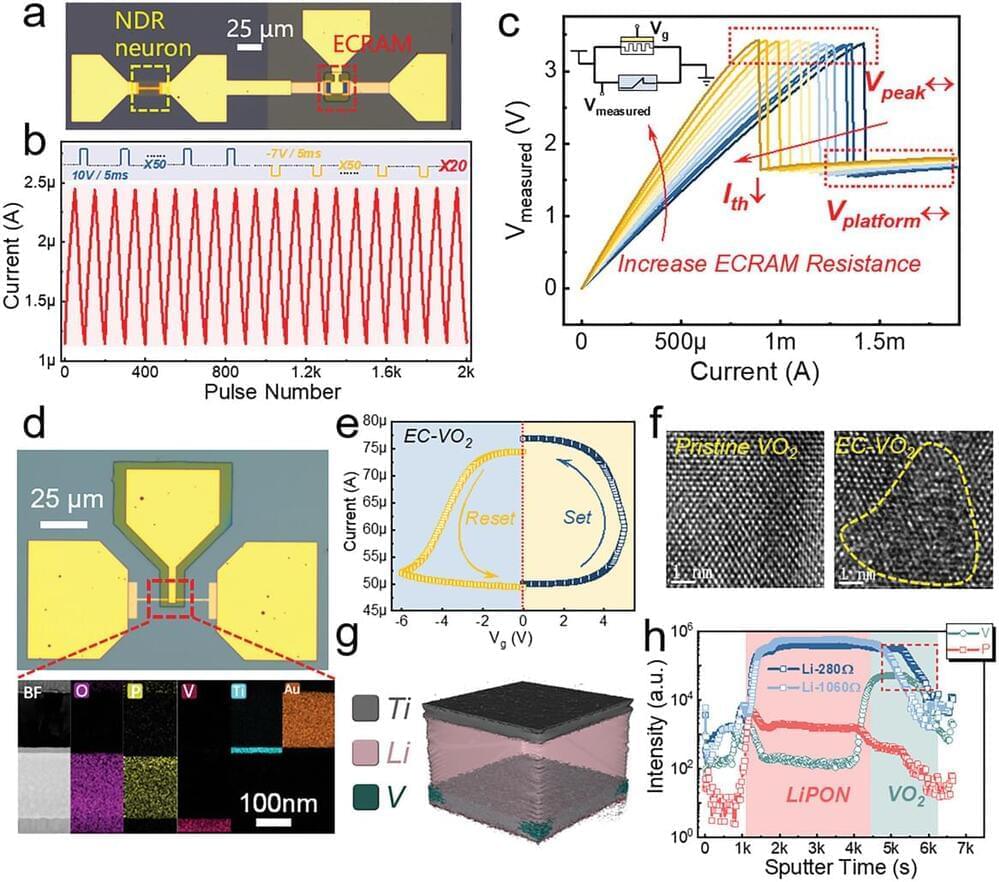
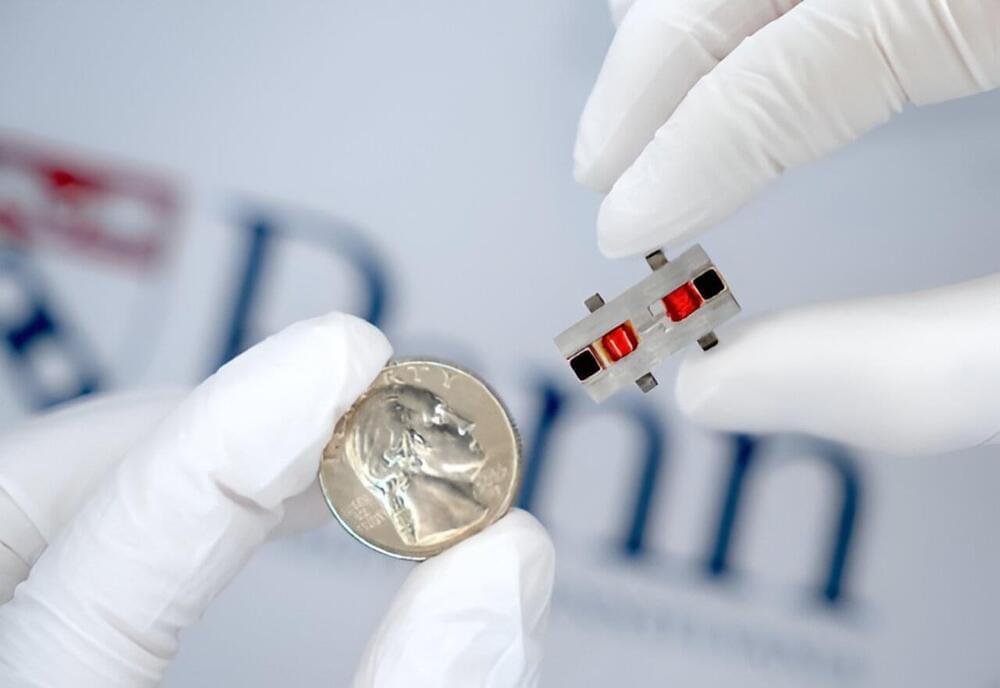
In the early 2010s, LightSquared, a multibillion-dollar startup promising to revolutionize cellular communications, declared bankruptcy. The company couldn’t figure out how to prevent its signals from interfering with those of GPS systems.



The climate transition is a materials transition. Decades of international diplomacy around oil, gas and pipelines are now giving way to conversations around the supply of critical raw materials. And not before time: to meet the EU’s energy and climate targets, we need to build the right technologies, in the right quantities, at the right speed. The problem is that many of these technologies are built with materials imported from just a handful of countries.
A study from Japan published in the International Journal of Computer Aided Engineering and Technology reveals a way to optimize the composition of functionally graded materials (FGMs). FGMs are advanced composite materials with a gradual variation in composition and properties across their volume, designed to optimize performance under specific loading conditions.
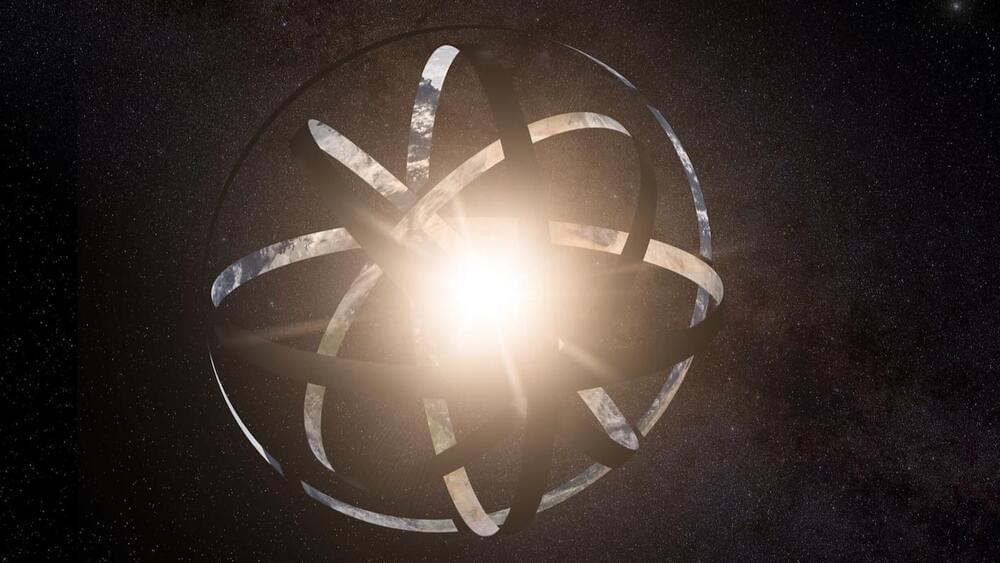

There are three ways to look for evidence of alien technological civilizations. One is to look out for deliberate attempts by them to communicate their existence, for example, through radio broadcasts. Another is to look for evidence of them visiting the solar system. And a third option is to look for signs of large-scale engineering projects in space.
A team of astronomers have taken the third approach by searching through recent astronomical survey data to identify seven candidates for alien megastructures, known as Dyson spheres, “deserving of further analysis.”
This is a detailed study looking for “oddballs” among stars—objects that might be alien megastructures. However, the authors are careful not to make any overblown claims. The seven objects, all located within 1,000 light-years of Earth, are “M-dwarfs”—a class of stars that are smaller and less bright than the sun.


Some of the hardest sectors to decarbonize are industries that require high temperatures like steel smelting and cement production. A new approach uses a synthetic quartz solar trap to generate temperatures of over 1,000 degrees Celsius (1,832 degrees Fahrenheit)—hot enough for a host of carbon-intensive industries.
While most of the focus on the climate fight has been on cleaning up the electric grid and transportation, a surprisingly large amount of fossil fuel usage goes into industrial heat. As much as 25 percent of global energy consumption goes towards manufacturing glass, steel, and cement.
Electrifying these processes is challenging because it’s difficult to reach the high temperatures required. Solar receivers, which use thousands of sun-tracking mirrors to concentrate energy from the sun, have shown promise as they can hit temperatures of 3,000 C. But they’re very inefficient when processes require temperatures over 1,000 C because much of the energy is radiated back out.