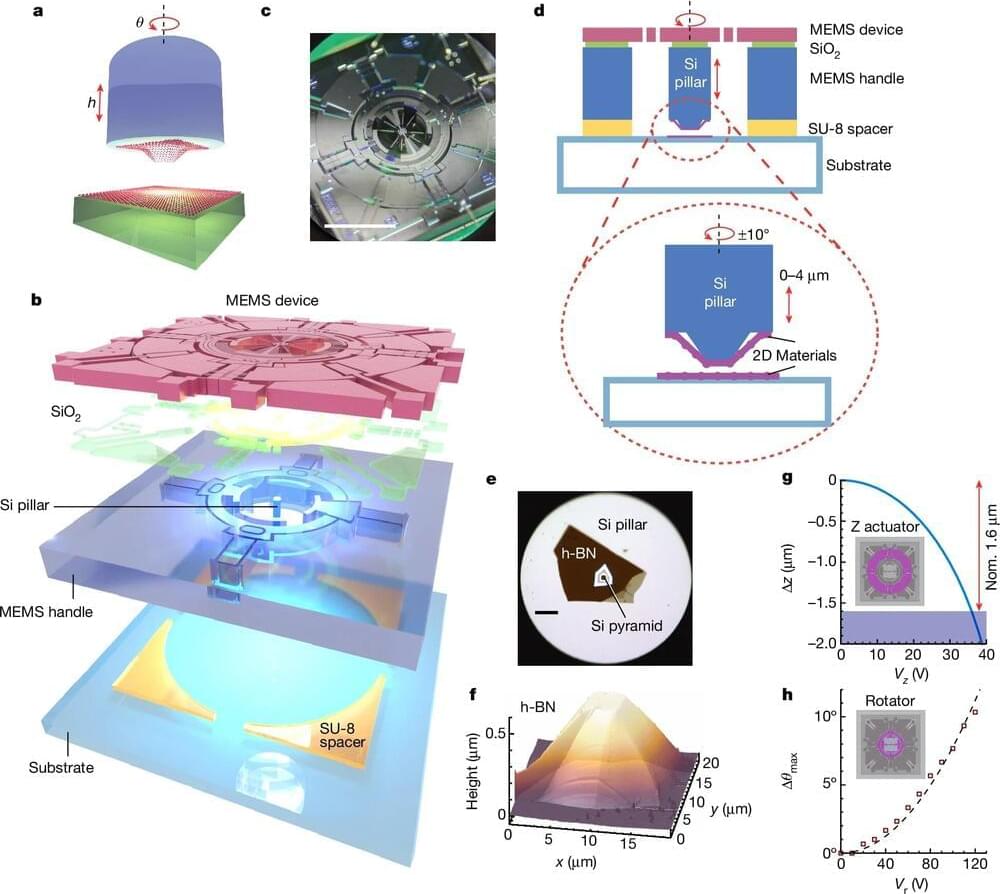
A discovery six years ago took the condensed-matter physics world by storm: Ultra-thin carbon stacked in two slightly askew layers became a superconductor, and changing the twist angle between layers could toggle their electrical properties. The landmark 2018 paper describing “magic-angle graphene superlattices” launched a new field called “twistronics,” and the first author was then-MIT graduate student and recent Harvard Junior Fellow Yuan Cao.
Together with Harvard physicists Amir Yacoby, Eric Mazur, and others, Cao and colleagues have built on that foundational work, smoothing a path for more twistronics science by inventing an easier way to twist and study many types of materials.
A new paper in Nature describes the team’s fingernail-sized machine that can twist thin materials at will, replacing the need to fabricate twisted devices one by one. Thin, 2D materials with properties that can be studied and manipulated easily have immense implications for higher-performance transistors, optical devices such as solar cells, and quantum computers, among other things.