The Hénon map: a two-dimensional map that sheds light on the fractal structure of strange attractors. Deriving the Hénon map. Analyzing the map. Simulations.
Reading: Strogatz, \
The Hénon map: a two-dimensional map that sheds light on the fractal structure of strange attractors. Deriving the Hénon map. Analyzing the map. Simulations.
Reading: Strogatz, \
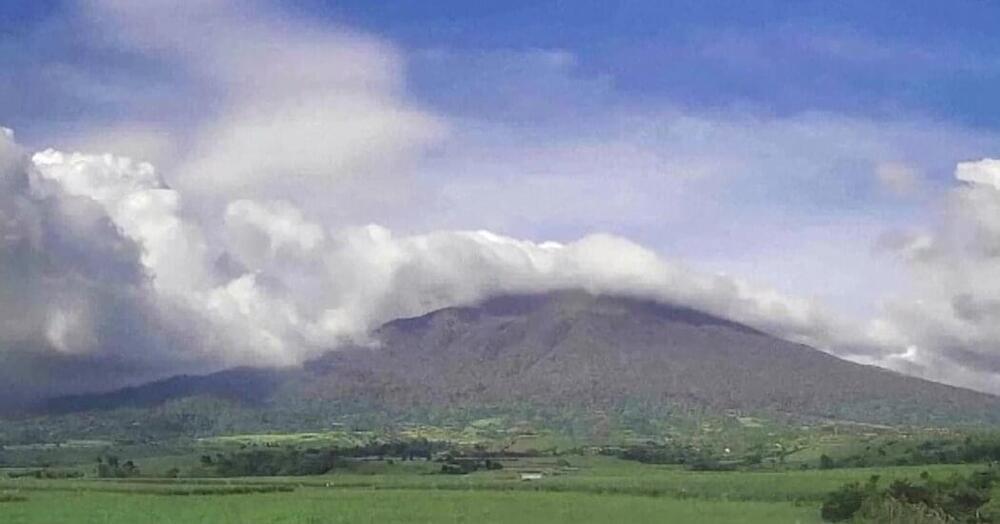


The Philippine authorities ordered nearly 90,000 people to evacuate after a volcano on the central island of Negros erupted, spewing a two-mile-high plume of deadly ash, lava and large rocks.
The volcano, Mount Kanlaon, erupted on Monday afternoon, and the authorities warned that it could happen again in the coming days.
“This is very destructive and it can burn everything in its path, including vegetation, buildings and humans,” said Teresito Bacolcol, the head of seismology at the Philippine Institute of Volcanology and Seismology. “This can kill.”

A team of Indian astronomers has made a fascinating discovery that could change how we think about how planets are born. The team, led by Liton Majumdar from the National Institute of Science Education and Research (NISER) in Odisha, studied a unique triple-star system called GG Tau A, located 489 light-years away from Earth, as mentioned in the latest report by India Today.
Synchron has developed a Brain-Computer Interface that uses pre-existing technologies such as the stent and catheter to allow insertion into the brain without the need for open brain surgery.
Read the CNET article for more info:
You Might Not Need Open Brain Surgery to Get Mind Control https://cnet.co/3sZ7k67
0:00 Intro.
0:25 History of Brain Chip Implants.
0:44 About Synchron.
0:54 How Synchron implants the interface.
1:55 How brain patterns transmit signals.
2:50 Risks and Concerns.
3:50 Patients and Clinical Testing.
4:25 Brain Health Monitoring.
5:04 Synchron Switch Price.
Never miss a deal again! See CNET’s browser extension 👉 https://bit.ly/3lO7sOU
Check out CNET’s Amazon Storefront: https://www.amazon.com/shop/cnet?tag=lifeboatfound-20.
Follow us on TikTok: / cnetdotcom.
Follow us on Instagram: / cnet.
Follow us on Twitter: / cnet.
Like us on Facebook: / cnet.
#WhatTheFuture #Synchron #BCI

Bacancy is proud to announce the launch of a new AI tool, MedPreGPT, to help doctors with medicine prescriptions. This system enables doctors who all are using it for internal purposes to give accurate prescription recommendations privately without wasting any time. Compared to AI models like ChatGPT, this tool is specially trained with vast medical data and makes relevant suggestions. This innovative tool is made to enhance patient care, reduce human errors, and streamline the prescription process.
Doctors are only humans and they indeed work under intense work pressure and workload. Mistakes can happen in such an environment. Today’s healthcare providers use ChatGPT and Google’s Gemini for medicine recommendations, which is not completely wrong, but those tools might give false information. Bacancy has recognized the problem and found MedPreGPT to give accurate medical prescriptions.
The following are features of MedPreGPT Provides AI-based prescription recommendations according to symptoms and history. It is integrated with electronic health records (EHRs) for workflow ease. It provides multilingual support for healthcare professionals across the world Provides healthcare providers with updates in real time, regarding the latest clinical guidelines and drug interactions to ensure true care.

In a recent study published in Nature Cancer, a team of researchers investigated the unique structure of deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) in extracellular vesicles (EVs) and its role in cancer progression.
The study examined how EV-DNA, through its association with histones, influences immune cell responses and impacts the pre-metastatic niche. It also explored how it could serve as a predictive biomarker for metastasis, especially in colorectal cancer.
The study highlights how EV-DNA packaging influences immune responses and its promise as a biomarker for assessing colorectal cancer metastasis risk.