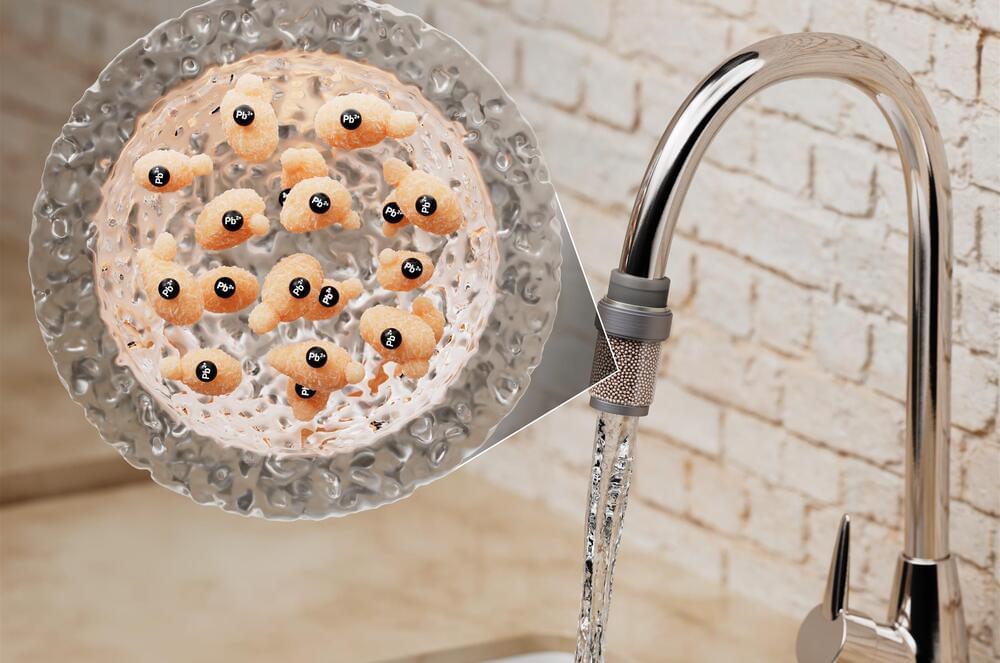
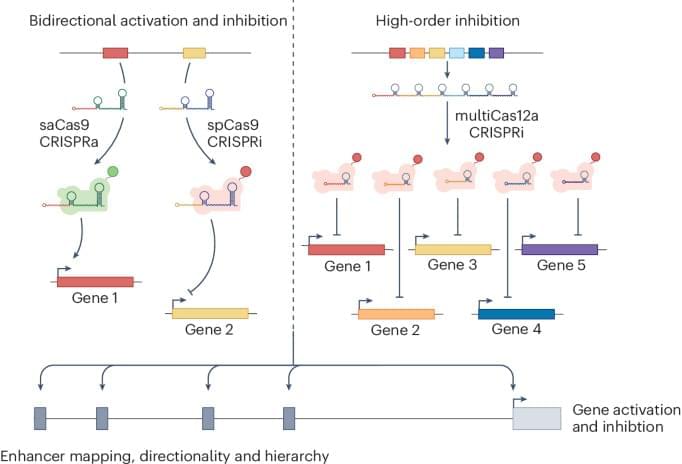
Two CRISPR tools for combinatorial genetic perturbations reveal gene regulatory networks.

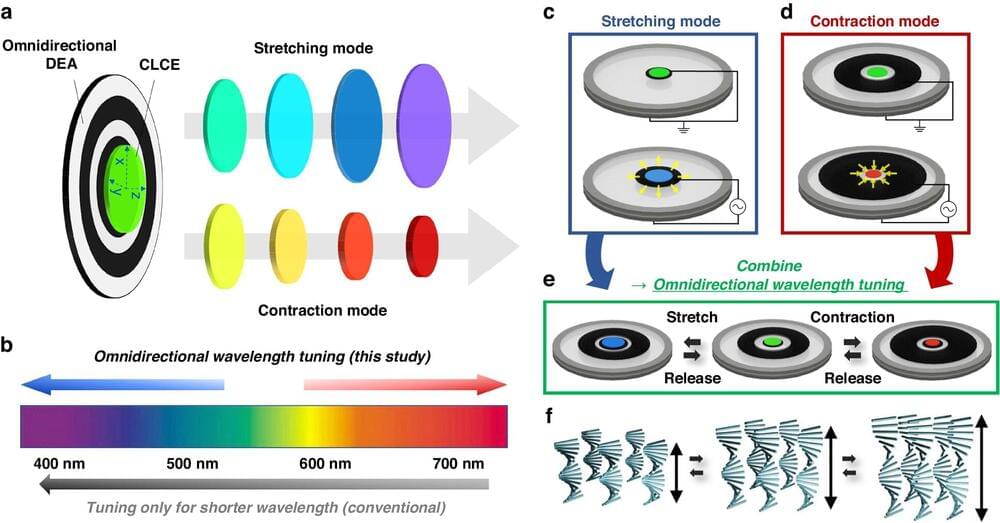
In the rapidly evolving field of photonics, an advancement has emerged from Korea, redefining the possibilities of structural color manipulation. Scientists have developed a pioneering technology capable of omnidirectional wavelength tuning, which promises to revolutionize a myriad of tunable photonic applications.

Immunity & Transformation by Brian ClementBrian Clement, Ph.D., L.N, Co-Director, Hippocrates WellnessGlobally-Renowned Speaker, Author, and Weight Loss and…

After a strong start to 2024, Hyundai expects the momentum to continue with some of the most affordable and efficient EVs on the US market. In an exclusive interview with Electrek, Hyundai Motor America CEO Randy Parker said the company is “humble and hungry” as it remains committed to EVs in the US.
Despite rivals pulling back, Hyundai is doubling down on its EV commitment as it looks to separate itself from the competition.
Its early dedication is already paying off. Hyundai is outpacing the US electric vehicle market with a wide-ranging lineup of award-winning EVs, including the IONIQ 5, IONIQ 6, and Kona Electric.

Check out the Space Time Merch Store https://www.pbsspacetime.com/shopSign Up on Patreon to get access to the Space Time Discord!https://www.patreon.com/pbssp…
Thanks to Keeps for sponsoring this video & for the free product! Head to http://keeps.com/eventhorizonshow to get a special offer. Individual results may va…
SpaceX has made significant advancements in the development and testing of the Starship rocket, with successful modifications, testing, and potential future launches without a license, as well as progress in the Falcon 9 rocket and challenges faced by ULA’s Vulcan Centaur Questions to inspire discussion What updates ha.
