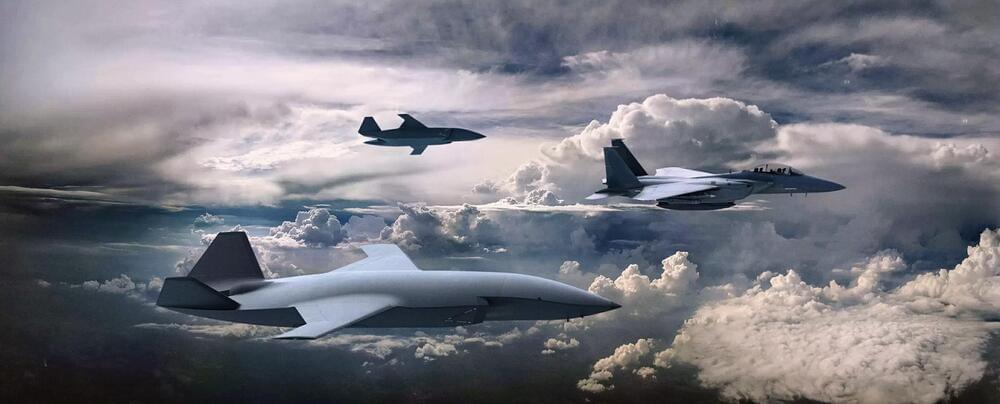
Chief of Staff Gen. David Allvin also did not explicitly say the Air Force would build its Next Generation Air Dominance fighter amid tight budgets.




“We need a defined framework, but instead what we see here is a fairly wild race between labs,” one journal editor told me during the ISSCR meeting. “The overarching question is: How far do they go, and where do we place them in a legal-moral spectrum? How can we endorse working with these models when they are much further along than we were two years ago?”
So where will the race lead? Most scientists say the point of mimicking the embryo is to study it during the period when it would be implanting in the wall of the uterus. In humans, this moment is rarely observed. But stem-cell embryos could let scientists dissect these moments in detail.
Yet it’s also possible that these lab embryos turn out to be the real thing—so real that if they were ever transplanted into a person’s womb, they could develop into a baby.
Elon Musk says Tesla could make 100 million Optimus robots a year, costing $10k-20k each, to do everything from babysitting to working in factories, leading to the population of humanoid robots exceeding that of humans.
https://youtube.com/global5gevolution click #subscribe.
#tesla #elonmusk #…
Non-personalized content and ads are influenced by things like the content you’re currently viewing and your location (ad serving is based on general location). Personalized content and ads can also include things like video recommendations, a customized YouTube homepage, and tailored ads based on past activity, like the videos you watch and the things you search for on YouTube. We also use cookies and data to tailor the experience to be age-appropriate, if relevant.

This study provides new insights into metformin’s effect on the molecular mechanisms inside cells and why it reduces proliferation of cancer cells, emphasising the role of miRNAs in colorectal cancer.
The authors suggest their findings highlight the potential for developing RNA therapeutics for cancer prevention and treatment and possibly for targeted interventions. Although there are several challenges in the field of miRNA therapeutics, this study could signal another step in their development as potential cancer treatments.
Now, however, astronomers Fan Zou and W. Niel Brandt, both of Penn State University, have led a team that connected the two mechanisms of black-hole growth from observations and simulations. The results may provide some answers at last.
Related: NASA telescope spots ‘cosmic fireworks’ and faint echos from the Milky Way’s supermassive black hole
“A very big question is how do these supermassive black holes grow so massive?” said Zou while presenting their work at the 244th meeting of the American Astronomical Society in Wisconsin… “To address that, we need to track the overall growth history of these supermassive black holes.”
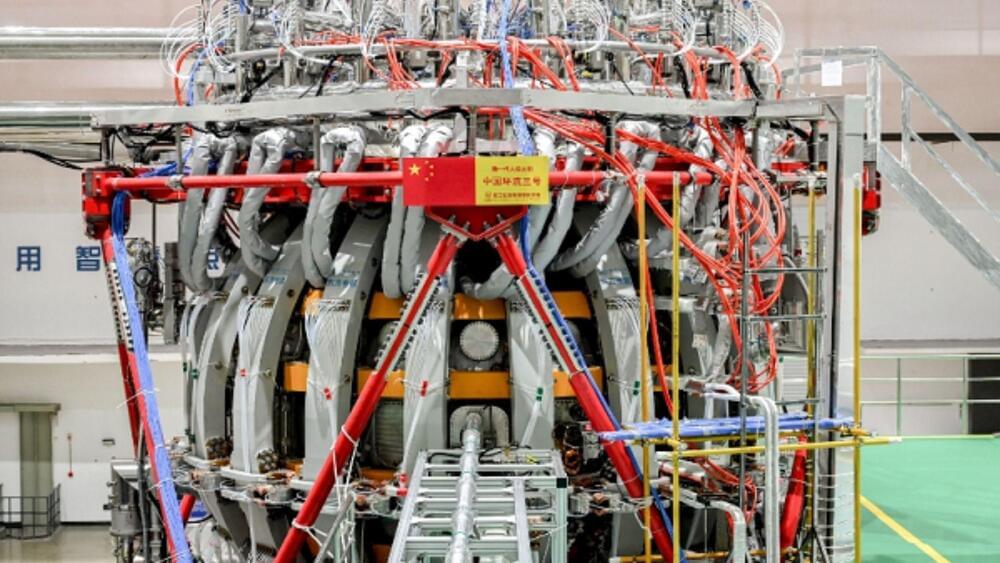
Chinese scientists have made a groundbreaking milestone in nuclear fusion. They have announced a major achievement in discovering an advanced magnetic field structure “for the first time in the world” using the Huanliu-3 (HL-3) tokamak, also known as China’s “artificial sun.”
The discovery is the result of the first round of international joint experiments conducted on the HL-3 tokamak, a project that opened to global collaboration at the end of 2023.
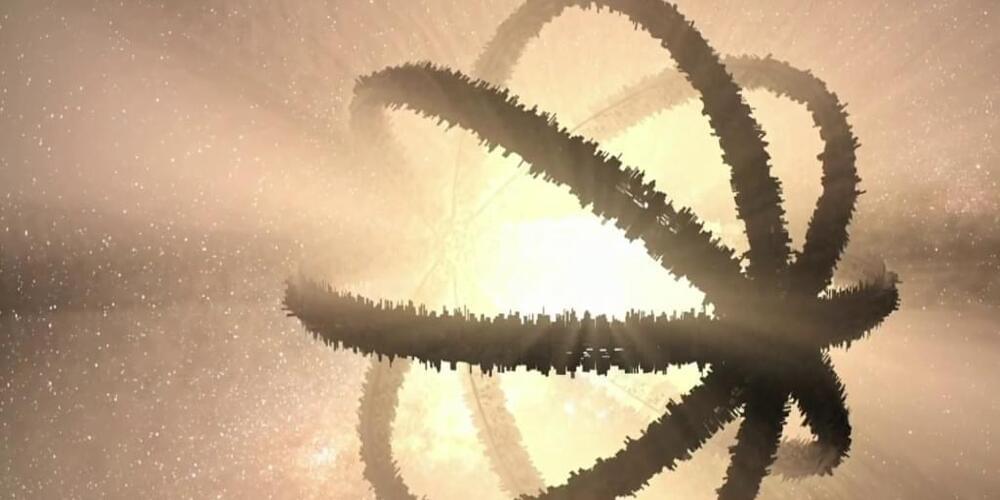

A group of researchers have identified at least seven stars that might be surrounded by advanced alien mega-structures known as “dyson spheres.” NBC News’ Ellison Barber speaks with Janna Levin, a professor of physics and astronomy at Barnard College, about the findings and whether the truth is out there.