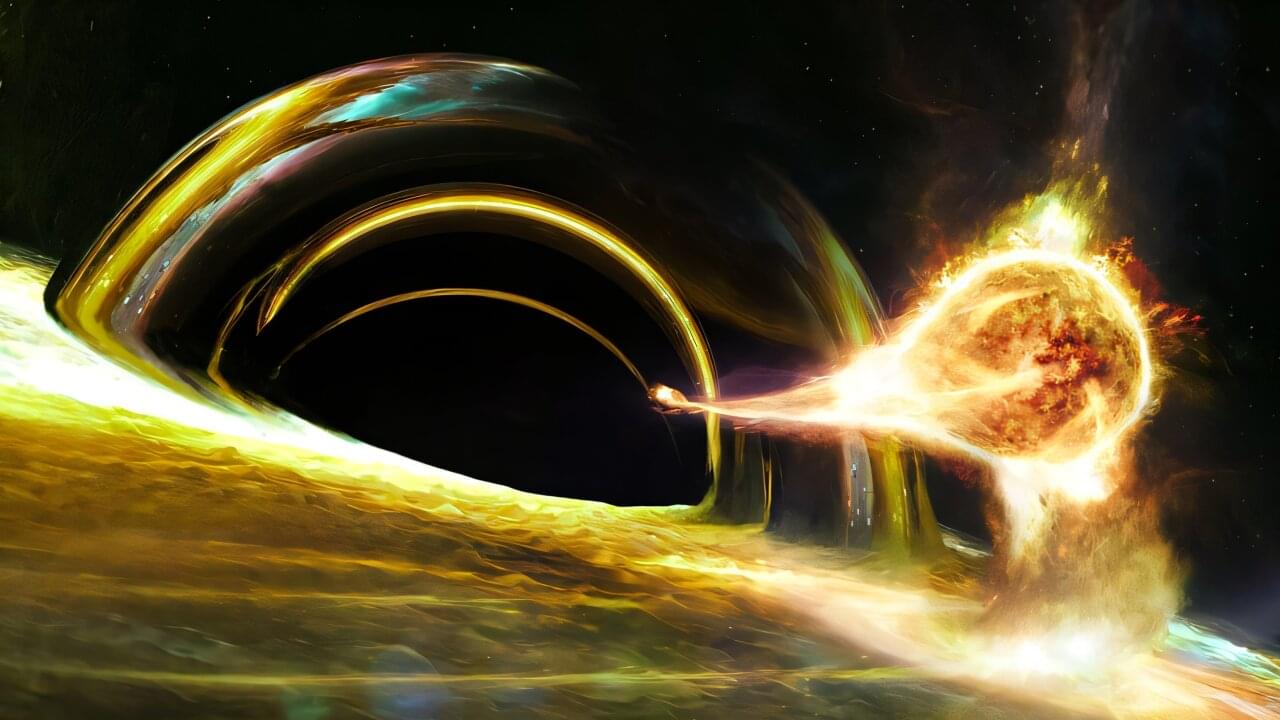
Lightning might not strike twice, but black holes apparently do. An international group of researchers led by Tel Aviv University astronomers observed a flare caused when a star falls onto a black hole and is destroyed.


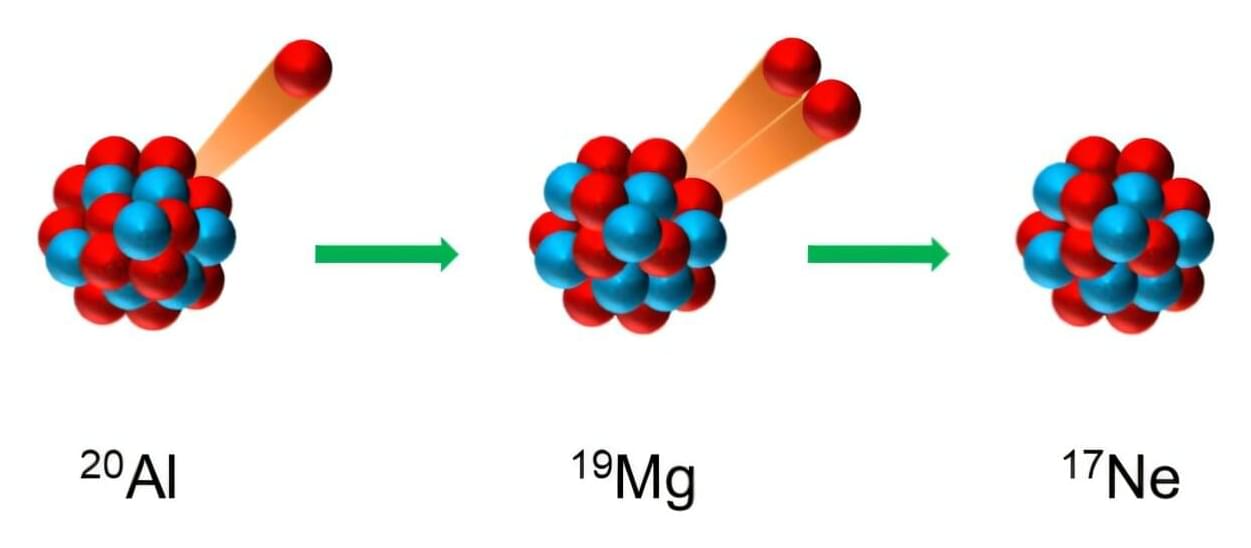
Radioactive decay is a fundamental process in nature by which an unstable atomic nucleus loses energy by radiation. Studying nuclear decay modes is crucial for understanding properties of atomic nuclei. In particular, exotic decay modes like proton emission provide essential spectroscopic tools for probing the structure of nuclei far from the valley of stability—the region containing stable nuclei on the nuclear chart.
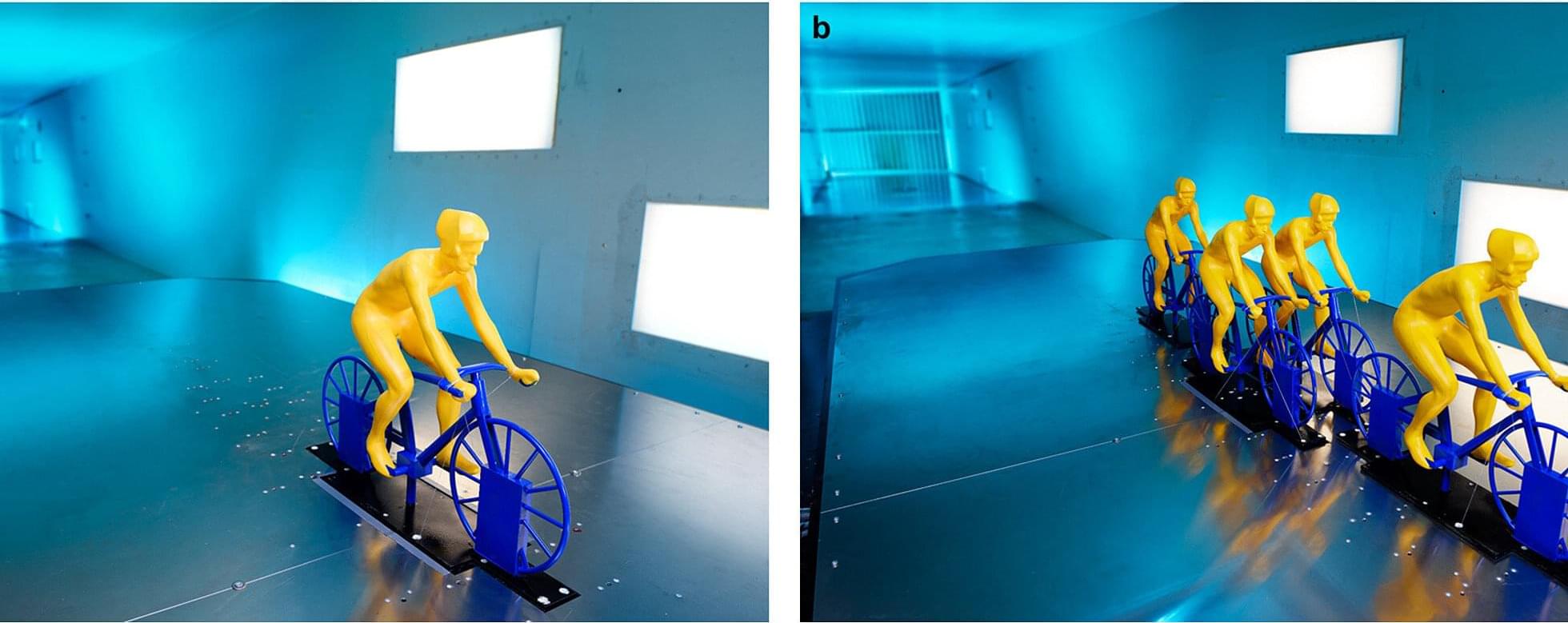
Professional cycling teams can reduce air drag for their protected rider by up to 76% by adopting specific formations different from the traditional single paceline, according to new research from Heriot-Watt University in partnership with the simulation software company, Ansys, part of Synopsys.
Despite the seemingly individual aspect of competitive cycling, it’s very much a team sport. In the Tour de France, each of the 23 teams has eight cyclists who all play a crucial part in the overall success of the team.
When a team leader is involved in a crash or a flat tire and he drops from the peloton or leading group in the race, his teammates will have the task to bring this protected rider back into the peloton or leading group, where riders closely follow one another to reduce air resistance. In doing so, the teammates will try to shield their protected rider from the wind thereby allowing him to save energy resources, at the expense of investing their own energy resources.



