This will enable us to increase our production rate significantly as we build toward our long-term goal of producing one Ship per day.



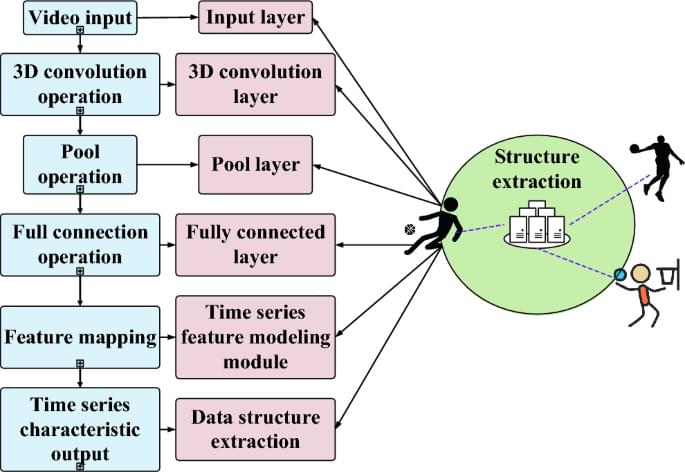
Wang, J., Zuo, L. & Cordente Martínez, C. Basketball technique action recognition using 3D convolutional neural networks. Sci Rep 14, 13,156 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-024-63621-8

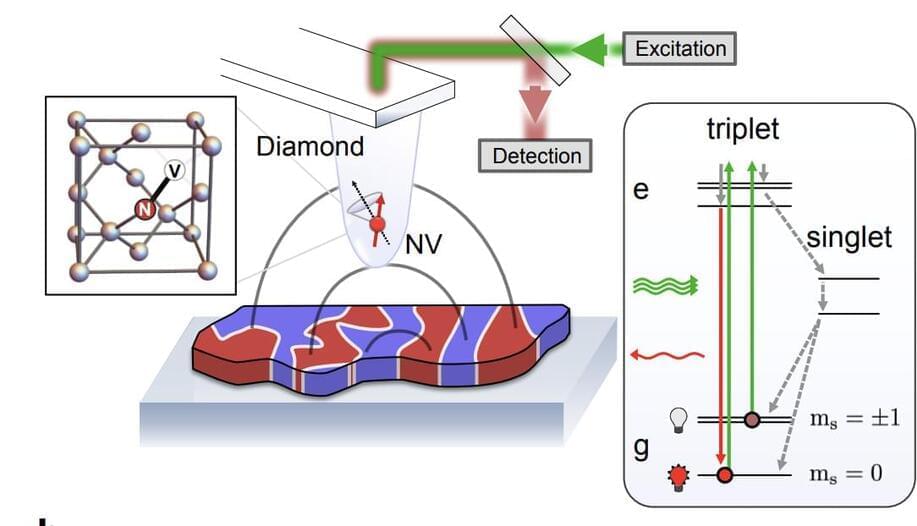
Researchers from Princeton University, University of California Santa Barbara, University of Basel, and ETH Zurich have discovered new applications for nitrogen vacancy (NV) centre quantum sensors in condensed matter physics. These sensors, which offer nanoscale resolution across a wide range of temperatures, have been used to measure static magnetic fields in condensed matter systems.
NV centres can probe beyond average magnetic fields, enabling high precision noise sensing in diverse systems. They offer several advantages over other nanoscale probes, including the ability to probe both static and dynamic properties in a momentum and frequency-resolved way.
Condensed matter physics is a field that studies the physical properties of condensed phases of matter, such as solids and liquids. Recently, researchers from Princeton University, University of California Santa Barbara, University of Basel, and ETH Zurich have discovered new opportunities in this field for nanoscale quantum sensors, specifically nitrogen vacancy (NV) centre quantum sensors. These sensors offer unique advantages in studying condensed matter systems due to their quantitative, noninvasive, physically robust nature, and their ability to offer nanoscale resolution across a wide range of temperatures.
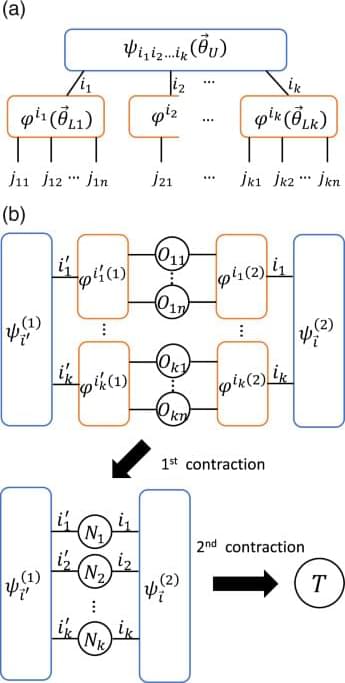
Kanno, S., Nakamura, H., Kobayashi, T. et al. npj Quantum Inf 10, 56 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41534-024-00851-8

I found this on NewsBreak: Space Engine Systems Successful in UK MoD Hypersonic Technology Challenge #Engineering
EDMONTON, Alberta—(BUSINESS WIRE)—May 29, 2024—
Space Engine Systems (SES), through its UK operations based out of Spaceport Cornwall (SES Ltd), has applied its aerospace technology expertise to a £1 Billion GBP ($1.27 Billion USD) challenge issued by the UK MoD linked to Hypersonic Technologies and was very recently notified that it had secured a place in the Hypersonic Technology and Capability Development Framework (HTCDF). DE&S to award contracts on £1 billion framework to develop UK’s first hypersonic missile — Defence Equipment & Support (mod.uk). This framework will enable the rapid development of advanced hypersonic missile capabilities, and related technology, over the next 7 years.
A new tool, described as “flying handcuffs,” will soon be used by San Francisco police. https://abc7ne.ws/3x2ZZVJ#restraint #police #handcuffs #crime #lasso #…
Strange underwater icicles form in the Earth’s coldest regions and freeze living organisms in place.
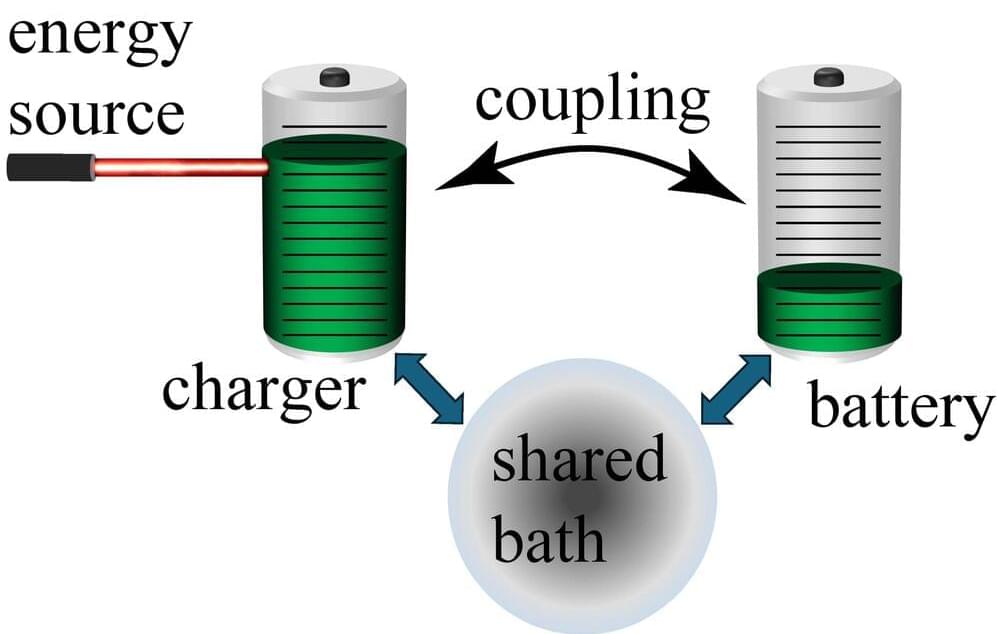
In physics, nonreciprocity occurs when a system’s response varies depending on the direction in which waves or signals are propagating within it. This asymmetry arises from a break in so-called time-reversal symmetry, which essentially means that a system’s processes observed as they evolve over time will be different compared to those processes observed on rewind.