Space Force technology is cutting edge.



A major question in physics is the maximum size of a system that can demonstrate quantum mechanical effects. This year’s Nobel Prize laureates conducted experiments with an electrical circuit in which they demonstrated both quantum mechanical tunnelling and quantised energy levels in a system big enough to be held in the hand.
Quantum mechanics allows a particle to move straight through a barrier, using a process called tunnelling. As soon as large numbers of particles are involved, quantum mechanical effects usually become insignificant. The laureates’ experiments demonstrated that quantum mechanical properties can be made concrete on a macroscopic scale.
In 1984 and 1985, John Clarke, Michel H. Devoret and John M. Martinis conducted a series of experiments with an electronic circuit built of superconductors, components that can conduct a current with no electrical resistance. In the circuit, the superconducting components were separated by a thin layer of non-conductive material, a setup known as a Josephson junction. By refining and measuring all the various properties of their circuit, they were able to control and explore the phenomena that arose when they passed a current through it. Together, the charged particles moving through the superconductor comprised a system that behaved as if they were a single particle that filled the entire circuit.


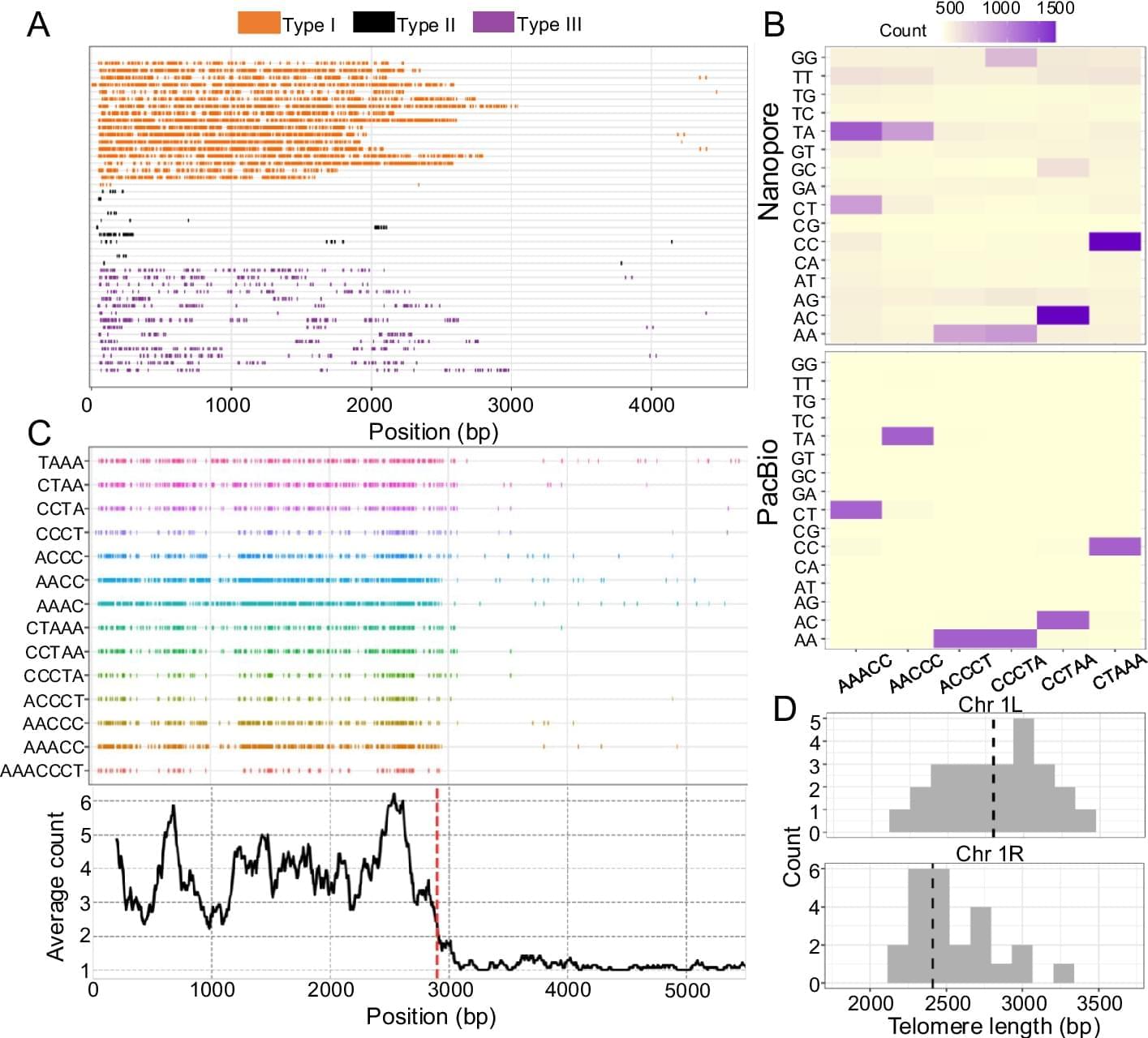
Long read sequencing technology (advanced by Pacific Biosciences (PacBio) and Oxford Nanopore Technologies (Nanopore)) is revolutionizing the genomics field [43] and it has major potential to be a powerful computational tool for investigating the telomere length variation within populations and between species. Read length from long read sequencing platforms is orders of magnitude longer than short read sequencing platforms (tens of kilobase pairs versus 100–300 bp). These long reads have greatly aided in resolving the complex and highly repetitive regions of the genome [44], and near gapless genome assemblies (also known as telomere-to-telomere assembly) are generated for multiple organisms [45, 46]. The long read sequences can also be used for estimating telomere length, since whole genome sequencing using a long read sequencing platform would contain reads that span the entire telomere and subtelomere region. Computational methods can then be developed to determine the telomere–subtelomere boundary and use it to estimate the telomere length. As an example, telomere-to-telomere assemblies have been used for estimating telomere length by analyzing the sequences at the start and end of the gapless chromosome assembly [47,48,49,50]. But generating gapless genome assemblies is resource intensive and cannot be used for estimating the telomeres of multiple individuals. Alternatively, methods such as TLD [51], Telogator [52], and TeloNum [53] analyze raw long read sequences to estimate telomere lengths. These methods require a known telomere repeat sequence but this can be determined through k-mer based analysis [54]. Specialized methods have also been developed to concentrate long reads originating from chromosome ends. These methods involve attaching sequencing adapters that are complementary to the single-stranded 3′ G-overhang of the telomere, which can subsequently be used for selectively amplifying the chromosome ends for long read sequencing [55,56,57,58]. While these methods can enrich telomeric long reads, they require optimization of the protocol (e.g., designing the adapter sequence to target the G-overhang) and organisms with naturally blunt-ended telomeres [59, 60] would have difficulty implementing the methods.
An explosion of long read sequencing data has been generated for many organisms across the animal and plant kingdom [61, 62]. A computational method that can use this abundant long read sequencing data and estimate telomere length with minimal requirements can be a powerful toolkit for investigating the biology of telomere length variation. But so far, such a method is not available, and implementing one would require addressing two major algorithmic considerations before it can be widely used across many different organisms. The first algorithmic consideration is the ability to analyze the diverse telomere sequence variation across the tree of life. All vertebrates have an identical telomere repeat motif TTAGGG [63] and most previous long read sequencing based computational methods were largely designed for analyzing human genomic datasets where the algorithms are optimized on the TTAGGG telomere motif. But the telomere repeat motif is highly diverse across the animal and plant kingdom [64,65,66,67], and there are even species in fungi and plants that utilize a mix of repeat motifs, resulting in a sequence complex telomere structure [64, 68, 69]. A new computational method would need to accommodate the diverse telomere repeat motifs, especially across the inherently noisy and error-prone long read sequencing data [70]. With recent improvements in sequencing chemistry and technology (HiFi sequencing for PacBio and Q20 + Chemistry kit for Nanopore) error rates have been substantially reduced to 1% [71, 72]. But even with this low error rate, a telomeric region that is several kilobase pairs long can harbor substantial erroneous sequences across the read [73] and hinder the identification of the correct telomere–subtelomere boundary. In addition, long read sequencers are especially error-prone to repetitive homopolymer sequences [74,75,76], and the GT-rich microsatellite telomere sequences are predicted to be an especially erroneous region for long read sequencing. A second algorithmic consideration relates to identifying the telomere–subtelomere boundary. Prior long read sequencing based methods [51, 52] have used sliding windows to calculate summary statistics and a threshold to determine the boundary between the telomere and subtelomere. Sliding window and threshold based analyses are commonly used in genome analysis, but they place the burden on the user to determine the appropriate cutoff, which for telomere length measuring computational methods may differ depending on the sequenced organism. In addition, threshold based sliding window scans can inflate both false positive and false negative results [77,78,79,80,81,82] if the cutoff is improperly determined.
Here, we introduce Topsicle, a computational method that uses a novel strategy to estimate telomere lengths from raw long read sequences from the entire whole genome sequencing library. Methodologically, Topsicle iterates through different substring sizes of the telomere repeat sequence (i.e., telomere k-mer) and different phases of the telomere k-mer are used to summarize the telomere repeat content of each sequencing read. The k-mer based summary statistics of telomere repeats are then used for selecting long reads originating from telomeric regions. Topsicle uses those putative reads from the telomere region to estimate the telomere length by determining the telomere–subtelomere boundary through a binary segmentation change point detection analysis [83]. We demonstrate the high accuracy of Topsicle through simulations and apply our new method on long read sequencing datasets from three evolutionarily diverse plant species (A. thaliana, maize, and Mimulus) and human cancer cell lines. We believe using Topsicle will enable high-resolution explorations of telomere length for more species and achieve a broad understanding of the genetics and evolution underlying telomere length variation.
Researchers from Integra Therapeutics, in partnership with the Pompeu Fabra University (UPF) and the Centre for Genomic Regulation (CRG), Spain, have used generative AI to design synthetic proteins that outperform naturally occurring proteins used for editing the human genome. Their use of generative AI focused on PiggyBac transposases, naturally occurring enzymes that have long been used for gene delivery and genetic engineering, and uncovered more than 13,000 previously unidentified PiggyBac sequences. The research, published in Nature Biotechnology, has the potential to improve current gene editing tools for the creation of CAR T and gene therapies.
“Our work expands the phylogenetic tree of PiggyBac transposons by two orders of magnitude, unveiling a previously unexplored diversity within this family of mobile genetic elements,” the researchers wrote.
For their work, the researchers first conducted extensive computational bioprospecting, screening more than 31,000 eukaryotic genomes to uncover the 13,000 new sequences. From this number, the team was able to validate 10 active transposases, two of which showed similar activity to PiggyBac transposases currently used in both research and clinical settings.
The new map of the Universe’s expansion history released by the DESI Collaboration offers hints at a breakdown of the standard model of cosmology.
For nearly a century, we have known that our Universe is expanding. For the past quarter-century, we have also known that this expansion is accelerating, a discovery that earned the 2011 Nobel Prize in Physics [1, 2]. But what is the mysterious “dark energy” that drives this acceleration? The simplest explanation involves what Einstein dubbed a “cosmological constant” (Λ) and implies that dark energy is a constant energy inherent to spacetime itself. This idea is the cornerstone of the standard model of cosmology, the Λ cold dark matter (ΛCDM) model, which for decades has consistently explained all available astronomical observations. Now high-precision measurements of the Universe’s expansion history are putting this model to its most stringent test yet. The Dark Energy Spectroscopic Instrument (DESI) has created a cosmic map of unprecedented scale (Fig. 1) [3–9].
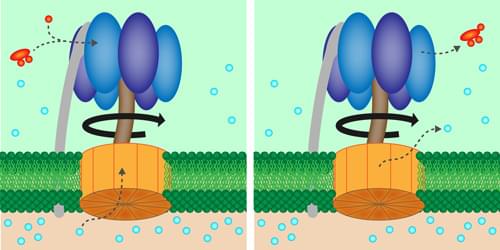
Turning a biologically important molecular motor at a constant rate saves energy, according to experiments.
Within every biological cell is an enzyme, called adenosine triphosphate (ATP) synthase, that churns out energy-rich molecules for fueling the cell’s activity. New experiments investigate the functioning of this “energy factory” by artificially cranking one of the enzyme’s molecular motors [1]. The results suggest that maintaining a fixed rotation rate minimizes energy waste caused by microscopic fluctuations. Future work could confirm the role of efficiency in the evolutionary design of biological motors.
ATP synthase consists of two rotating molecular motors, Fo and F1, that are oriented along a common rotation axis and locked together so that the rotation of Fo exerts a torque on the shaft in the middle of F1. The resulting motion within F1 helps bring together the chemical ingredients of the molecule ATP, which stores energy that can later be used in cellular processes.
A clever mathematical tool known as virtual particles unlocks the strange and mysterious inner workings of subatomic particles. What happens to these particles within atoms would stay unexplained without this tool. The calculations using virtual particles predict the bizarre behavior of subatomic particles with such uncanny accuracy that some scientists think “they must really exist.”
Virtual particles are not real—it says so right in their name—but if you want to understand how real particles interact with each other, they are unavoidable. They are essential tools to describe three of the forces found in nature: electromagnetism, and the strong and weak nuclear forces.
Real particles are lumps of energy that can be “seen” or detected by appropriate instruments; this feature is what makes them observable, or real. Virtual particles, on the other hand, are a sophisticated mathematical tool and cannot be seen. Physicist Richard Feynman invented them to describe the interactions between real particles.