Elon Musk said Starlink’s direct-to-cellular service would provide free emergency services at SpaceX seeks FCC approval for the technology.



We’ve reached a new milestone in the uncanny valley, folks: AIs are now Rickrolling humans.
In a now-viral post on X-formerly-Twitter, Flo Crivello, the CEO of the AI assistant firm Lindy, explained how this bizarre memetic situation featuring Rick Astley’s 1987 hit “Never Gonna Give You Up” came to pass.
Known as “Lindys,” the company’s AI assistants are intended to help customers with various tasks. Part of a Lindy’s job is to teach clients how to use the platform, and it was during this task that the AI helper provided a link to a video tutorial that wasn’t supposed to exist.

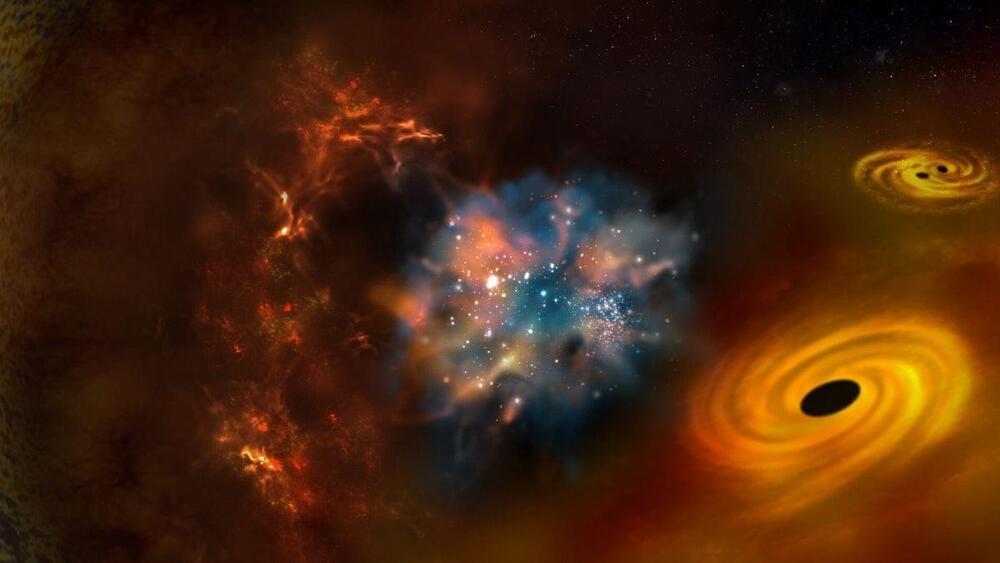
Physicists Successfully Demonstrate Quantum Energy Teleportation in Lab Experiments
TL;DR
Bob finds himself in need of energy — he wants to charge that fanciful quantum battery — but all he has access to is empty space. Fortunately, his friend Alice has a fully equipped physics lab in a far-off location. Alice measures the field in her lab, injecting energy into it there and learning about its fluctuations. This experiment bumps the overall field out of the ground state, but as far as Bob can tell, his vacuum remains in the minimum-energy state, randomly fluctuating. But then Alice texts Bob her findings about the vacuum around her location, essentially telling Bob when to plug in his battery. After Bob reads her message, he can use the newfound knowledge to prepare an experiment that extracts energy from the vacuum — up to the amount injected by Alice.
Scraps of DNA discarded by our neurons’ power units are being absorbed into our nuclear genome far more frequently than assumed, potentially putting our brains at greater risk of developing life-threatening conditions.
An investigation by a team of researchers led by Columbia University in the US has found individuals with higher numbers of nuclear mitochondrial insertions – or NUMTs (pronounced new-mites) – in their brain cells are more likely to die earlier than those with fewer DNA transfers.
Mitochondria serve as our cells’ batteries, churning out energy in a form of chemical currency that suits most of our body’s metabolic needs. Once a discrete microbial organism in its own right, these tiny powerhouses were co-opted by our unicellular ancestors billions of years in the past, genes and all.
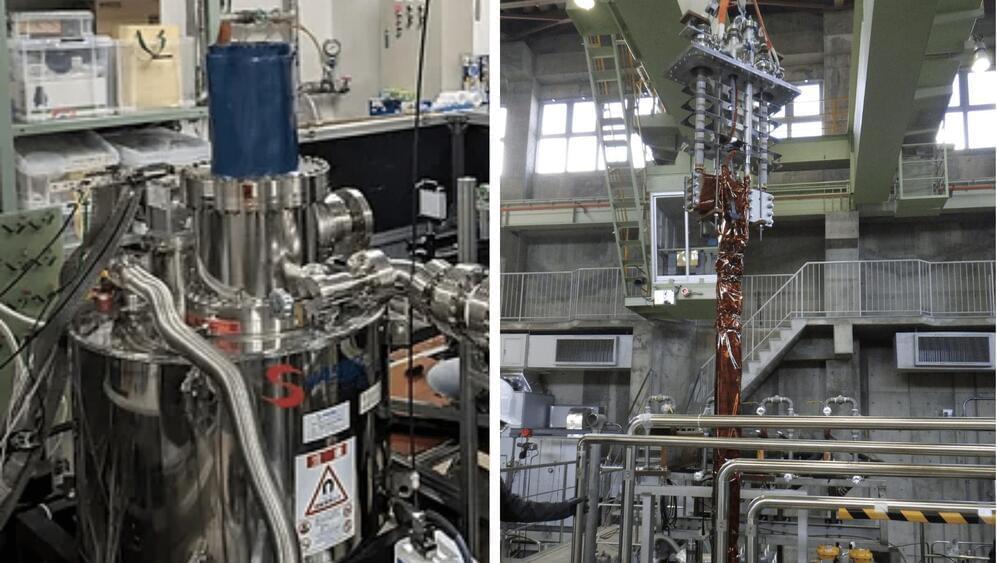


“If pursued, we might see by the end of the decade advances in AI as drastic as the difference between the rudimentary text generation of GPT-2 in 2019 and the sophisticated problem-solving abilities of GPT-4 in 2023,” Epoch wrote in a recent research report detailing how likely it is this scenario is possible.
But modern AI already sucks in a significant amount of power, tens of thousands of advanced chips, and trillions of online examples. Meanwhile, the industry has endured chip shortages, and studies suggest it may run out of quality training data. Assuming companies continue to invest in AI scaling: Is growth at this rate even technically possible?
In its report, Epoch looked at four of the biggest constraints to AI scaling: Power, chips, data, and latency. TLDR: Maintaining growth is technically possible, but not certain. Here’s why.
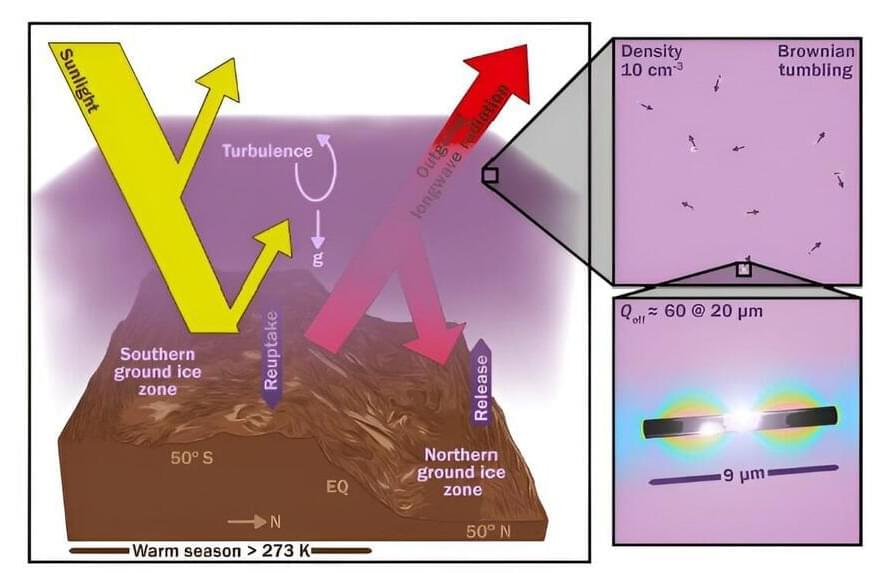
A small team of engineers and geophysicists from Northwestern University, the University of Chicago, and the University of Central Florida has found, via modeling, that creating millions of metal nanorods from material on the Martian surface and then blasting them into the atmosphere would be a more efficient way to heat the planet than generating greenhouse gases. Their paper is published in the journal Science Advances.
Science fiction writers have for many years envisioned a future when Mars is made habitable through terraforming techniques, allowing humans to survive without the need for special buildings and spacesuits. Recently, scientists have begun looking at the possibility, though most project ideas are far less ambitious.
Instead of completely transforming the planet, many are looking at simply warming it up a bit to make it more habitable. Most such ideas have centered on releasing greenhouse gases into the atmosphere to capture more heat from the sun. Unfortunately, there are few ingredients on the Martian surface that could be used to create and release such gases.

A study out recently has prompted much media attention about the role of plastics in developing autism.
In particular, the study focused on exposure to a component of hard plastics—bisphenol A, or BPA—in the womb and the risk of boys developing this neurodevelopmental disorder.
Importantly, the study doesn’t show plastics containing BPA cause autism.
