GM software VP Baris Cetinok tells InsideEVs how the Blazer EV was diagnosed, tested and put back on sale after being grounded for months.
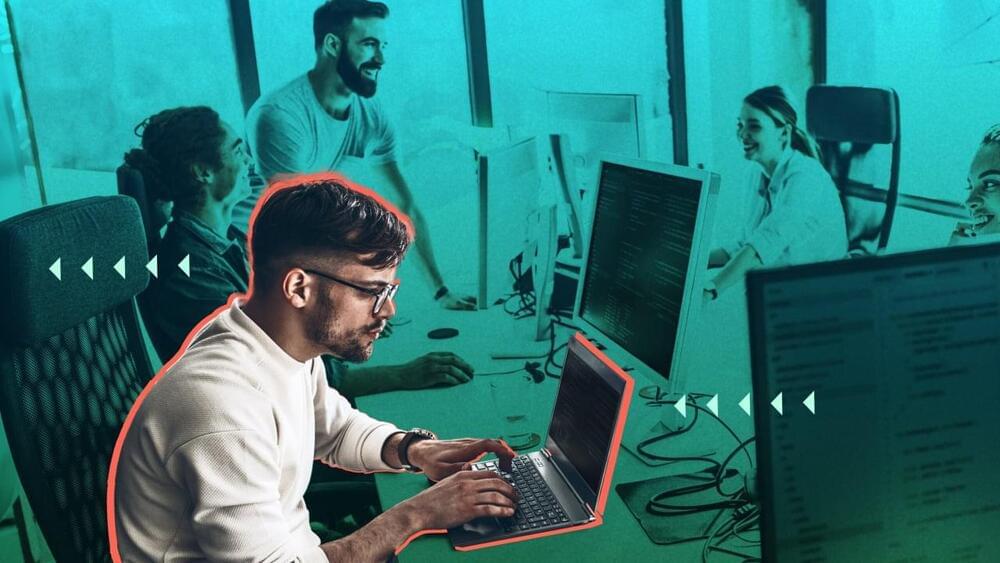



How will that situation change development teams? A common ratio of developers to testers is three to one. At a big bank with 40,000 software engineers, 10,000 might do security, reliability, and quality control. But the AI effect is like squeezing a balloon so it expands on the other side. The coding productivity jump is offset by a dramatic increase in cycles spent on testing.
How Development Teams Can Get Ahead
For software teams, the pressure is on to adapt. Companies that want to stay ahead of the game should first get a handle on a long-time adversary: toil.




The motions within the molecule provide a new way to compare the structures and functions of similar proteins.
Proteins play a central role in nearly every biological process, and they often change shape as they function. Over the past decade, a research team has developed a method of analysis that can help make sense of the available atomic-scale structural data and reveal the key physical distortions that underlie protein functions. Now the team has shown that the technique provides a consistent way of comparing proteins from different species, demonstrating similar structural changes in many of them [1]. The researchers believe that the technique will help biologists better understand the cross-species variations among proteins.
Proteins are linear chains of amino acids that fold up into specific three-dimensional shapes. Although there are lots of atomic-scale data on the structural changes that protein molecules execute as they function, researchers have had few quantitative methods to extract insights from these data, says biophysicist Pablo Sartori of the Gulbenkian Institute of Science in Portugal. One challenge, he says, is the arbitrary choice one makes when comparing two similar protein structures, such as the structures of a protein in two different conformations. “If you align region A of the protein, then region B shows displacement. If you align region B, then region A shows displacement. If you align the average, then both are displaced a bit.” Another problem is that the relative displacement is often not the quantity that best reflects the structural changes associated with protein function.

The perplexing phenomenon of homochirality in life, where biomolecules exist in only one of two mirror-image forms, remains unexplained despite historical attention from scientific figures like Pasteur, Lord Kelvin, and Pierre Curie. Recent research suggests the combination of electric and magnetic fields might influence this preference through experiments showing enantioselective effects on chiral molecules interacting with magnetized surfaces, offering indirect evidence towards understanding this mystery.
The phenomenon known as homochirality of life, which refers to the exclusive presence of biomolecules in one of their two possible mirror-image configurations within living organisms, has intrigued several prominent figures in science. This includes Louis Pasteur, who first identified molecular chirality, William Thomson (also known as Lord Kelvin), and Pierre Curie, a Nobel Laureate.
A conclusive explanation is still lacking, as both forms have, for instance, the same chemical stability and do not differ from each other in their physicochemical properties. The hypothesis, however, that the interplay between electric and magnetic fields could explain the preference for one or the other mirror-image form of a molecule – so-called enantiomers – emerged early on.

For over ten years, physicists have been able to pinpoint the exact positions of individual atoms with a precision finer than one-thousandth of a millimeter using a specialized microscope. However, this method has so far only provided the x and y coordinates. Information on the vertical position of the atom – i.e., the distance between the atom and the microscope objective – is lacking.
A new method has now been developed that can determine all three spatial coordinates of an atom with one single image. This method – developed by the University of Bonn and University of Bristol – is based on an ingenious physical principle. The study was recently published in the specialist journal Physical Review A.