongoing urgency in selecting a final landing site prior to landing astronauts on the Moon with the Artemis III in the next few years, along with landing the first woman and person of color on the lunar surface, as well. The selected regions will provide scientific opportunities based on geology, terrain, and access to water ice, the latter of which can be used for fuel, drinking, creating oxygen through electrolysis, and much more.
NASA has identified the following potential landing regions not listed in priority: Peak near Cabeus B, Haworth, Malapert Massif, Mons Mouton Plateau, Mons Mouton, Nobile Rim 1, Nobile Rim 2, de Gerlache Rim 2, Slater Plain. Each landing region consists of several square miles with more precise landing sites being determined later.