Typeset using LATEX twocolumn style in AASTeX7.0.
Technosignature Searches of Interstellar Objects.
James R. A. Davenport.
1 Sofia Z. Sheikh.
2, 3 Steve Croft.
4, 2, 3 Brian C. Lacki.


More than 5,000 planets have been discovered beyond our solar system, allowing scientists to explore planetary evolution and consider the possibility of extraterrestrial life. Now, a UC Riverside study published in Physical Review D suggests that exoplanets, which are planets orbiting stars outside our solar system, could also serve as tools to investigate dark matter.
The researchers examined how dark matter, which makes up 85% of the universe’s matter, might affect Jupiter-sized exoplanets over long periods of time. Their theoretical calculations suggest dark matter particles could gradually collect in the cores of these planets. Although dark matter has never been detected in laboratories, physicists are confident it exists.
“If the dark matter particles are heavy enough and don’t annihilate, they may eventually collapse into a tiny black hole,” said paper first author Mehrdad Phoroutan-Mehr, a graduate student in the Department of Physics and Astronomy who works with Hai-Bo Yu, a professor of physics and astronomy. “This black hole could then grow and consume the entire planet, turning it into a black hole with the same mass as the original planet. This outcome is only possible under the superheavy non-annihilating dark matter model.”


Cybersecurity researchers have discovered a malicious npm package that comes with stealthy features to inject malicious code into desktop apps for cryptocurrency wallets like Atomic and Exodus on Windows systems.
The package, named nodejs-smtp, impersonates the legitimate email library nodemailer with an identical tagline, page styling, and README descriptions, attracting a total of 347 downloads since it was uploaded to the npm registry in April 2025 by a user named “nikotimon.” It’s currently no longer available.
“On import, the package uses Electron tooling to unpack Atomic Wallet’s app.asar, replace a vendor bundle with a malicious payload, repackage the application, and remove traces by deleting its working directory,” Socket researcher Kirill Boychenko said.

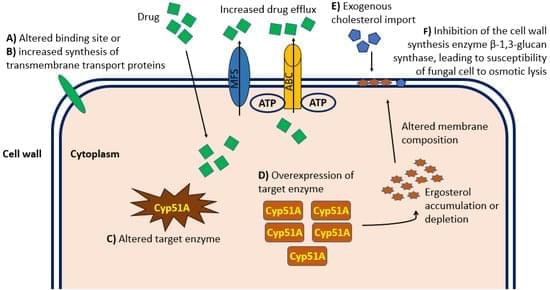
Fungal infections, named mycosis, can cause severe invasive and systemic diseases that can even lead to death. In recent years, epidemiological data have recorded an increase in cases of severe fungal infections, caused mainly by a growing number of immunocompromised patients and the emergence of fungal pathogenic forms that are increasingly resistant to antimycotic drug treatments. Consequently, an increase in the incidence of mortality due to fungal infections has also been observed. Among the most drug-resistant fungal forms are those belonging to the Candida and Aspergillus spp. Some pathogens are widespread globally, while others are endemic in some areas only. In addition, some others may represent a health threat for some specific subpopulations and not for the general public. In contrast to the extensive therapeutic armamentarium available for the antimicrobial chemotherapeutic treatment of bacteria, for fungal infections there are only a few classes of antimycotic drugs on the market, such as polyenes, azoles, echinocandins, and a few molecules are under trial. In this review, we focused on the systemic mycosis, highlighted the antifungal drug compounds available in the pipeline, and analyzed the main molecular mechanisms for the development of antifungal resistance to give a comprehensive overview and increase awareness on this growing health threat.


