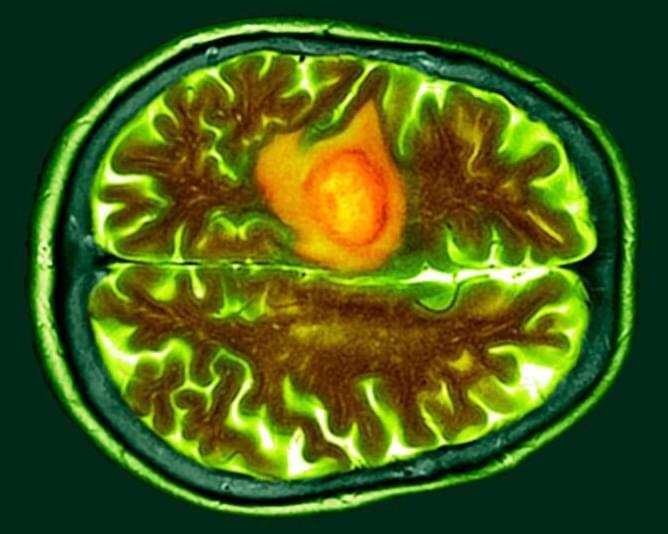
Two early clinical trials that together included nine patients suggest that a treatment called CAR-T therapy could treat glioblastoma, but its long-term effects are unknown.
Conversations between Wikipedia editors following CNET’s AI scandal reflect the reputational hazards of AI content and dubious ownership.
According to the CDC, more than 140,000 Americans are dying each year from alcohol-related causes, and the rate of deaths has been rising for years, especially during the pandemic.
The idea: For occasional drinkers, alcohol causes the brain to release more dopamine, a chemical that makes you feel good. Chronic alcohol use, however, causes the brain to produce, and process, less dopamine, and this persistent dopamine deficit has been linked to alcohol relapse.
There is currently no way to reverse the changes in the brain brought about by AUD, but a team of US researchers suspected that an in-development gene therapy for Parkinson’s disease might work as a dopamine-replenishing treatment for alcoholism, too.
The concept of “love languages” has had a vice grip on pop psychology for decades — and now, some scientists are calling bull.
These data centers are even more power hungry than traditional ones, and as every tech company pivots to AI, the energy demand steepens.
The highest sea cliffs in England have been hiding the oldest fossilized forest yet found on planet Earth. The long-lost ecosystem’s palm-like trees, called Calamophytons, are 390 million years old.
That’s roughly three or four million years older than the previous record holder, found across the Atlantic in New York State.
In southwest England, the red sandstone rock face where scientists found the imprints of logs, roots, and twigs was once considered “barren of trace fossils”
“Semiparametric Token-Sequence Co-Supervision”
We introduce semiparametric token-sequence co-supervision, which trains LM by simultaneously leveraging supervision from a parametric token and a nonparametric sequence embedding space.
✅ Paper: https://arxiv.org/abs/2403.09024 ✅ Code: https://avatars.githubusercontent.com/u/44370759?s=64&v=4
Contribute to kaistAI/Semiparametric_Token-Sequence_Co-Supervision development by creating an account on GitHub.
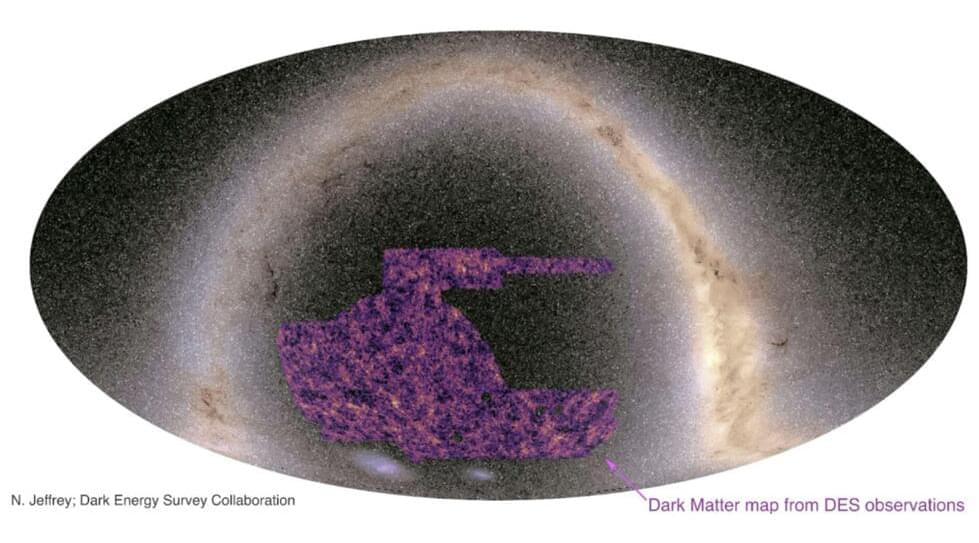
New research in Physical Review Letters (PRL) has proposed a novel method to detect light dark matter candidates using laser interferometry to measure the oscillatory electric fields generated by these candidates.
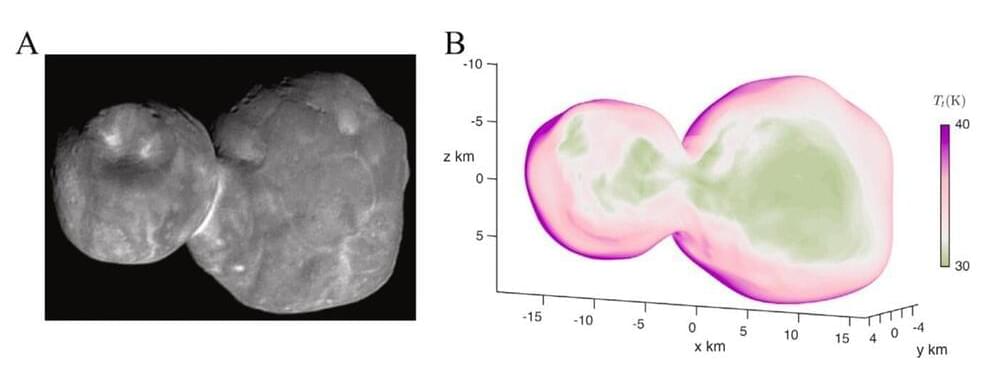
A paper recently published in Icarus presents findings about the Kuiper Belt Object 486,958 Arrokoth, shedding new light on the preservation of volatile substances like carbon monoxide (CO) in such distant celestial bodies.