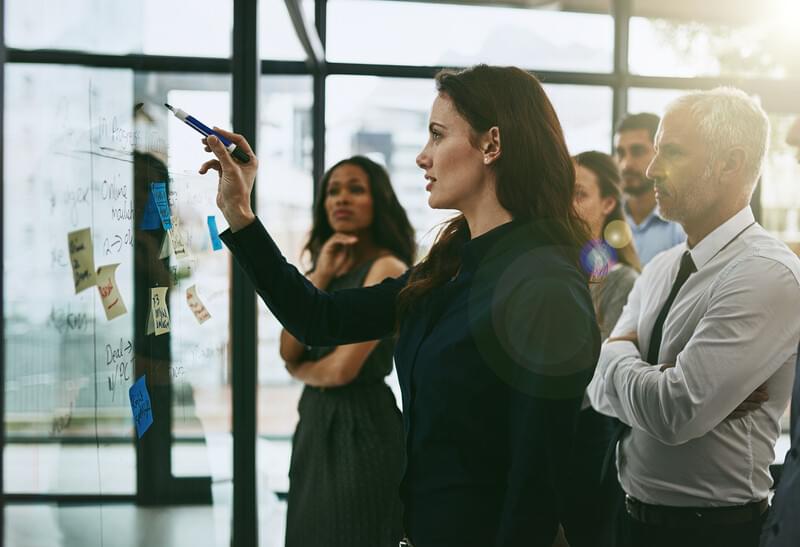
Bacterium could head off food versus fuel dilemma by producing chemicals from agricultural waste.

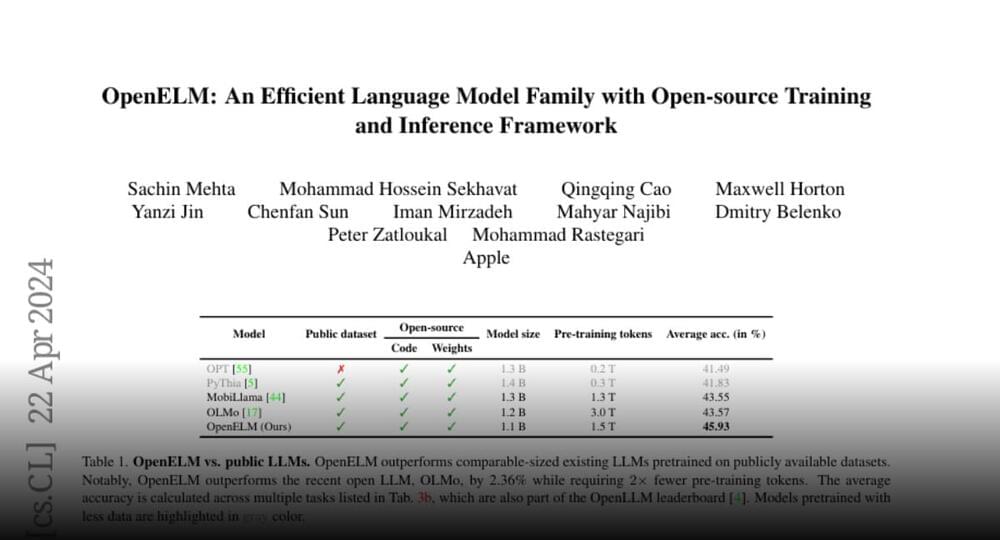
Apple presents OpenELM An Efficient Language Model Family with Open-source Training and Inference Framework.
Apple presents OpenELM
An Efficient Language Model Family with Open-source Training and Inference Framework.
The reproducibility and transparency of large language models are crucial for advancing open research, ensuring the trustworthiness of results, and…
Join the discussion on this paper page.

That led the Microsoft Research machine learning expert to wonder how much an AI model could learn using only words a 4-year-old could understand – and ultimately to an innovative training approach that’s produced a new class of more capable small language models that promises to make AI more accessible to more people.
Large language models (LLMs) have created exciting new opportunities to be more productive and creative using AI. But their size means they can require significant computing resources to operate.
While those models will still be the gold standard for solving many types of complex tasks, Microsoft has been developing a series of small language models (SLMs) that offer many of the same capabilities found in LLMs but are smaller in size and are trained on smaller amounts of data.
Regenerating damaged tissues or organs has been a dream of scientists for decades. Now, researchers at the FMI and Novartis Biomedical Research have discovered a new molecule that activates a protein involved in regeneration. The tool holds promise for advancing our understanding of how organisms repair damaged tissue.
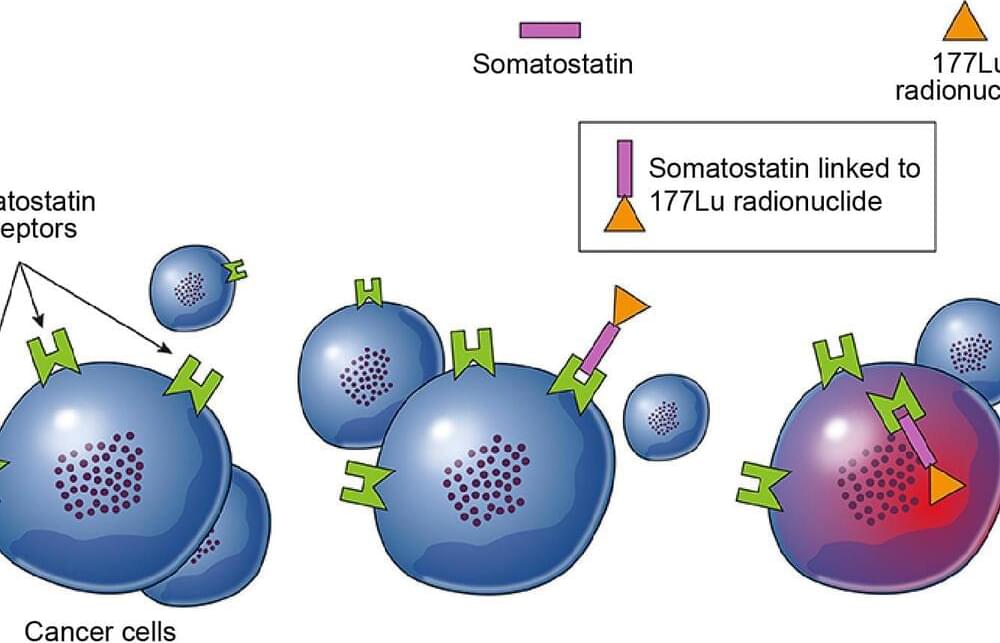
People with advanced neuroendocrine tumors in the digestive system may benefit from a treatment combination that includes the drug Lu 177-dotatate (Lutathera), according to the results of a first-of-its-kind clinical trial.
All participants in the trial, called NETTER-2, had advanced neuroendocrine tumors in the gastrointestinal tract or pancreas that had not yet been treated.
Those who received Lu 177-dotatate plus octreotide (Sandostatin) lived almost three times as long without their cancer getting worse (progression-free survival) as those who received octreotide alone—a median of nearly 23 months, versus 8.5 months. And the number of people whose tumors shrank, sometimes completely, was nearly five times greater in those who received both drugs compared to those who only received octreotide.
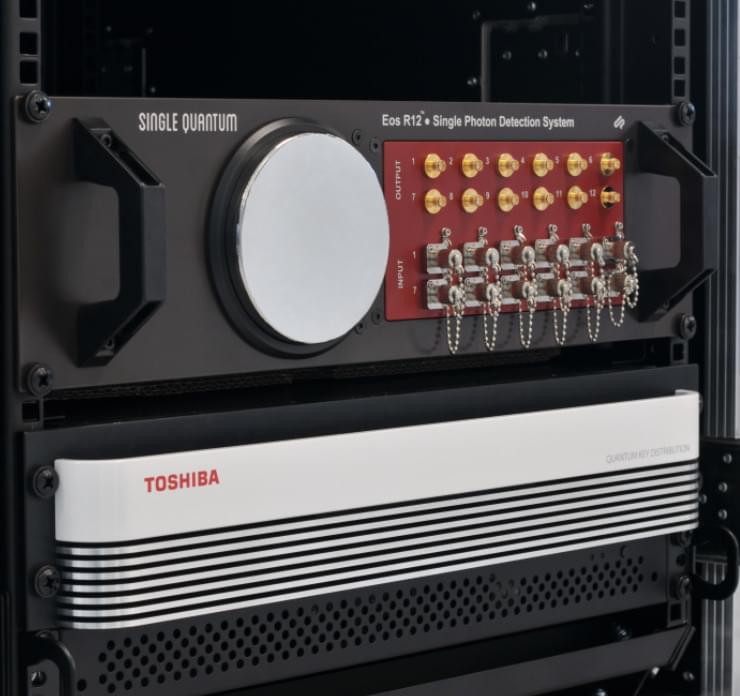


PRESS RELEASE — Toshiba Europe Ltd. and Single Quantum B.V. have collaborated to test and validate long-distance deployments of Quantum Key Distribution (QKD) technology. Following extended validation testing of Toshiba’s QKD technology and Single Quantum’s superconducting nanowire single photon detectors (SNSPDs), both companies are pleased to announce a solution that substantially extends the transmission range for QKD deployment over fibre connections, up to and beyond 300km.
QKD uses the quantum properties of light to generate quantum secure keys that are immune to decryption by both high performance conventional and quantum computers. Toshiba’s QKD is deployed over fibre networks, either coexisting with conventional data transmissions on deployed ‘lit’ fibres, or on dedicated quantum fibres.
Toshiba’s unique QKD technology can deliver quantum secure keys in a single fibre optic link at distances of up to 150km using standard integrated semiconductor devices. Achieving longer distance QKD fibre transmission is challenging due to the attenuation of the quantum signals along the fibre length, (the optical loss of the fibre link). To provide extended QKD transmission, operators typically concatenate fibre links together with trusted nodes along the fibre route which house QKD systems that relay the secret keys.

