RushThis belongs to anthem recordsthis is not my property and this is only being used for entertainment purposes.
Get the latest international news and world events from around the world.
Dark matter’s search could be end by a nearby supernova explosion
Researchers at UC Berkeley proposed that axions, hypothetical particles, could be detected shortly after a supernova’s gamma rays. They suggest that the Fermi Gamma-ray Space Telescope has a 1 in 10 chance of observing this phenomenon. Axions would be produced during the early moments of a star’s collapse and would then transform into high-energy gamma rays in the star’s magnetic field.

Generative AI Could Generate Millions More Tons of E-Waste by 2030
Generative AI could saddle the planet with heaps more hazardous waste.
Every time generative artificial intelligence drafts an e-mail or conjures up an image, the planet pays for it. Making two images can consume as much energy as charging a smartphone; a single exchange with ChatGPT can heat up a server so much that it requires a bottle’s worth of water to cool. At scale, these costs soar. By 2027, the global AI sector could annually consume as much electricity as the Netherlands, according to one recent estimate. And a new study in Nature Computational Science identifies another concern: AI’s outsize contribution to the world’s mounting heap of electronic waste. The study found that generative AI applications alone could add 1.2 million to five million metric tons of this hazardous trash to the planet by 2030, depending on how quickly the industry grows.

Mathematicians’ Newest Assistants Are Artificially Intelligent
AI-human collaboration could possibly achieve superhuman greatness in mathematics.
Mathematicians explore ideas by proposing conjectures and proving them with theorems. For centuries, they built these proofs line by careful line, and most math researchers still work like that today. But artificial intelligence is poised to fundamentally change this process. AI assistants nicknamed “co-pilots” are beginning to help mathematicians develop proofs—with a real possibility this will one day let humans answer some problems that are currently beyond our mind’s reach.

Are you drinking toxic water? Study discovers new chemical that has been present in water for about a century
Is the chemical toxic?
While the scientists are unsure about the toxicity of the chemical, it is concerning since chloronitramide anion bears resemblance to other chemicals that are toxic in nature. David Wahman, one of the study’s authors and a research environmental engineer at the Environmental Protection Agency, said, “It has similarity to other toxic molecules. We looked for it in 40 samples in 10 US chlorinated drinking water systems located in seven states. We did find it in all the samples.”

Why clean air is a luxury that many can’t afford
Although almost everyone in the world now breathes air that is polluted in some way, the unfolding story of air pollution is one of environmental inequality.
Every time Mithilesh turns on her stove to cook, her eyes begin to burn. The small home the 29-year-old housewife shares with her husband, daughter, son and elderly in-laws in the slums of the Indian capital Delhi quickly fills up with smoke, making it hard for anyone to see.
Mithilesh has cooked over a traditional chulha – a metal coated combustor stove that uses firewood as fuel – since she was 13 years old. She often has difficulty breathing and experiences uncontrolled bouts of coughing.
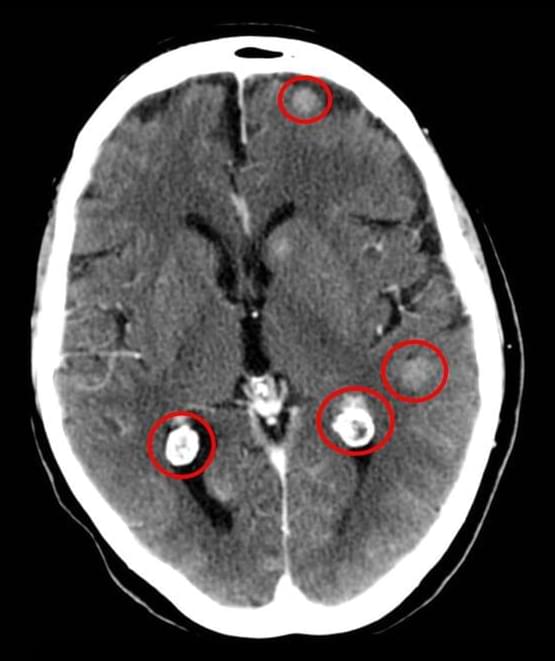
Lorbrena Effective as Initial Treatment of ALK-Positive NSCLC
The drug lorlatinib (Lorbrena) is superior to crizotinib (Xalkori) as an initial treatment for people with advanced non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) that has changes in the ALK gene, according to new results from a global clinical trial.
The findings are the latest from the CROWN study. Participants were randomly assigned to receive either lorlatinib or crizotinib as a treatment for advanced lung tumors with ALK gene mutations, a disease called ALK-positive lung cancer.
Several years ago, study investigators reported that participants who received lorlatinib went longer without the disease worsening, known as progression-free survival, than those who received crizotinib.
