Developed at Caltech, a new robot is a humanoid that can launch an M4 drone, switching between different modes of motion, with wheels that can become rotors.
Get the latest international news and world events from around the world.

Physicists demonstrate the constancy of the speed of light with unprecedented accuracy
In 1887, one of the most important experiments in the history of physics took place. American scientists Michelson and Morley failed to measure the speed of Earth by comparing the speed of light in the direction of Earth’s motion with that perpendicular to it. That arguably most important zero measurement in the history of science led Einstein to postulate that the speed of light is constant and consequently to formulate his theory of special relativity.
This theory implies that all laws of physics are the same, independent of the relative motion between observers—a concept known as Lorentz invariance.
Meanwhile, quantum theory has been developed, with Lorentz invariance at the heart of all its theoretical frameworks, in particular quantum field theory and the Standard Model of Particle Physics. The latter is the most precisely tested theory ever developed and has been verified to incredible precision.

Princeton’s new quantum chip marks a major step toward quantum advantage
A Princeton team built a new tantalum-silicon qubit that survives for over a millisecond, far surpassing today’s best devices. The design tackles surface defects and substrate losses that have limited transmon qubits for years. Easy to integrate into existing quantum chips, the approach could make processors like Google’s vastly more powerful.

Quantum computers could be powerful enough to decrypt Bitcoin sometime after 2030, CEO of Nvidia’s quantum partner says
“You should have a few good years ahead of you but I wouldn’t hold my Bitcoin,” Peronnin said, laughing. “They need to fork [move to a stronger blockchain] by 2030, basically. Quantum computers will be ready to be a threat a bit later than that,” he said.
Quantum doesn’t just threaten Bitcoin, of course, but all banking encryption. And it is likely that in all these cases companies are developing quantum resistant tools to upgrade their existing security systems.
Defensive security algorithms are improving, Peronnin said, so it’s not certain when the blockchain will become vulnerable to a quantum attack. But “the threshold for such an event is coming closer to us year by year,” he said.
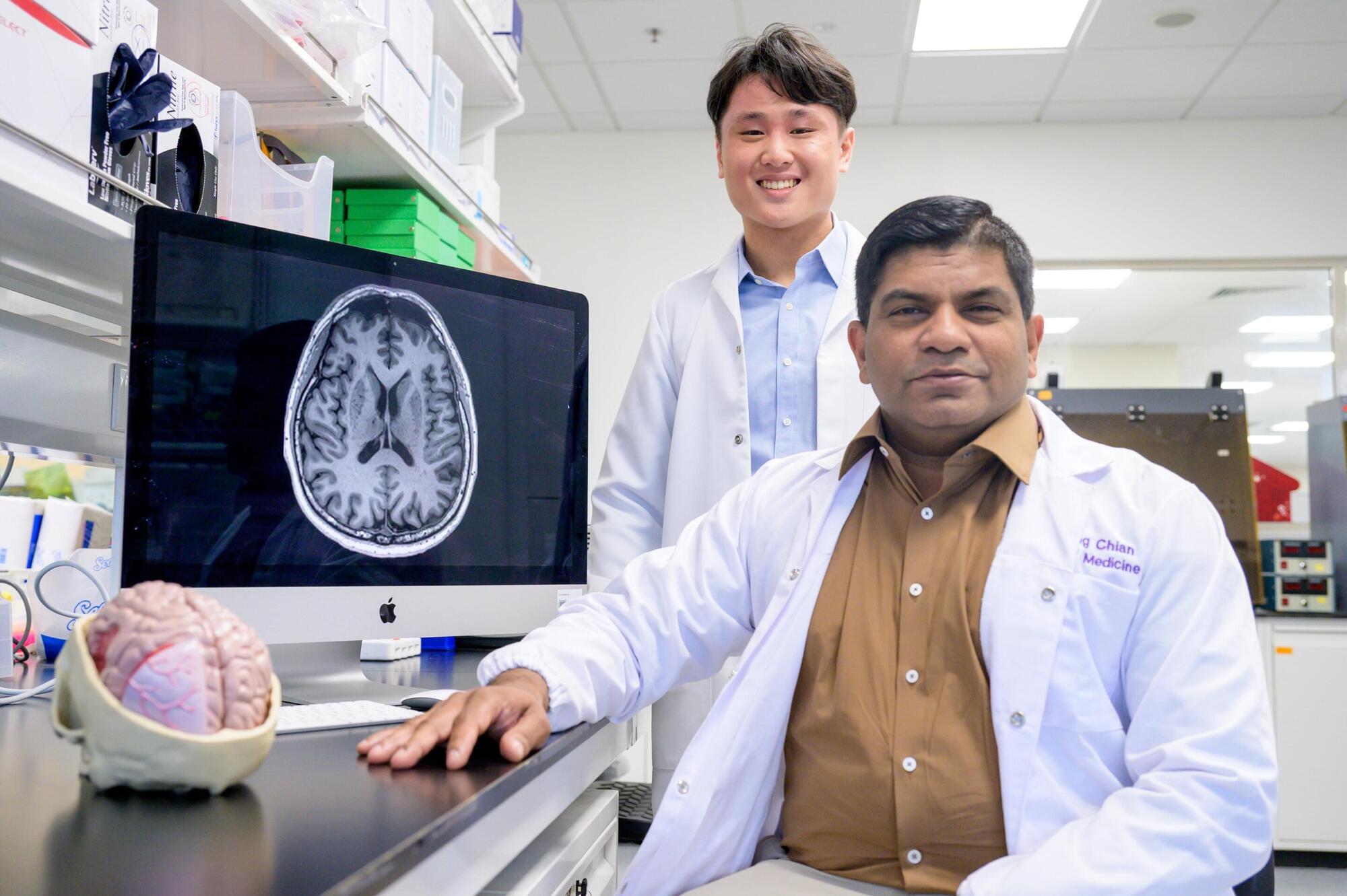

Clogged ‘drains’ in the brain likely an early-warning sign of Alzheimer’s disease
“Drains” in the brain, responsible for clearing toxic waste in the organ, tend to get clogged up in people who show signs of developing Alzheimer’s disease, a study by researchers from Nanyang Technological University, Singapore (NTU Singapore) has discovered.
This suggests that such clogged drains, a condition known as “enlarged perivascular spaces,” are a likely early-warning sign for Alzheimer’s, a common form of dementia.
“Since these brain anomalies can be visually identified on routine magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) scans performed to evaluate cognitive decline, identifying them could complement existing methods to detect Alzheimer’s earlier, without having to do and pay for additional tests,” said Associate Professor Nagaendran Kandiah from NTU’s Lee Kong Chian School of Medicine (LKCMedicine) who led the study.
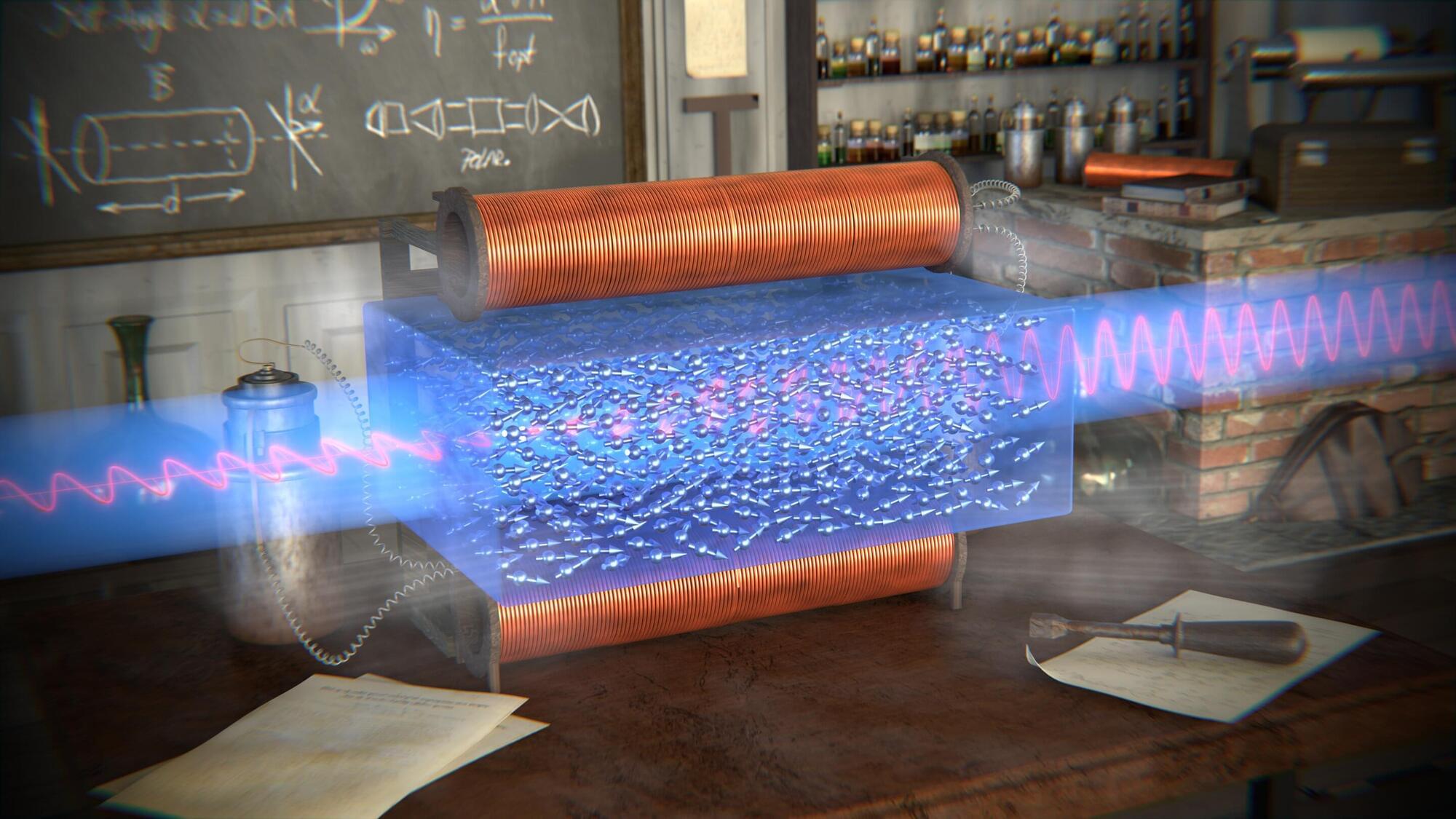
New magnetic component discovered in the Faraday effect after nearly two centuries
Researchers at the Hebrew University of Jerusalem discovered that the magnetic component of light plays a direct role in the Faraday effect, overturning a 180-year-old assumption that only its electric field mattered.
Their findings, published in Scientific Reports, show that light can magnetically influence matter, not just illuminate it. The discovery opens new possibilities in optics, spintronics, and quantum technologies.
The study was led by Dr. Amir Capua and Benjamin Assouline from the Institute of Electrical Engineering and Applied Physics at the Hebrew University of Jerusalem. It presents the first theoretical proof that the oscillating magnetic field of light directly contributes to the Faraday effect, a phenomenon in which the polarization of light rotates as it passes through a material exposed to a constant magnetic field.
‘Blood clots surge like never before…’: Dr McCullough’s chilling revelations on mRNA COVID vaccines
321 watching now • Started streaming on Nov 17, 2025 • #news #latestnews #economictimes
“Microtubules as Fractal Time Crystals: implications for life and consciousness” by Stuart Hameroff
This is a ~1 hour 20 min talk and discussion titled(https://hameroff.arizona.edu/).
JWST Just Finds Objects Much Older Than The Universe & Nobel Scientist Claims It’s Another Universe
#webbtelescopeimage.
#darkmatter #darkenergy #einstein #blackhole #cosmicmicrowavebackground #bigbang #oldergalaxies.
Evidence of Primordial black hole — https://www.sciencealert.com/jwst-may-have-found-the-first-d…black-hole mysterious red dots — https://archive.ph/8UUt4
Most distant objects ever discovered candidates-https://arxiv.org/abs/2503.
Scientists are starting to rethink what they thought they knew about the universe, thanks to the latest discoveries from the James Webb Space Telescope. In its new images of the farthest regions of space, Webb has revealed things that current theories simply cannot explain.
For the first time, scientists may have found signs of an entirely new kind of black hole—something that challenges the traditional Big Bang model. Webb has also uncovered record-breaking distant galaxies that look far stranger than expected, leaving experts puzzled. On top of that, the telescope has spotted many mysterious objects in huge numbers—but no one really knows what they are.
Even more surprising, some of these discoveries suggest that our universe could be part of something much bigger and stranger than we ever imagined. Let’s explore what scientists have actually discovered—and how these findings suggest that something may exist beyond our universe.